Difference between revisions of "Dental Explorer"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
m (Text replace - "[[Category:Waltham reviewing" to "[[Category:Waltham reviewed") |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
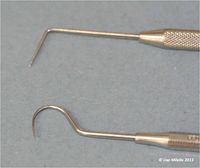
[[File:Explorer probes.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Different examples of explorer probes<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]]<br><br> | [[File:Explorer probes.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Different examples of explorer probes<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]]<br><br> | ||
The dental explorer or probe, is a sharp-ended instrument. | The dental explorer or probe, is a sharp-ended instrument. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 4: | ||
It is used to check for hard tissue defects, for example: | It is used to check for hard tissue defects, for example: | ||
*To determine the presence of [[Dental Caries|caries]] | *To determine the presence of [[Dental Caries|caries]] | ||
| − | *To explore other [[ | + | *To explore other [[Enamel Organ#Enamel|enamel]] and [[Enamel Organ#Dentin|dentin]] defects, such as fractured teeth and [[FORL|odontoclastic resorptive lesions]] |
The explorer is also useful for tactile examination of the subgingival tooth surfaces. Subgingival calculus and odontoclastic resorptive lesions may be identified in this way. | The explorer is also useful for tactile examination of the subgingival tooth surfaces. Subgingival calculus and odontoclastic resorptive lesions may be identified in this way. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Oral Examination Instruments - Small Animal]] | [[Category:Oral Examination Instruments - Small Animal]] | ||
[[Category:Waltham reviewed]] | [[Category:Waltham reviewed]] | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 30 September 2014
The dental explorer or probe, is a sharp-ended instrument.
It is used to check for hard tissue defects, for example:
- To determine the presence of caries
- To explore other enamel and dentin defects, such as fractured teeth and odontoclastic resorptive lesions
The explorer is also useful for tactile examination of the subgingival tooth surfaces. Subgingival calculus and odontoclastic resorptive lesions may be identified in this way. Dental explorers are available in various shapes, usually straight or curved. The Shepherds hook pattern is frequently used in veterinary dentistry, but a probe with a 90 degree bend is often easier to use, and more useful.