Difference between revisions of "Electrocardiography"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
Siobhanbrade (talk | contribs) m |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | + | Electrocardiography is one of the most commonly found piece of monitoring equipment in modern veterinary practices. It detects the electrical activity of the heart through 3 electrodes. These electrodes are most commonly placed on the 2 forelimbs and the left hindlimb. The electrodes are attached to the patient via ECG pads (most commonly), crocodile clips (more common in horses) and transcutaneous needles (rare). Frequently, additional electrode gel or alcohol is required to improve contact between the patient and electrodes. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The electrodes are attached to the patient via | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The ECG can determine the rate, rhythm and nature of cardiac depolarisation and repolarisation. It can also indicate changes in myocardial mass, conductivity between the heart and skin and the presence of metabolic abnormalities affect the heart. | ||
| + | Indication of metabolic abnormalities affecting the myocardium | ||
| + | Indication of alterations in conductivity between heart and skin | ||
| − | The | + | To interpret an ECG it is necessary to understand the path of depolarisation through the heart: |
| − | + | The sino-atrial node depolarises spontaneously and this wave of depolarisation spreads through the atria. The impulse is then conducted through AV node slowly. Then it rapidly passes through the bundle of His and bundle branches, spreading through the ventricular myocardium. The myocardium then remains depolarised for a period before repolarising. This depolarisation and repolarisation are detected as potential differences on the skin surface - producing the classic shape of the ECG trace. | |
| − | |||
==Reading an ECG Trace== | ==Reading an ECG Trace== | ||
| − | An ECG | + | An ECG supplies information about the electrical activity of the heart only. It indicates the heart rate and rhythm and can be used to detect any arrhythmias. It does not supply information about cardiac function. It is important to remember to treat the patient not the ECG! |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:ECG.jpg|left|]] | [[Image:ECG.jpg|left|]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
| Line 61: | Line 39: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 80: | Line 60: | ||
| − | + | These 5 features should be assessed in every ECG that you interpret. | |
The following questions should be asked when interpreting every ECG: | The following questions should be asked when interpreting every ECG: | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | '''Is E.C.G. of diagnostic quality?''' | ||
It is important that no artefact is present on the trace. Interference from electrical equipment and fluorescent lighting (50Hz interference) and movement should be prevented. The ECG should be calibrated for both paper speed and vertical sensitivity, and the trace should remain within the paper edges. All leads should be demonstrated. | It is important that no artefact is present on the trace. Interference from electrical equipment and fluorescent lighting (50Hz interference) and movement should be prevented. The ECG should be calibrated for both paper speed and vertical sensitivity, and the trace should remain within the paper edges. All leads should be demonstrated. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | '''What is the heart rate?''' | ||
Heart rate can be calculated using one of the following two methods: | Heart rate can be calculated using one of the following two methods: | ||
'''(1) Instantaneous heart rate''' | '''(1) Instantaneous heart rate''' | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | 1500/R-R interval (25 mm/sec) | |
| + | |||
| + | 3000/R-R interval (50 mm/sec) | ||
'''(2) Number of R-R intervals in 6 seconds x 10''' | '''(2) Number of R-R intervals in 6 seconds x 10''' | ||
| Line 100: | Line 84: | ||
Where multiple rhythms exist, the rate of all rhythms present should be calculated. | Where multiple rhythms exist, the rate of all rhythms present should be calculated. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''What is the heart rhythm?''' | |
| + | |||
| + | It is important to interpret whether the heart rate is regular or irregular, and if it is irregular whether it is regularly irregular or irregularly irregular. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''What is the mean electrical axis?''' | |
This figure is of limited value in small animals. It can give some indication of ventricular enlargement and the presence of intraventricular conduction defects. | This figure is of limited value in small animals. It can give some indication of ventricular enlargement and the presence of intraventricular conduction defects. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''What are the individual complex measurements?''' | |
| − | + | Changes in the morphology of the complexes are classed as a change in the shape, size or duration of the P wave, QRS complex or T wave. The magnitude and duration of deflections may be altered by regional changes in myocardial mass and alterations in conduction. This can be caused by hypertrophy of the myocardium, electrolyte abnormalities or an alterations in autonomic tone within the heart. | |
| − | + | You should record whether all the deflections are the same, as some variations may be normal. | |
