Difference between revisions of "Small Animal Dermatology Q&A 12"
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 23:13, 31 July 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more small animal dermatological questions |
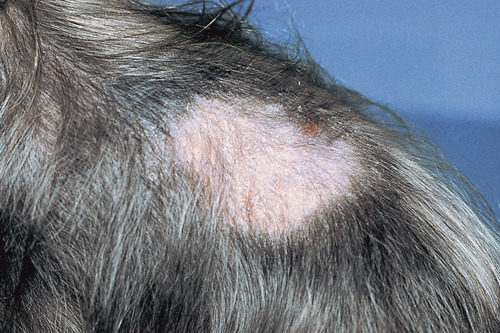
In January, a 1-year-old dog is presented for treatment of ‘ringworm’. The owner reports the dog has developed a ‘ringworm’ lesion on its dorsal back. There are two other dogs in the house along with three indoor cats, and none of these animals show signs of skin disease. The dog in question sleeps with the owner and she doesn’t have skin lesions. Dermatological examination reveals a focal area of non-inflammatory hair loss in the right lateral lumbosacral area. A Wood’s lamp examination is negative. The medical record indicates the dog received a subcutaneous injection of glucocorticoids 3.5 months ago at the end of September for seasonal atopy. The location of the injection was recorded as ‘subcutaneous over on the dorsum’. The dog is frequently groomed, and the owner has a penchant for having ribbons braided into the dog’s hair coat.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What are the most common differential diagnoses for acquired noninflammatory focal alopecia, and what diagnostic tests should be performed? | Differential diagnoses include
The anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids could be masking the inflammation usually associated with an infectious disease such as
Traction alopecia is a clinical syndrome seen in small breed dogs that have ribbons, barrettes, or bows tied too tightly into their hair coat. The tension on the hair follicles results in damage to the vasculature and permanent loss of hair follicles. |
Link to Article | |
| The skin biopsy findings revealed a focal area of thinning of the dermis and epidermis and atrophy of the hair follicles. What is the most likely diagnosis, and what management recommendations should be made? | The skin biopsy findings were interpreted as compatible with an endocrine alopecia. This was a case of post-steroid injection alopecia. The dog’s hair regrew over the next 6 months, and the lesion recurred in the fall when the dog again received a glucocorticoid injection. |
Link to Article | |
| List the major etiologies that cause focal damage to hair follicles and give at least one disease example in each category. |
|
Link to Article | |