Difference between revisions of "Rabbit Medicine and Surgery Q&A 07"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
Caecotrophs may remain uneaten or be abnormally soft for many reasons: | Caecotrophs may remain uneaten or be abnormally soft for many reasons: | ||
| − | *Vertebral pain or restriction of movement (e.g. spondylosis, spondylitis) so that the rabbit cannot bend to reach the anus to eat its caecotrophs. | + | *Vertebral pain or restriction of movement (e.g. spondylosis, spondylitis) so that the |
| + | rabbit cannot bend to reach the anus to eat its caecotrophs. | ||
*Obesity – the rabbit cannot physically reach its anus to eat the caecotrophs. | *Obesity – the rabbit cannot physically reach its anus to eat the caecotrophs. | ||
*Dental or other oral pain. | *Dental or other oral pain. | ||
Revision as of 09:54, 11 August 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Rabbit Medicine and Surgery questions |
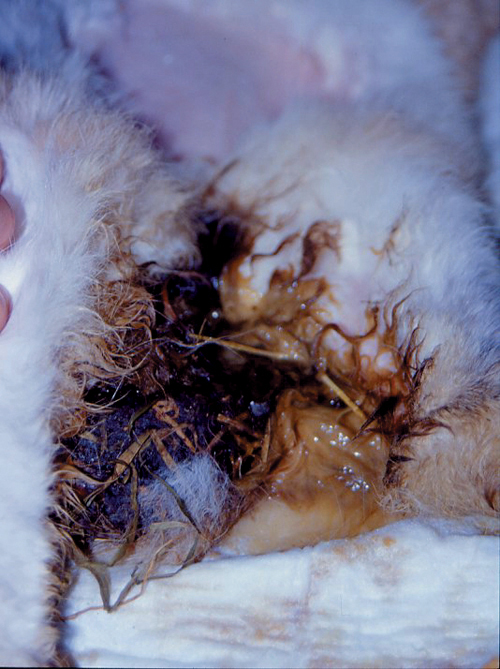
This rabbit presents to you with soft faecal material caked around its perineum. The owner reports that it has diarrhoea.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| How can you determine if this is indeed true diarrhoea? | True diarrhoea needs to be distinguished from uneaten caecotrophs or abnormally soft caecotrophs that adhere to the perineum.
|
Link to Article | |
| If you determine that true diarrhoea is not present, what can cause this presentation? | Caecotrophs may remain uneaten or be abnormally soft for many reasons:
rabbit cannot bend to reach the anus to eat its caecotrophs.
|
Link to Article | |