Difference between revisions of "Small Animal Dermatology Q&A 11"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Template:Manson Moriello}} centre|500px<br> <br /> '''A 6-month old Siamese cat with multiple cutaneous nodules on its head, fac...") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:Manson Moriello}} | {{Template:Manson Moriello}} | ||
| − | [[Image:Small Animal Dermatology Q&A | + | [[Image:Small Animal Dermatology Q&A 10.jpg|centre|500px]]<br> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
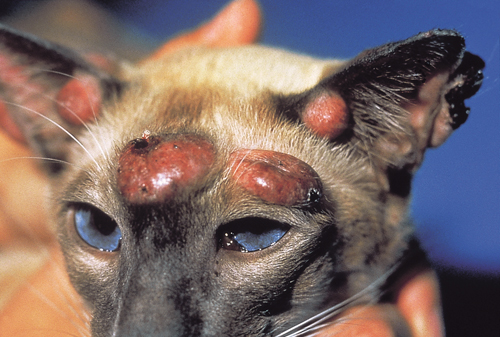
| − | ''' | + | '''A 6-month old Siamese cat with multiple cutaneous nodules on its head, face, and ears is presented for examination. Skin biopsy findings reveal a histiocytic MCT.''' |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<FlashCard questions="3"> | <FlashCard questions="3"> | ||
| − | |q1=What is the | + | |q1=What is the cat’s prognosis? |
|a1= | |a1= | ||
| − | + | *The prognosis is good. These tumors in young Siamese cats (<4 years of age) usually undergo spontaneous remission. | |
| − | |l1= | + | *These lesions also can be seen in non-Siamese kittens and will also resolve spontaneously. |
| − | |q2=What clinical | + | *Adult cats of other breeds with widespread lesions should be evaluated carefully as these cats tend to have visceral involvement. |
| + | |l1= | ||
| + | |q2=What are the three major clinical presentations of MCT in cats? | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| − | + | The three forms of clinical presentation are cutaneous, lymphoreticular or visceral, and gastrointestinal. | |
| − | + | #The visceral form involves a combination of the liver, spleen and/or abdominal lymph nodes. | |
| − | + | #The cutaneous form is limited to the skin. | |
| − | * | + | #The gastrointestinal form is usually a primary tumor and is the third most common intestinal tumor in cats after lymphoma and adenocarcinoma (Thamm and Vail, 2001). These tumors usually arise from the small intestine. Eosinophilia may be present.<br><br> |
| − | * | + | Clinical signs of lymphoreticular and gastrointestinal MCTs are indistinguishable: |
| − | |l2= | + | *vomiting, |
| − | |q3=What | + | *diarrhoea, |
| + | *depression, | ||
| + | *weight loss, and | ||
| + | *anorexia. | ||
| + | |l2= | ||
| + | |q3=What are the two histological subtypes of cutaneous MCT in cats? | ||
|a3= | |a3= | ||
| − | + | The two histological subtypes of feline mast cells are the histiocytic and mast cell type. | |
| − | |l3= | + | #The histiocytic type occurs in young cats (<4 years of age) and is most common in Siamese cats. It frequently presents as subcutaneous nodules. Histologically, the mast cells are poorly granulated and lymphoid aggregates are common. Many of these tumors will spontaneously regress. |
| + | #The ‘mast cell form’ of cutaneous MCT tends to occur in mixed breed shorthaired cats. Lesions tend to be solitary and are discrete, nodular, papular, or plaque-like lesions in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue. It can also present as ‘miliary dermatitis’. | ||
| + | |l3= | ||
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
{{#tag:imagemap|Image:Next Question.png{{!}}center{{!}}200px | {{#tag:imagemap|Image:Next Question.png{{!}}center{{!}}200px | ||
| − | rect 0 0 860 850 [[Small Animal Dermatology Q&A | + | rect 0 0 860 850 [[Small Animal Dermatology Q&A 11|Next question]] |
desc none}} | desc none}} | ||
[[Category:Small Animal Dermatology Q&A]] | [[Category:Small Animal Dermatology Q&A]] | ||
Revision as of 10:10, 6 June 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more small animal dermatological questions |
A 6-month old Siamese cat with multiple cutaneous nodules on its head, face, and ears is presented for examination. Skin biopsy findings reveal a histiocytic MCT.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is the cat’s prognosis? |
|
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| What are the three major clinical presentations of MCT in cats? | The three forms of clinical presentation are cutaneous, lymphoreticular or visceral, and gastrointestinal.
Clinical signs of lymphoreticular and gastrointestinal MCTs are indistinguishable:
|
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| What are the two histological subtypes of cutaneous MCT in cats? | The two histological subtypes of feline mast cells are the histiocytic and mast cell type.
|
[[|Link to Article]] | |