Difference between revisions of "Rabbit Medicine and Surgery Q&A 15"
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
*modified transudates seen secondary to neoplasia, lung lobe torsion or diaphragmatic hernia; | *modified transudates seen secondary to neoplasia, lung lobe torsion or diaphragmatic hernia; | ||
*haemothorax – seen in viral haemorrhagic disease, coagulopathies or trauma. | *haemothorax – seen in viral haemorrhagic disease, coagulopathies or trauma. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1= |
|q2= Based on the radiographic findings, what immediate treatment would you consider? | |q2= Based on the radiographic findings, what immediate treatment would you consider? | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
*Sedation is often not required in debilitated animals, although diazepam (0.5–1 mg/kg i/v or i/m) or midazolam (1–2 mg/kg i/v or i/m) may be used if necessary. <br><br> | *Sedation is often not required in debilitated animals, although diazepam (0.5–1 mg/kg i/v or i/m) or midazolam (1–2 mg/kg i/v or i/m) may be used if necessary. <br><br> | ||
In this case 20 ml of a serosanguinous fluid was obtained from both left and right sides of the chest. It was found to be a modified transudate with a protein of 22.4 g/l (2.4 g/dl) (ref: 25–30 g/l [2.5–3 g/dl]) and a nucleated cell count of 2 × 109/l (2000/μl) (ref: 1–7 × 109/l [1000–7000/μl]). No organisms were cultured. | In this case 20 ml of a serosanguinous fluid was obtained from both left and right sides of the chest. It was found to be a modified transudate with a protein of 22.4 g/l (2.4 g/dl) (ref: 25–30 g/l [2.5–3 g/dl]) and a nucleated cell count of 2 × 109/l (2000/μl) (ref: 1–7 × 109/l [1000–7000/μl]). No organisms were cultured. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2= |
|q3=What further diagnostic tests might be helpful? | |q3=What further diagnostic tests might be helpful? | ||
|a3= | |a3= | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
#Echocardiography should be carried out to characterize any cardiac disease further. | #Echocardiography should be carried out to characterize any cardiac disease further. | ||
#Electrocardiography, blood pressure measurement and routine blood tests are useful in reaching a definitive diagnosis and treatment plan. | #Electrocardiography, blood pressure measurement and routine blood tests are useful in reaching a definitive diagnosis and treatment plan. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3= |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Revision as of 12:23, 25 August 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Rabbit Medicine and Surgery questions |
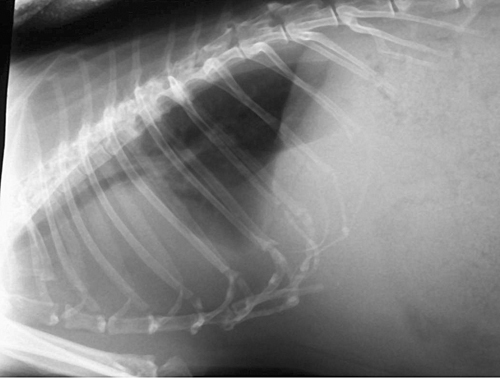
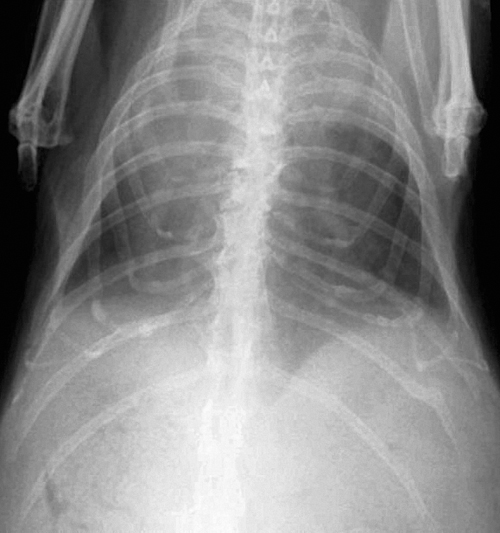
A seven-year-old intact male English rabbit, housed indoors, presents with acute onset tachypnoea and laboured breathing. There is a three-month history of weight loss, hindlimb weakness and rapid fatigue. The rabbit is alert, thin and weak. The mucous membranes are pale, with prolonged capillary refill time. A good response is noted to oxygen administration. The rabbit is sedated with intravenous midazolam and lateral and ventrodorsal radiographs of the thorax are taken.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What are the differential diagnoses in this case? | Congestive heart failure (myocardial, valvular and congenital disease) is seen in middle-aged to older rabbits. The weakness, weight loss and rapid fatigue observed, although non-specific signs, should arouse suspicion of cardiac or lower respiratory disease.
|
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| Based on the radiographic findings, what immediate treatment would you consider? | The radiographs show a pleural effusion. Immediate thoracocentesis will help stabilize the rabbit as well as determine the type of effusion.
In this case 20 ml of a serosanguinous fluid was obtained from both left and right sides of the chest. It was found to be a modified transudate with a protein of 22.4 g/l (2.4 g/dl) (ref: 25–30 g/l [2.5–3 g/dl]) and a nucleated cell count of 2 × 109/l (2000/μl) (ref: 1–7 × 109/l [1000–7000/μl]). No organisms were cultured. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| What further diagnostic tests might be helpful? |
|
[[|Link to Article]] | |