Difference between revisions of "Bone Response to Damage"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (45 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Bones|'''BACK TO BONES''']]</center></big> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Introduction=== | |
| + | |||
| + | *Bone is a hard, highly specialised connective tissue | ||
| + | *Consists of interconnected cells embedded in a calcified, collagenous matrix | ||
| + | *Living, dynamic, responsive tissue, growing and remodelling throughout life | ||
| + | *Pathogenesis of many bone diseases is complex | ||
| + | **May involve genetic defects, diet or infection or a combination of these | ||
| + | *'''Function''': | ||
| + | **Support/protection | ||
| + | **Movement | ||
| + | **Stem cell storage | ||
| + | **Mineral storage | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Normal structure=== | ||
| + | [[Image:Bone micro structure.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Microscopic bone (Courtesy of RVC Histology images)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Cells''' | ||
| + | **'''Osteoblasts''' | ||
| + | ***Mesenchymal cells | ||
| + | ***Arise from bone marrow stroma | ||
| + | ***Histologically: | ||
| + | ****Plump and cuboidal when active | ||
| + | ****Basophilic cytoplasm | ||
| + | ****When inactive - less cytoplasm -> flattened | ||
| + | ***Produce bone matrix = '''osteoid''' - uncalcified | ||
| + | ****Homogeneous substance | ||
| + | ****Stains light pink with H&E | ||
| + | ***Cell membranes are rich in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) | ||
| + | ****Possibly involved in pumping calcium across membranes | ||
| + | ***Promoted by growth factors | ||
| + | ***Have receptors for [[Bones - normal#Bone resorption|PTH]] | ||
| + | ****They contract in response -> space for osteoclasts to attach | ||
| + | **'''Osteocytes''' | ||
| + | ***Osteoblasts that have become surrounded by mineralised bone matrix | ||
| + | ***Occupy cavities called '''lacunae''' | ||
| + | ***Contact osteoblasts and each other with cytoplasmic processes | ||
| + | ****Reach through canaliculi in mineralised bone matrix | ||
| + | ***Regulate composition of bone fluid | ||
| + | **'''Osteoclasts''' | ||
| + | ***Histologically: | ||
| + | ****Large, often multinucleated cells | ||
| + | ****Acidophilic cytoplasm | ||
| + | ***Derived from haematopoietic stem cells | ||
| + | ***Responsible for bone resorption | ||
| + | ****Firstly dissolve mineral followed by collagen | ||
| + | ****Use brush border for this | ||
| + | ***Sit in bone surface depression - '''Howship's lacuna''' | ||
| + | ***Do <u>not</u> have receptors for PTH | ||
| + | ***Have receptors for [[Bones - normal#Bone resorption|calcitonin]] | ||
| + | ****Involute their brush border in response | ||
| + | ****Detach from bone surface | ||
| + | *'''Matrix''': | ||
| + | **Osteoid | ||
| + | ***Type I collagen forms the backbone of the matrix (90%) | ||
| + | ****Molecules in staggered rows | ||
| + | ***Non-collagenous protein forming amorphous ground substance (10%) | ||
| + | **Mineral | ||
| + | ***Crystalline lattice of calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate | ||
| + | ***Also contains Mg, Mn, Zn, Cu, Na, F | ||
| + | ***Accounts for 65% of bone | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bone organisation=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Patterns of collagen deposition: | ||
| + | **'''Woven bone''': | ||
| + | ***"Random weave" which is only a normal feature in the foetus | ||
| + | ***Coarse collagen fibres | ||
| + | ***Later removed by osteoclasts and replaced by lamellar bone | ||
| + | ***In adults it is a sign of a pathological condition (e.g. fracture, inflammation, neoplasia) | ||
| + | **'''Lamellar bone''': | ||
| + | ***Orderly layers which are much stronger than woven bone | ||
| + | ***Fine collagen fibres in concentric or parallel laminae | ||
| + | ***Two main types: | ||
| + | ****'''Compact bone (cortical)''' | ||
| + | *****Forms 80% of total bone mass | ||
| + | *****Consists of cells and interstitial substance - 30% ossein (type of collagen) and 70% minerals, especially calcium phosphate | ||
| + | *****Forms the shell of long bone shafts - contain [[Haversian systems]] | ||
| + | ****'''Cancellous bone (spongy or trabecular)''' | ||
| + | *****Made up of plates, tubes or bars arranged in lines of stress | ||
| + | *****In vertebrae, flat bones and epiphyses of long bones | ||
| + | *****Contains no Haversian systems | ||
| + | **'''Laminar bone''' | ||
| + | ***Formed on periosteal surface of diaphysis | ||
| + | ***Accomodates rapid growth of large dogs and farm animals | ||
| + | ***Plates of woven bone from within the periosteum | ||
| + | ***Concentric plates | ||
| + | ***As it forms, it fuses with the bone surface | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Periosteum and blood supply=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Specialised sheath of connective tissue covering bone except at the articular surfaces | ||