| − | + | Variation in P-wave | |
| + | May be normal - wandering pacemaker | ||
| + | May indicate atrial ectopy | ||
| + | P-wave should be positive in lead II | ||
| + | Variation in QRS complex | ||
| + | Some variation may be normal | ||
| + | May indicate variable conduction | ||
| + | May indicate electrical alternans | ||
| − | + | No P to every QRS. | |
| + | This means that the ventricular depolarisation has not been preceded by a normal atrial depolarisation | ||
| + | Premature complexes | ||
| + | Ventricular premature | ||
| + | Junctional premature | ||
| + | Sinus arrest with escape complexes | ||
| + | Ventricular escape | ||
| + | Junctional escape | ||
| + | No organised atrial depolarisation | ||
| + | Atrial standstill | ||
| + | Atrial fibrillation | ||
| − | + | No QRS to every P. | |
| + | Failure of AV conduction | ||
| + | Second degree AV block | ||
| + | Intermittent failure of AV conduction | ||
| + | Mobitz type I - Prolongation of P-R interval | ||
| + | Mobitz type II - No prolongation of P-R interval | ||
| + | Third degree AV block | ||
| + | Complete failure of AV conduction | ||
| + | Complete AV dissociation | ||
| − | + | Consistently and reasonably related. | |
| + | Marked variation in P-R intervals may suggest AV dissociation | ||
| + | Can occur with | ||
| + | Ventricular rhythm disturbances | ||
| + | Junctional rhythm disturbances | ||
| + | Third degree AV block | ||
| − | + | AV dissociation: | |
| + | Map out P-P intervals, Map out R-R intervals, Map out P-R intervals | ||
| + | If P-P interval is relatively consistent, R-R interval is relatively consistent but P-R interval is highly variable then you have Atrioventricular dissociation | ||
| + | Where atrioventricular dissociation occurs the origin of the ventricular depolarisation must be within the ventricle or the AV junction | ||
| − | + | Alterations in intervals: | |
| − | + | May reflect alterations in myocardial mass | |
| + | Increased P-wave amplitude may reflect right atrial enlargement | ||
| + | Increased R-wave amplitude may reflect changes in ventricular myocardium | ||
| + | Increased T-wave amplitude | ||
| + | May occur with drugs, electrolyte and acid-base disturbances | ||
| + | May be normal in dogs | ||
| − | + | Common problems: | |
| − | + | Differentiation of artefact from rhythm disturbance | |
| − | + | Determining the origin of non-sinus depolarisations | |
| + | Determining the significance of E.C.G. abnormalities which may be present. | ||
| − | + | Abnormalities of generation or conduction of the depolarisation can arise for various reasons | |
| − | + | Intrinsic cardiac disease | |
| + | Hypoxia | ||
| + | Autonomic influence | ||
| + | Mechanical abnormalities | ||
| + | Metabolic abnormalities | ||
| + | Electrolyte disturbances | ||
| + | Drugs | ||
| − | + | ==Summary== | |
| − | + | ECG represents electrical activity recorded at the skin surface as a consequence of depolarisation and repolarisation | |
| − | + | Unique in ability to provide information about cardiac rhythm | |
| − | + | Able to provide clues about hypertrophy and some metabolic disturbances | |
| − | + | Understanding physiology and applying logical rules aids interpretation | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Normal organised pattern of depolarisation and repolarisation of the heart leads to regular detectable potential differences between points on skin surface | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Is there a P for every QRS? | |
| − | + | *Is there a QRS for every P? | |
| + | *Are they all reasonably related? | ||
| + | *Are they all the same? | ||
| + | *Is rhythm regular or irregular? | ||
| + | *Is the arrhythmia regularly irregular or irregularly irregular? | ||
[[Category:Monitoring Anaesthesia]] | [[Category:Monitoring Anaesthesia]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category: To Do - Siobhan Brade]] |
| − | |||
Revision as of 10:36, 11 August 2011
Introduction
Electrocardiography is one of the most commonly found piece of monitoring equipment in modern veterinary practices. It detects the electrical activity of the heart through 3 electrodes. These electrodes are most commonly placed on the 2 forelimbs and the left hindlimb. The electrodes are attached to the patient via ECG pads (most commonly), crocodile clips (more common in horses) and transcutaneous needles (rare). Frequently, additional electrode gel or alcohol is required to improve contact between the patient and electrodes.
The ECG can determine the rate, rhythm and nature of cardiac depolarisation and repolarisation. It can also indicate changes in myocardial mass, conductivity between the heart and skin and the presence of metabolic abnormalities affect the heart. Indication of metabolic abnormalities affecting the myocardium Indication of alterations in conductivity between heart and skin
To interpret an ECG it is necessary to understand the path of depolarisation through the heart: The sino-atrial node depolarises spontaneously and this wave of depolarisation spreads through the atria. The impulse is then conducted through AV node slowly. Then it rapidly passes through the bundle of His and bundle branches, spreading through the ventricular myocardium. The myocardium then remains depolarised for a period before repolarising. This depolarisation and repolarisation are detected as potential differences on the skin surface - producing the classic shape of the ECG trace.
