Difference between revisions of "Cowdriosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
}} | }} | ||
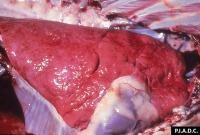
[[File:Heartwater 1.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Pulmonary oedema in goat with heartwater. Copyright AFSPH Iowa State.]] | [[File:Heartwater 1.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Pulmonary oedema in goat with heartwater. Copyright AFSPH Iowa State.]] | ||
| + | [[File:Heartwater 2|thumb|200px|right|''C. ruminantium'' in neutrophil from peripheral blood smear of a goat with heartwater. Copyright CFSPH Iowa State.]] | ||
===Heartwater=== | ===Heartwater=== | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 7 June 2011
| Cowdria ruminantium | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Bacteria |
| Phylum | Proteobacteria |
| Class | Alphaproteobacteria |
| Order | Rickettsiales |
| Family | Ehrlichiaceae |
| Genus | Cowdria |
| Species | C. ruminantium |
File:Heartwater 2
C. ruminantium in neutrophil from peripheral blood smear of a goat with heartwater. Copyright CFSPH Iowa State.
Heartwater
- Severe disease of ruminants in sub-Saharan Africa caused by Cowdria ruminantium
- Vectors include Amblyomma ticks
- Carrier status can occur for up to 8 months in adult cattle and wildebeest
- Clinical disease in calves and lambs
- Clinical signs
- Incubation period 4 weeks
- Acute fever
- Neurological signs including chewing, twitching of eyelids, circling, high-stepping gait, convulsions and recumbency; can be fatal
- Subacute cases suffer from hydropericardium, hydrothorax and pulmonary oedema and congestion; splenomegaly and haemorrhages may occur
- Diagnosis
- Clinical and post mortem findings in endemic areas suggestive
- Orgnisms present in nuclei of endothelial cells in Giemsa-stained brain tissue
- PCR, indirect immunofluorescence, ELISA and western blot
- Treatment and control
- Tetracyclines during early disease
- Immunisation using infected blood