| + | *Inner layer | ||
| + | **Merges with the outer layer of bone | ||
| + | **Contains osteoblasts and osteoprogenitor stem cells in young animals and in adults with fractures or disease | ||
| + | *Damage to the periosteum invokes a hyperplastic reaction of the inner layer | ||
| + | *The blood supply to the mature bone enters via the periosteum | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Endosteum''' lines the marrow cavity | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bone development=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Two main types of bone development: | ||
| + | **'''Endochondral ossification''' (cartilage model) | ||
| + | ***Long bones mainly - physis and metaphysis | ||
| + | ***Mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondroblasts | ||
| + | ****Produce scaffold of mineralised cartilage on which osteoblasts deposit bone | ||
| + | ***Vascularised | ||
| + | ***Developed centres of ossification | ||
| + | ****Primary (diaphyseal) | ||
| + | ****Secondary (epiphyseal) | ||
| + | **'''Intramembranous ossification''' | ||
| + | ***Flat bones mainly (e.g. skull), shaft of long bones | ||
| + | ***Mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts | ||
| + | ***No cartilage precursor template | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Physis (Growth plate)=== | ===Physis (Growth plate)=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
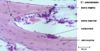
| + | [[Image:Growth plate.jpg|left|thumb|100px|<small><center>Growth plate (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Growth plate closer.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Growth plate magnified(Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Originates from the cartilage model that remains only at the junction of the diaphyseal and epiphyseal centres | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Cartilage of metaphyseal growth plate is divided into: (from right to left on the magnified image) | ||
| + | ** - Resting (reserve) zone | ||
| + | ** - Proliferative zone | ||
| + | ** - Hypertrophic zone | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
*Site of many '''congenital''' or '''nutritional''' bone diseases in the growing animal | *Site of many '''congenital''' or '''nutritional''' bone diseases in the growing animal | ||
| Line 20: | Line 147: | ||
*'''Closes and ossifies''' at maturity | *'''Closes and ossifies''' at maturity | ||
**Regulated by androgens | **Regulated by androgens | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | |
| + | ===Bone resorption=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Mediated by two hormones: | ||
| + | **'''Parathyroid hormone (PTH)''' | ||
| + | ***Produced by <u>chief cells in the parathyroid glands</u> in response to <u>decreased</u> serum calcium | ||
| + | ***In response, osteoclasts increase in number and resorb mineralised matrix - increase Ca in blood | ||
| + | **'''Calcitonin''' | ||
| + | ***Produced by <u>C-cells in the thyroid glands</u> in response to <u>increased</u> serum calcium | ||
| + | ***Inhibits osteoclasts | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bone dynamics=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Bone growth and maintenance of normal structure are directly related to mechanical forces | ||
| + | *Mechanical forces generate bioelectrical potentials (piezoelectricity) | ||
| + | **These potentials strengthen bone | ||
| + | **Inactivity reduces the potentials -> bone loss | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In neonates: | ||
| + | **Bone growth predominates | ||
| + | **Modelling is important | ||
| + | *In adults: | ||
| + | **Formation of bone is balanced by resorption - remodelling | ||
| + | **Continues throughout life under the influence of hormones and mechanical pressure | ||
| + | **Bone resorption may exceed formation in pathological states (hormonal, trauma, nutritional) or in old age and disuse | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <big><center>[[Bones|'''BACK TO BONES''']]</center></big> | ||
Revision as of 08:43, 10 October 2007
Introduction
- Bone is a hard, highly specialised connective tissue
- Consists of interconnected cells embedded in a calcified, collagenous matrix
- Living, dynamic, responsive tissue, growing and remodelling throughout life
- Pathogenesis of many bone diseases is complex
- May involve genetic defects, diet or infection or a combination of these
- Function:
- Support/protection
- Movement
- Stem cell storage
- Mineral storage
Normal structure
- Cells
- Osteoblasts
- Mesenchymal cells
- Arise from bone marrow stroma
- Histologically:
- Plump and cuboidal when active
- Basophilic cytoplasm
- When inactive - less cytoplasm -> flattened
- Produce bone matrix = osteoid - uncalcified
- Homogeneous substance
- Stains light pink with H&E
- Cell membranes are rich in alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- Possibly involved in pumping calcium across membranes
- Promoted by growth factors