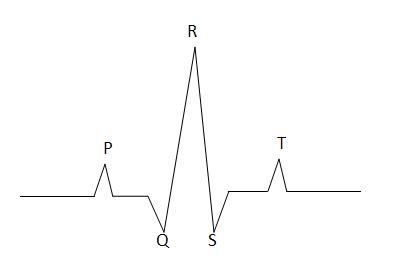
Reading an ECG Trace
An ECG supplies information about the electrical activity of the heart only. It indicates the heart rate and rhythm and can be used to detect any arrhythmias. It does not supply information about cardiac function. It is important to remember to treat the patient not the ECG!
| Stage | Represents |
|---|---|
| P | Atrial Depolarisation |
| QRS | Ventricular Depolarisation |
| T | Ventricular Repolarisation |
A Normal ECG Trace
Before you interpret abnormal ECG's you must know what a normal ECG looks like:
- A P-wave precedes every QRS complex
- A QRS complex follows every P-wave
- P and QRS are consistently and reasonably related
- P and QRS will all appear the same
- They will occur at a normal rate
These 5 features should be assessed in every ECG that you interpret.
The following questions should be asked when interpreting every ECG:
Is E.C.G. of diagnostic quality?
It is important that no artefact is present on the trace. Interference from electrical equipment and fluorescent lighting (50Hz interference) and movement should be prevented. The ECG should be calibrated for both paper speed and vertical sensitivity, and the trace should remain within the paper edges. All leads should be demonstrated.
What is the heart rate?
Heart rate can be calculated using one of the following two methods:
(1) Instantaneous heart rate
1500/R-R interval (25 mm/sec)
3000/R-R interval (50 mm/sec)
(2) Number of R-R intervals in 6 seconds x 10
Where multiple rhythms exist, the rate of all rhythms present should be calculated.
What is the heart rhythm?
It is important to interpret whether the heart rate is regular or irregular, and if it is irregular whether it is regularly irregular or irregularly irregular.
What is the mean electrical axis?
This figure is of limited value in small animals. It can give some indication of ventricular enlargement and the presence of intraventricular conduction defects.
What are the individual complex measurements?
Changes in the morphology of the complexes are classed as a change in the shape, size or duration of the P wave, QRS complex or T wave. The magnitude and duration of deflections may be altered by regional changes in myocardial mass and alterations in conduction. This can be caused by hypertrophy of the myocardium, electrolyte abnormalities or an alterations in autonomic tone within the heart.
You should record whether all the deflections are the same, as some variations may be normal.
Variation in P-wave May be normal - wandering pacemaker May indicate atrial ectopy P-wave should be positive in lead II Variation in QRS complex Some variation may be normal May indicate variable conduction May indicate electrical alternans
No P to every QRS. This means that the ventricular depolarisation has not been preceded by a normal atrial depolarisation Premature complexes Ventricular premature Junctional premature Sinus arrest with escape complexes Ventricular escape Junctional escape No organised atrial depolarisation Atrial standstill Atrial fibrillation
No QRS to every P. Failure of AV conduction Second degree AV block Intermittent failure of AV conduction Mobitz type I - Prolongation of P-R interval Mobitz type II - No prolongation of P-R interval Third degree AV block Complete failure of AV conduction Complete AV dissociation
Consistently and reasonably related. Marked variation in P-R intervals may suggest AV dissociation Can occur with Ventricular rhythm disturbances Junctional rhythm disturbances Third degree AV block
AV dissociation: Map out P-P intervals, Map out R-R intervals, Map out P-R intervals If P-P interval is relatively consistent, R-R interval is relatively consistent but P-R interval is highly variable then you have Atrioventricular dissociation Where atrioventricular dissociation occurs the origin of the ventricular depolarisation must be within the ventricle or the AV junction
Alterations in intervals: May reflect alterations in myocardial mass Increased P-wave amplitude may reflect right atrial enlargement Increased R-wave amplitude may reflect changes in ventricular myocardium Increased T-wave amplitude May occur with drugs, electrolyte and acid-base disturbances May be normal in dogs
Common problems: Differentiation of artefact from rhythm disturbance Determining the origin of non-sinus depolarisations Determining the significance of E.C.G. abnormalities which may be present.
Abnormalities of generation or conduction of the depolarisation can arise for various reasons Intrinsic cardiac disease Hypoxia Autonomic influence Mechanical abnormalities Metabolic abnormalities Electrolyte disturbances Drugs
Summary
ECG represents electrical activity recorded at the skin surface as a consequence of depolarisation and repolarisation Unique in ability to provide information about cardiac rhythm Able to provide clues about hypertrophy and some metabolic disturbances Understanding physiology and applying logical rules aids interpretation
Normal organised pattern of depolarisation and repolarisation of the heart leads to regular detectable potential differences between points on skin surface
- Is there a P for every QRS?
- Is there a QRS for every P?
- Are they all reasonably related?
- Are they all the same?
- Is rhythm regular or irregular?
- Is the arrhythmia regularly irregular or irregularly irregular?