Difference between revisions of "Hindbrain - Anatomy & Physiology"
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ==Introduction== | |
| − | + | The hind brain is also called the rhombencephalon and is the brain stem that provides the connection between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain. The hind brain contains many vital structures including the Medulla Oblongata, the Pons (the link between the cerebellum, forebrain and mid-brain) and the majority of the cranial nerves, III to XII. In general the brain stem governs essential functions that are carried out sub-consciously via reflexes. | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | As well as containing numerous cranial nerves, the hind brain also contains many 'Extra-pyramidal Pathways' which include the Reticular Formation, the Olivary Nucleus and the Pontine Nuclei. It also contains Cerebellar pathways and peduncles facilitating a connection from the brain stem to the cerebellum. There are also a number of 'Pyramidal Pathways' and afferent pathways including the Cuneate and Gracile pathways. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Hind Brain Development== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Hind Brain Functions== | |
| + | ===Medulla Oblongata=== | ||
| + | Nuclei in the Medulla Oblongata control the level of heart activity including rate and contractility. The Medulla Oblongata also controls other related functions including blood pressure and distribution of blood to different organs. In conjunction with the nuclei found in the Pons, the Medulla Oblongata also exerts an influence on respiratory movements. The respiratory centre in the Medulla Oblongata is affected by various types of drugs including opiods such as Morphine. These types of drugs often suppress the activity of the neurones in the respiratory nuclei. | ||
| − | + | ===Pons=== | |
| + | As shown above, the Pons is able to exert some influence on respiratory movements and in some studies has also been shown to influence many digestive processes. | ||
| + | ===Cranial Nerves=== | ||
| − | + | ==Structure and Function== | |
| − | + | {| style="width:75%; height:200px" border="1" | |
| − | + | ! | |
| − | + | !'''Structures Present''' | |
| − | + | !'''Function''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Hindbrain|Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)''' | |
| + | | '''Myelencephalon''' - [[#Medulla Oblongata|Medulla Oblongata]] | ||
| + | '''Metencephalon''' - [[#Pons|Pons]] and [[#Cerebellum|Cerebellum]] | ||
| + | | '''[[#Medulla Oblongata|Medulla Oblongata]]''' - Cranial nerves, hearing, visceral fibres | ||
| + | '''[[#Pons|Pons]]''' - Fibres to [[Forebrain - Anatomy & Physiology#Cerebral Cortex|cerebrum]] | ||
| − | + | [[#Cerebellum|'''Cerebellum''']] - Posture, balance etc | |
| − | [[ | + | | |
| + | |} | ||
| + | ===Medulla Oblongata=== | ||
| + | ===Pons=== | ||
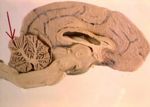
===Cerebellum=== | ===Cerebellum=== | ||
[[Image:braincerebellumarrow.jpg|thumb|right|150px|The location of the cerebellum. Image courtesy of BioMed Archive]] | [[Image:braincerebellumarrow.jpg|thumb|right|150px|The location of the cerebellum. Image courtesy of BioMed Archive]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | The | + | * The cerebellum: |
| + | ** Inhibits upper motor neurons | ||
| + | ** Co-ordinates movement | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Species Differences== | ||
| + | * The size of the brain differs between species, but otherwise the structure is quite constant. | ||
| + | ==Links== | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{unfinished}} |
| − | |||
[[Category:Nervous System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Nervous System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | [[Category:A&P | + | [[Category:To Do - A&P]] |
Revision as of 12:39, 6 August 2011
Introduction
The hind brain is also called the rhombencephalon and is the brain stem that provides the connection between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain. The hind brain contains many vital structures including the Medulla Oblongata, the Pons (the link between the cerebellum, forebrain and mid-brain) and the majority of the cranial nerves, III to XII. In general the brain stem governs essential functions that are carried out sub-consciously via reflexes.
As well as containing numerous cranial nerves, the hind brain also contains many 'Extra-pyramidal Pathways' which include the Reticular Formation, the Olivary Nucleus and the Pontine Nuclei. It also contains Cerebellar pathways and peduncles facilitating a connection from the brain stem to the cerebellum. There are also a number of 'Pyramidal Pathways' and afferent pathways including the Cuneate and Gracile pathways.
Hind Brain Development
Hind Brain Functions
Medulla Oblongata
Nuclei in the Medulla Oblongata control the level of heart activity including rate and contractility. The Medulla Oblongata also controls other related functions including blood pressure and distribution of blood to different organs. In conjunction with the nuclei found in the Pons, the Medulla Oblongata also exerts an influence on respiratory movements. The respiratory centre in the Medulla Oblongata is affected by various types of drugs including opiods such as Morphine. These types of drugs often suppress the activity of the neurones in the respiratory nuclei.
Pons
As shown above, the Pons is able to exert some influence on respiratory movements and in some studies has also been shown to influence many digestive processes.
Cranial Nerves
Structure and Function
| Structures Present | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon) | Myelencephalon - Medulla Oblongata
Metencephalon - Pons and Cerebellum |
Medulla Oblongata - Cranial nerves, hearing, visceral fibres
Cerebellum - Posture, balance etc |
Medulla Oblongata
Pons
Cerebellum
- The cerebellum:
- Inhibits upper motor neurons
- Co-ordinates movement
Species Differences
- The size of the brain differs between species, but otherwise the structure is quite constant.
Links
| This article is still under construction. |