Difference between revisions of "Mammary Gland - Horse Anatomy"
(Created page with "{{unfinished}} ==Overview== The '''mamma (pleural = mammae) ''' is the glandular structure associated with a '''papilla '''(teat) and may contains two ducts in the mare. The '...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{unfinished}} | {{unfinished}} | ||
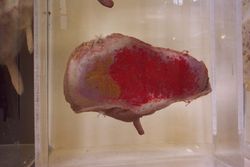
| + | [[Image:Equine mammary gland.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Dissection of the Equine Mammary Gland, Courtesy of Andrew Crook, Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The '''mamma (pleural = mammae) ''' is the glandular structure associated with a '''papilla '''(teat) and may contains two ducts in the mare. The '''udder''' is a term designating all the mammae in the mare. The mammary glands of the mare are close together, forming a small udder in the inguinal region. There is an '''intermammary groove''' separating the left and right halves. Each half comprises a single mammary complex, which each has two mammary units. The '''lobes''' are the internal compartments of the mamma, separated by adipose tissue. The lobes are divided into '''lobules''', consisting of connective tissue containing '''alveoli''', which are clusters of milk secreting cells. The '''lactiferous ducts''' are large ducts conveying milk from the alveoli to the '''lactiferous sinus'''. The openings of the lactiferous ducts convey milk formed in the alveolus to the gland sinus. | The '''mamma (pleural = mammae) ''' is the glandular structure associated with a '''papilla '''(teat) and may contains two ducts in the mare. The '''udder''' is a term designating all the mammae in the mare. The mammary glands of the mare are close together, forming a small udder in the inguinal region. There is an '''intermammary groove''' separating the left and right halves. Each half comprises a single mammary complex, which each has two mammary units. The '''lobes''' are the internal compartments of the mamma, separated by adipose tissue. The lobes are divided into '''lobules''', consisting of connective tissue containing '''alveoli''', which are clusters of milk secreting cells. The '''lactiferous ducts''' are large ducts conveying milk from the alveoli to the '''lactiferous sinus'''. The openings of the lactiferous ducts convey milk formed in the alveolus to the gland sinus. | ||
Revision as of 13:14, 28 November 2012
| This article is still under construction. |
Overview
The mamma (pleural = mammae) is the glandular structure associated with a papilla (teat) and may contains two ducts in the mare. The udder is a term designating all the mammae in the mare. The mammary glands of the mare are close together, forming a small udder in the inguinal region. There is an intermammary groove separating the left and right halves. Each half comprises a single mammary complex, which each has two mammary units. The lobes are the internal compartments of the mamma, separated by adipose tissue. The lobes are divided into lobules, consisting of connective tissue containing alveoli, which are clusters of milk secreting cells. The lactiferous ducts are large ducts conveying milk from the alveoli to the lactiferous sinus. The openings of the lactiferous ducts convey milk formed in the alveolus to the gland sinus.
The lactiferous sinus (milk sinus) is the milk storage cavity within the teat and glandular body. The gland sinus is part of the milk sinus within the glandular body and the teat sinus is part of the milk sinus within the teat.
The teat is the projecting part of the mammary gland containing part of the milk sinus. The papillary duct (teat canal) is the canal leading from the teat sinus to the teat opening and may be single or multiple. The ostium (teat opening) is the opening of the papillary duct and the exit point for milk or entrance point for bacteria. The sphincter consists of muscular fibres surrounding the teat opening that prevent milk flow except during suckling or milking. The teats are short in the mare. In late pregnancy, sebacious secretions, epithelial debris and colustrum escape and accumulate around the teat; giving it a waxy appearance. This 'waxing up' can be a sign of impending parturition.
Vasculature
Arteries
The main blood supply to the inguinal mammary glands is from the external pudendal artery. This arises indirectly from the external iliac artery via the deep femoral artery. The external pudendal artery passes through the inguinal canal.
Veins
The thoracic and cranial abdominal mammary glands drain via cranial superficial epigastric veins into the internal thoracic vein. Caudal abdominal and inguinal mammary glands drain via caudal superficial epigastric veins into the external pudendal vein.
Lymphatics
The more caudal mammary glands drain to the superficial inguinal lymph node and the more cranial mammary glands to the axillary or sternal lymph nodes.
Innervation
Somatic innervation is via the ventral rami of the spinal nerves. Mammary branches of the pudendal nerve supply the caudal aspect of the udder. There is sympathetic innervation to the blood vessels and teat sphincter smooth muscle. Mammary glands also have major influence from endocrine hormones.