Difference between revisions of "Small Animal Dermatology Q&A 07"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
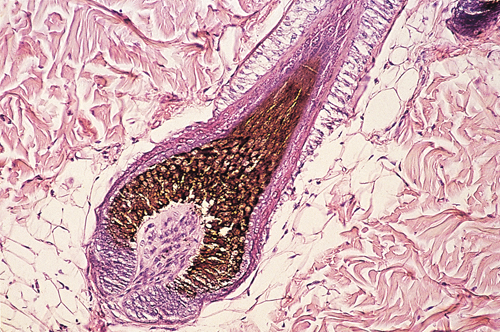
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Template:Manson Moriello}} centre|500px<br> <br /> '''A photomicrograph of a cross section of a hair bulb is shown.''' <br /> ...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
#During telogen, or the resting stage, the hair stops growing and is retained in the hair follicle as a dead hair. A telogen hair is characterized as a small hair, approximately one-third the length of the anagen hair. Hairs continue to grow until they reach a preset length and then enter the resting phase. The hair will remain in this state until a new hair starts to grow, pushes the old hair out, and the old hair is shed. <br><br> | #During telogen, or the resting stage, the hair stops growing and is retained in the hair follicle as a dead hair. A telogen hair is characterized as a small hair, approximately one-third the length of the anagen hair. Hairs continue to grow until they reach a preset length and then enter the resting phase. The hair will remain in this state until a new hair starts to grow, pushes the old hair out, and the old hair is shed. <br><br> | ||
Hairs in dogs and cats are replaced in a mosaic pattern with peaks of hair loss/replacement in the spring and fall. The other two most common replacement patterns are seasonal and waves. | Hairs in dogs and cats are replaced in a mosaic pattern with peaks of hair loss/replacement in the spring and fall. The other two most common replacement patterns are seasonal and waves. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1= |
|q2=What factors influence hair growth in animals? | |q2=What factors influence hair growth in animals? | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
*local factors that directly influence the growth of hair follicles. <br> | *local factors that directly influence the growth of hair follicles. <br> | ||
The most important of these factors are photoperiod and ambient temperature. | The most important of these factors are photoperiod and ambient temperature. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2= |
|q3=Describe the basic anatomy of a hair follicle. | |q3=Describe the basic anatomy of a hair follicle. | ||
|a3= | |a3= | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
#The isthmus consists of the area between the opening of the sebaceous duct and the attachment of the arrector pili muscle. | #The isthmus consists of the area between the opening of the sebaceous duct and the attachment of the arrector pili muscle. | ||
#The inferior segment extends from the attachment of the arrector pili muscle to the dermal hair papilla. | #The inferior segment extends from the attachment of the arrector pili muscle to the dermal hair papilla. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3= |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Revision as of 09:44, 6 June 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more small animal dermatological questions |
A photomicrograph of a cross section of a hair bulb is shown.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What are the stages of the hair cycle, and what are the most common patterns of growth in dogs and cats? | There are three stages or cycles in hair growth.
Hairs in dogs and cats are replaced in a mosaic pattern with peaks of hair loss/replacement in the spring and fall. The other two most common replacement patterns are seasonal and waves. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| What factors influence hair growth in animals? | The hair cycle of animals is controlled by a number of factors including:
The most important of these factors are photoperiod and ambient temperature. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| Describe the basic anatomy of a hair follicle. | Hair follicles are divided into three major anatomical regions: the infundibulum, isthmus, and the inferior segment.
|
[[|Link to Article]] | |