Difference between revisions of "Small Animal Soft Tissue Surgery Q&A 21"
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:Soft Tissue Sx 21.jpg|centre|500px]] | [[Image:Soft Tissue Sx 21.jpg|centre|500px]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
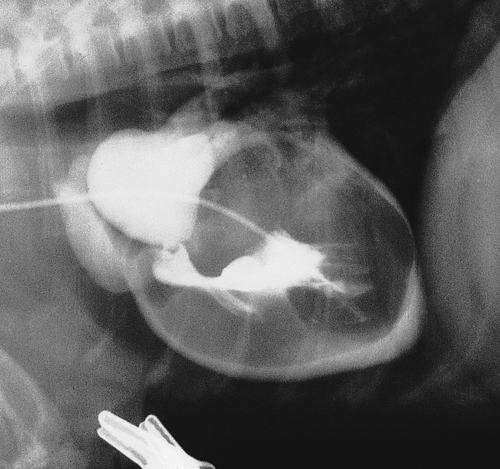
| − | '''You are presented with a one | + | '''You are presented with a one-yearold, female Giant Schnauzer for its annual vaccinations. On auscultation of the chest you detect a murmur. Part of your diagnostic evaluation includes a selective right ventricular angiogram. The radiograph pictured demonstrates the lesion.''' |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 13: | ||
There is also poststenotic dilation of the pulmonary artery. | There is also poststenotic dilation of the pulmonary artery. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1= |
|q2=Describe the murmur you would hear with this type of lesion. | |q2=Describe the murmur you would hear with this type of lesion. | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
Crescendo–decrescendo systolic murmur heard best on the left side at the base of the heart. | Crescendo–decrescendo systolic murmur heard best on the left side at the base of the heart. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2= |
|q3=What ECG findings would you expect with this lesion? | |q3=What ECG findings would you expect with this lesion? | ||
|a3= | |a3= | ||
| Line 27: | Line 23: | ||
Tall P waves, S waves greater than 0.35 mV in lead II and greater than 0.05 mV in lead I, presence of S waves in leads I, II, III and aVF, and deep Q waves (>0.5 mV) in leads I, II, III and aVF are consistent with right-sided cardiac enlargement. | Tall P waves, S waves greater than 0.35 mV in lead II and greater than 0.05 mV in lead I, presence of S waves in leads I, II, III and aVF, and deep Q waves (>0.5 mV) in leads I, II, III and aVF are consistent with right-sided cardiac enlargement. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3= |
|q4=What therapy would you recommend, and what would determine if medical or surgical therapy were indicated? | |q4=What therapy would you recommend, and what would determine if medical or surgical therapy were indicated? | ||
|a4= | |a4= | ||
| Line 41: | Line 37: | ||
Many dogs are asymptomatic and those with clinical signs generally have pressure gradients which warrant surgery. If left untreated, signs of right-sided heart failure develop and may be managed medically. | Many dogs are asymptomatic and those with clinical signs generally have pressure gradients which warrant surgery. If left untreated, signs of right-sided heart failure develop and may be managed medically. | ||
| − | |l4= | + | |l4= |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Revision as of 09:07, 5 September 2011
You are presented with a one-yearold, female Giant Schnauzer for its annual vaccinations. On auscultation of the chest you detect a murmur. Part of your diagnostic evaluation includes a selective right ventricular angiogram. The radiograph pictured demonstrates the lesion.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| Name the cardiac lesion. | Subvalvular pulmonic stenosis with muscular infundibular stenosis. There is also poststenotic dilation of the pulmonary artery. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| Describe the murmur you would hear with this type of lesion. | Crescendo–decrescendo systolic murmur heard best on the left side at the base of the heart. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| What ECG findings would you expect with this lesion? | ECG changes would be consistent with right-sided cardiac enlargement and right axis deviation. Tall P waves, S waves greater than 0.35 mV in lead II and greater than 0.05 mV in lead I, presence of S waves in leads I, II, III and aVF, and deep Q waves (>0.5 mV) in leads I, II, III and aVF are consistent with right-sided cardiac enlargement. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| What therapy would you recommend, and what would determine if medical or surgical therapy were indicated? | The decision between medical and surgical management of pulmonic stenosis is generally based on the pressure gradient between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. A catheter is placed through the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery, and pressures are monitored as the catheter is withdrawn through the stenosis. The pressure in the pulmonary artery is lower than that of the right ventricle because of obstructed flow. Surgery is recommended in adult dogs if right ventricular systolic pressure is 120 mmHg or greater (in immature dogs greater than 70 mmHg), or if the gradient across the stenosis is greater than 100 mmHg. No specific medical therapy is indicated for the management of pulmonic stenosis. Many dogs are asymptomatic and those with clinical signs generally have pressure gradients which warrant surgery. If left untreated, signs of right-sided heart failure develop and may be managed medically. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |