Difference between revisions of "Avian Medicine Q&A 09"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | [[File:Manson_logo.gif|90px|Mansonlogo]] | | align="center" | [[File:Manson_logo.gif|90px|Mansonlogo]] | ||
| − | | align="left" | This question was provided by [[:Category:Manson|Manson Publishing]] as part of the [[OVAL Project]]. See more [[Category: Avian Medicine Q&A|Avian Medicine questions]] | + | | align="left" | This question was provided by [[:Category:Manson|Manson Publishing]] as part of the [[OVAL Project]]. See more [[:Category: Avian Medicine Q&A|Avian Medicine questions]] |
|} | |} | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
rect 0 0 860 850 [[Avian Medicine Q&A 10|Next question]] | rect 0 0 860 850 [[Avian Medicine Q&A 10|Next question]] | ||
desc none}} | desc none}} | ||
| − | [[Category: Avian Medicine Q&A | + | [[Category: Avian Medicine Q&A]] |
Latest revision as of 13:56, 1 September 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Avian Medicine questions |
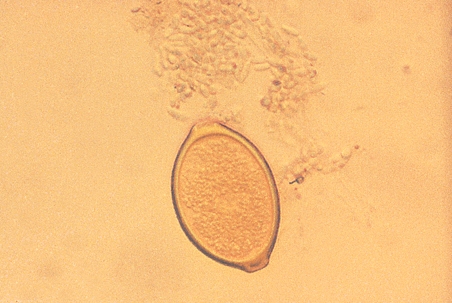
A wild neighbourhood peacock is presented for the treatment of a leg fracture. Subsequent health assessment includes a faecal flotation. Moderate numbers of ova were visualized.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| Identify the ovum. | The ovum is that of Capillaria sp.
|
Link to Article | |
| How would you treat this parasite? | Treatment of this parasite can be challenging. The parasite often exhibits multiple drug resistance. Fenbendazole, mebendazole and ivermectin have been used.
Repeat faecal flotations should always be carried out following the discovery of this parasite, to ensure that therapy has been effective. |
Link to Article | |
| How would you prevent infestation with this parasite? | If the peacock is released back into its habitual environment, reinfection is likely. Periodic testing and reworming is recommended.
|
Link to Article | |