- Have receptors for PTH
- They contract in response -> space for osteoclasts to attach
- Osteocytes
- Osteoblasts that have become surrounded by mineralised bone matrix
- Occupy cavities called lacunae
- Contact osteoblasts and each other with cytoplasmic processes
- Reach through canaliculi in mineralised bone matrix
- Regulate composition of bone fluid
- Osteoclasts
- Histologically:
- Large, often multinucleated cells
- Acidophilic cytoplasm
- Derived from haematopoietic stem cells
- Responsible for bone resorption
- Firstly dissolve mineral followed by collagen
- Use brush border for this
- Sit in bone surface depression - Howship's lacuna
- Do not have receptors for PTH
- Have receptors for calcitonin
- Involute their brush border in response
- Detach from bone surface
- Histologically:
- Osteoblasts
- Matrix:
- Osteoid
- Type I collagen forms the backbone of the matrix (90%)
- Molecules in staggered rows
- Non-collagenous protein forming amorphous ground substance (10%)
- Type I collagen forms the backbone of the matrix (90%)
- Mineral
- Crystalline lattice of calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate
- Also contains Mg, Mn, Zn, Cu, Na, F
- Accounts for 65% of bone
- Osteoid
Bone organisation
- Patterns of collagen deposition:
- Woven bone:
- "Random weave" which is only a normal feature in the foetus
- Coarse collagen fibres
- Later removed by osteoclasts and replaced by lamellar bone
- In adults it is a sign of a pathological condition (e.g. fracture, inflammation, neoplasia)
- Lamellar bone:
- Orderly layers which are much stronger than woven bone
- Fine collagen fibres in concentric or parallel laminae
- Two main types:
- Compact bone (cortical)
- Forms 80% of total bone mass
- Consists of cells and interstitial substance - 30% ossein (type of collagen) and 70% minerals, especially calcium phosphate
- Forms the shell of long bone shafts - contain Haversian systems
- Cancellous bone (spongy or trabecular)
- Made up of plates, tubes or bars arranged in lines of stress
- In vertebrae, flat bones and epiphyses of long bones
- Contains no Haversian systems
- Compact bone (cortical)
- Laminar bone
- Formed on periosteal surface of diaphysis
- Accomodates rapid growth of large dogs and farm animals
- Plates of woven bone from within the periosteum
- Concentric plates
- As it forms, it fuses with the bone surface
- Woven bone:
Periosteum and blood supply
- Specialised sheath of connective tissue covering bone except at the articular surfaces
- Inner layer
- Merges with the outer layer of bone
- Contains osteoblasts and osteoprogenitor stem cells in young animals and in adults with fractures or disease
- Damage to the periosteum invokes a hyperplastic reaction of the inner layer
- The blood supply to the mature bone enters via the periosteum
- Endosteum lines the marrow cavity
Bone development
- Two main types of bone development:
- Endochondral ossification (cartilage model)
- Long bones mainly - physis and metaphysis
- Mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondroblasts
- Produce scaffold of mineralised cartilage on which osteoblasts deposit bone
- Vascularised
- Developed centres of ossification
- Primary (diaphyseal)
- Secondary (epiphyseal)
- Intramembranous ossification
- Flat bones mainly (e.g. skull), shaft of long bones
- Mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts
- No cartilage precursor template
- Endochondral ossification (cartilage model)
Physis (Growth plate)
- Originates from the cartilage model that remains only at the junction of the diaphyseal and epiphyseal centres
- Cartilage of metaphyseal growth plate is divided into: (from right to left on the magnified image)
- - Resting (reserve) zone
- - Proliferative zone
- - Hypertrophic zone
- Site of many congenital or nutritional bone diseases in the growing animal
- Open in neonates and growing animals
- Chondrocyte proliferation balances cell maturation and death
- Closes and ossifies at maturity
- Regulated by androgens
Bone resorption
- Mediated by two hormones:
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Produced by chief cells in the parathyroid glands in response to decreased serum calcium
- In response, osteoclasts increase in number and resorb mineralised matrix - increase Ca in blood
- Calcitonin
- Produced by C-cells in the thyroid glands in response to increased serum calcium
- Inhibits osteoclasts
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Bone dynamics
- Bone growth and maintenance of normal structure are directly related to mechanical forces
- Mechanical forces generate bioelectrical potentials (piezoelectricity)
- These potentials strengthen bone
- Inactivity reduces the potentials -> bone loss
- In neonates:
- Bone growth predominates
- Modelling is important
- In adults:
- Formation of bone is balanced by resorption - remodelling
- Continues throughout life under the influence of hormones and mechanical pressure
- Bone resorption may exceed formation in pathological states (hormonal, trauma, nutritional) or in old age and disuse