Difference between revisions of "Avian Medicine Q&A 20"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|q1= List those medical causes of feather plucking which are or may be infectious, contagious or transmissible. | |q1= List those medical causes of feather plucking which are or may be infectious, contagious or transmissible. | ||
|a1= PBFD (circovirus); budgerigar fledgeling disease (Polyomavirus: French moult); ectoparasites (e.g. ''Dermanyssus gallinae''); endoparasites (e.g. Giardia sp.); chlamydiosis; fungal dermatitis. | |a1= PBFD (circovirus); budgerigar fledgeling disease (Polyomavirus: French moult); ectoparasites (e.g. ''Dermanyssus gallinae''); endoparasites (e.g. Giardia sp.); chlamydiosis; fungal dermatitis. | ||
| − | |l1=Feather Plucking | + | |l1=Feather Plucking |
|q2= List the non-infectious medical, including metabolic, causes of feather plucking. | |q2= List the non-infectious medical, including metabolic, causes of feather plucking. | ||
|a2= Bacterial dermatitis; pulpitis or folliculitis; allergy; hepatitis; hypothyroidism; skin neoplasia; follicular cysts; post-traumatic injury, or arthritic or scar tissue pain; nutritional deficiency (e.g. hypovitaminosis A; B vitamin deficiencies; essential amino acid deficiencies (e.g. lysine)). | |a2= Bacterial dermatitis; pulpitis or folliculitis; allergy; hepatitis; hypothyroidism; skin neoplasia; follicular cysts; post-traumatic injury, or arthritic or scar tissue pain; nutritional deficiency (e.g. hypovitaminosis A; B vitamin deficiencies; essential amino acid deficiencies (e.g. lysine)). | ||
| − | |l2=Feather Plucking | + | |l2=Feather Plucking |
|q3= Describe the diagnosis of the aetiologies described in q1. | |q3= Describe the diagnosis of the aetiologies described in q1. | ||
|a3= PCR for PBFD and BFD; physical examination at day and night for ectoparasites; faecal examination for endoparasites; PCR/ELISA (antigen/antibody) for chlamydiosis; skin scrape microscopic examination and culture for fungal dermatitis; stained impression smear, culture and sensitivity for bacterial infections. Also, haematology | |a3= PCR for PBFD and BFD; physical examination at day and night for ectoparasites; faecal examination for endoparasites; PCR/ELISA (antigen/antibody) for chlamydiosis; skin scrape microscopic examination and culture for fungal dermatitis; stained impression smear, culture and sensitivity for bacterial infections. Also, haematology | ||
and biochemistry, thyroid stimulation test, biopsy and histopathology, improved diet and monitoring response to therapy. | and biochemistry, thyroid stimulation test, biopsy and histopathology, improved diet and monitoring response to therapy. | ||
| − | |l3=Feather Plucking | + | |l3=Feather Plucking |
|q4= List the environmental causes of feather plucking. | |q4= List the environmental causes of feather plucking. | ||
|a4= Excess tobacco smoke; excessively dry atmosphere; excessive day length in direct sunlight; lack of environmental enrichment. | |a4= Excess tobacco smoke; excessively dry atmosphere; excessive day length in direct sunlight; lack of environmental enrichment. | ||
| − | |l4=Feather Plucking | + | |l4=Feather Plucking |
|q5= List the psychological causes of feather plucking. | |q5= List the psychological causes of feather plucking. | ||
|a5= Attention seeking; boredom; overcrowding; environmental change or lack of routine; sexual frustration; excessive preening; post untidy feather or wing clipping. | |a5= Attention seeking; boredom; overcrowding; environmental change or lack of routine; sexual frustration; excessive preening; post untidy feather or wing clipping. | ||
| − | |l5=Feather Plucking | + | |l5=Feather Plucking |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Revision as of 23:14, 21 August 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Avian Medicine questions |
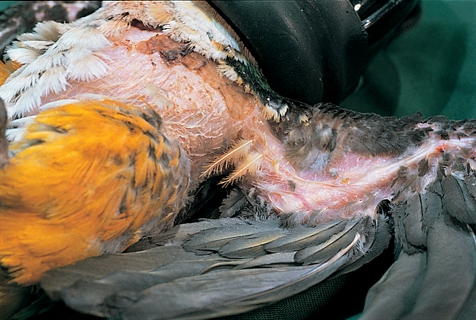
This bird has been feather plucking.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| List those medical causes of feather plucking which are or may be infectious, contagious or transmissible. | PBFD (circovirus); budgerigar fledgeling disease (Polyomavirus: French moult); ectoparasites (e.g. Dermanyssus gallinae); endoparasites (e.g. Giardia sp.); chlamydiosis; fungal dermatitis.
|
Link to Article | |
| List the non-infectious medical, including metabolic, causes of feather plucking. | Bacterial dermatitis; pulpitis or folliculitis; allergy; hepatitis; hypothyroidism; skin neoplasia; follicular cysts; post-traumatic injury, or arthritic or scar tissue pain; nutritional deficiency (e.g. hypovitaminosis A; B vitamin deficiencies; essential amino acid deficiencies (e.g. lysine)).
|
Link to Article | |
| Describe the diagnosis of the aetiologies described in q1. | PCR for PBFD and BFD; physical examination at day and night for ectoparasites; faecal examination for endoparasites; PCR/ELISA (antigen/antibody) for chlamydiosis; skin scrape microscopic examination and culture for fungal dermatitis; stained impression smear, culture and sensitivity for bacterial infections. Also, haematology
and biochemistry, thyroid stimulation test, biopsy and histopathology, improved diet and monitoring response to therapy. |
Link to Article | |
| List the environmental causes of feather plucking. | Excess tobacco smoke; excessively dry atmosphere; excessive day length in direct sunlight; lack of environmental enrichment.
|
Link to Article | |
| List the psychological causes of feather plucking. | Attention seeking; boredom; overcrowding; environmental change or lack of routine; sexual frustration; excessive preening; post untidy feather or wing clipping.
|
Link to Article | |