Difference between revisions of "Small Animal Abdominal and Metabolic Disorders Q&A 01"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
The absence of radiographic changes is expected and is the reason such a diagnosis is difficult to make routinely. | The absence of radiographic changes is expected and is the reason such a diagnosis is difficult to make routinely. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1= |
|q2=How is it related to the enteropathy? | |q2=How is it related to the enteropathy? | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
As well as prednisolone and azathioprine treatment for the LPE, this dog was treated with heparin and low doses of aspirin, and it made a good recovery. | As well as prednisolone and azathioprine treatment for the LPE, this dog was treated with heparin and low doses of aspirin, and it made a good recovery. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2= |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Revision as of 13:21, 26 October 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Small Animal Abdominal and Metabolic Disorders Q&A. |
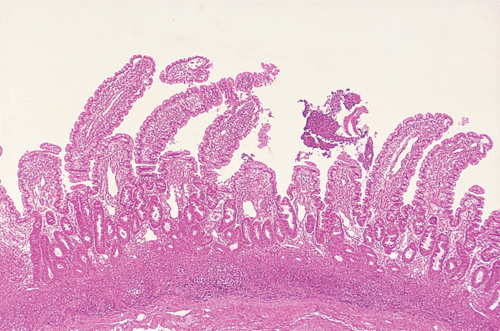
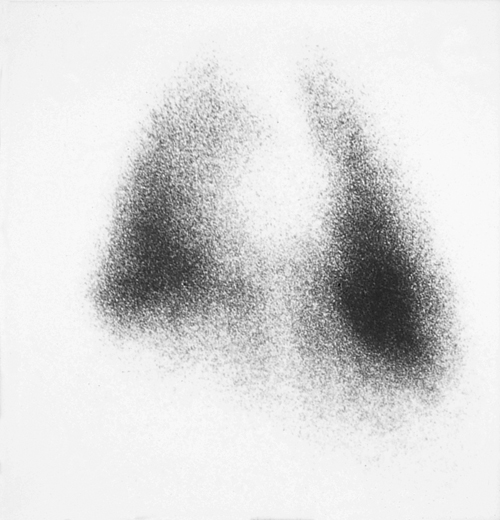
A six-year-old, neutered female Springer Spaniel suffering from chronic diarrhoea and weight loss suddenly develops ascites and dyspnoea. The dog has panhypoproteinaemia (albumin 13 g/l, globulin 12 g/l) and the ascitic fluid is a transudate. A protein-losing enteropathy is suspected and endoscopic biopsy ultimately confirms severe lymphocytic-plasmacytic enteritis (LPE). Chest radiographs reveal minimal pleural effusion, insufficient to explain the degree of dyspnoea exhibited by the patient. Although the lung parenchyma appears normal radiographically, a scintigraphic perfusion study is abnormal; this indicates impaired pulmonary perfusion, especially of the caudal tip of the right caudal lung lobe.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is the cause of the dyspnoea? | Pulmonary thromboembolism. A scintigraphic perfusion study is performed by injecting 99mtechnetium-labelled albumin microaggregates into the cephalic vein. The aggregates lodge in the first capillary bed they pass through (i.e. the pulmonary vasculature) and are detected by a gamma camera. All normally perfused lung will be visible scintigraphically but lack of perfusion will be indicated by a lack of scintillation. The lack of activity in the caudal tip of the left diaphragmatic is typical of a pulmonary thromboembolism. The absence of radiographic changes is expected and is the reason such a diagnosis is difficult to make routinely. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| How is it related to the enteropathy? | Thromboembolism is a well recognized feature of the nephrotic syndrome, and is believed to be associated with the urinary loss of small anticoagulant factors, especially antithrombin III. Both pulmonary and renal thromboembolism are not infrequently reported at postmortem examination of dogs with protein-losing enteropathies, but are rarely diagnosed antemortem. The mechanism of thrombosis is presumably the same as for protein-losing nephropathies, and massive thrombosis may be an unexpected cause of death in these patients. As well as prednisolone and azathioprine treatment for the LPE, this dog was treated with heparin and low doses of aspirin, and it made a good recovery. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |