Difference between revisions of "Rectum - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO ALIMENTARY - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | |
| + | <big><center>[[Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO LARGE INTESTINE - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The rectum lies between the terminal portion of the descending [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology|colon]] and [[Anus - Anatomy & Physiology|anus]]. It is empty most of the time, except after the mass movements of the [[Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology|large intestine]] which move faeces into the rectum. This stimulates defeaction, which may happen when an animal is frightened. | The rectum lies between the terminal portion of the descending [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology|colon]] and [[Anus - Anatomy & Physiology|anus]]. It is empty most of the time, except after the mass movements of the [[Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology|large intestine]] which move faeces into the rectum. This stimulates defeaction, which may happen when an animal is frightened. | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| − | + | *Exists dorsal to the [[Reproductive System|reproductive organs]], [[Urinary System - Anatomy & Physiology|bladder]] and [[Urethra - Anatomy & Physiology|urethra]]. | |
| + | *The cranial portion of the rectum is attached to the dorsal body wall by a short mesorectum which is a continuation of the mesocolon. | ||
| + | *The mesorectum is reflected to continue with the parietal [[Peritoneal cavity - Anatomy & Physiology|peritoneum]] of the pelvic cavity and to cover the [[Urinary System - Anatomy & Physiology|urogenital organs]] ventrally. | ||
| + | **This forms the '''rectogenital pouch'''. | ||
| + | **Therefore the most distal part of the rectum is retroperitoneal. | ||
| + | ***This distal, retroperitoneal part is directly attached to the [[Female Reproductive Tract -The Vagina/Vestibule - Anatomy & Physiology|vagina]] in the female and to the [[Urethra - Anatomy & Physiology|urethra]] in the male. | ||
| + | ***The retroperitoneal space is filled with soft tissue rich in fat. | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
'''Defeacation''' | '''Defeacation''' | ||
| + | *After the mass movements of the [[Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology|large intestine]], the rectum becomes filled with faeces. | ||
| + | *This stimulates pressue sensitive cells in the wall of the rectum and initiates the defeacation reflex. | ||
| + | *The reflex causes a forceful contraction of the rectum, and relaxation of the internal anal sphincter. | ||
| + | **This produces the conscious sensation of the need to empty the bowel. | ||
| + | **Some species (see [[#Species Differences|species differences]]) are able to voluntarily keep the external anal sphincter closed if defeacation is not suitable in the situation. | ||
| + | ***This reduces the defeaction reflex and reduces the conscious perception of needing to empty the bowel, until another mass movement occurs and a fresh reflex is created. | ||
| − | + | ==Histology== | |
| + | |||
| + | ===Rectum=== | ||
| + | *Epithelium is columnar. | ||
| + | *Goblet cells are present in the mucosa. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Recto-Anal Junction=== | ||
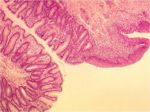
| + | [[Image:Recto-Anal Junction.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Recto-Anal Junction © RVC 2008]] | ||
| + | *Termination of the lamina muscularis and longitudinal layer of the tunica muscularis. | ||
| + | *The circular layer of the tunica muscularis forms the internal anal sphincter. | ||
| + | *The external anal sphincter is formed from skeletal muscle. | ||
| + | *Epithelium changes from columnar to stratified squamous non-keratinised. | ||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
===Carnivore=== | ===Carnivore=== | ||
| − | + | *Control over the external anal sphincter is learned early in life. | |
| − | + | *Defeaction reflex increased by contraction of the abdominal muscles and closure of the vocal cords to increase the pressure in the abdominal cavity. | |
===Ruminant=== | ===Ruminant=== | ||
| + | *Appears to lack the ability to control the external anal sphincter. | ||
| − | + | ===[[Hindgut Fermenters - Anatomy & Physiology|Equine]]=== | |
| − | + | *Appears to lack the ability to control the external anal sphincter. | |
| − | ===Equine=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| + | *[[The Small and Large Intestines|Pathology Of The Small and Large Intestines]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO ALIMENTARY - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | |
| − | < | + | <big><center>[[Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO LARGE INTESTINE - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 11:07, 24 July 2008
Introduction
The rectum lies between the terminal portion of the descending colon and anus. It is empty most of the time, except after the mass movements of the large intestine which move faeces into the rectum. This stimulates defeaction, which may happen when an animal is frightened.
Structure
- Exists dorsal to the reproductive organs, bladder and urethra.
- The cranial portion of the rectum is attached to the dorsal body wall by a short mesorectum which is a continuation of the mesocolon.
- The mesorectum is reflected to continue with the parietal peritoneum of the pelvic cavity and to cover the urogenital organs ventrally.
Function
Defeacation
- After the mass movements of the large intestine, the rectum becomes filled with faeces.
- This stimulates pressue sensitive cells in the wall of the rectum and initiates the defeacation reflex.
- The reflex causes a forceful contraction of the rectum, and relaxation of the internal anal sphincter.
- This produces the conscious sensation of the need to empty the bowel.
- Some species (see species differences) are able to voluntarily keep the external anal sphincter closed if defeacation is not suitable in the situation.
- This reduces the defeaction reflex and reduces the conscious perception of needing to empty the bowel, until another mass movement occurs and a fresh reflex is created.
Histology
Rectum
- Epithelium is columnar.
- Goblet cells are present in the mucosa.
Recto-Anal Junction
- Termination of the lamina muscularis and longitudinal layer of the tunica muscularis.
- The circular layer of the tunica muscularis forms the internal anal sphincter.
- The external anal sphincter is formed from skeletal muscle.
- Epithelium changes from columnar to stratified squamous non-keratinised.
Species Differences
Carnivore
- Control over the external anal sphincter is learned early in life.
- Defeaction reflex increased by contraction of the abdominal muscles and closure of the vocal cords to increase the pressure in the abdominal cavity.
Ruminant
- Appears to lack the ability to control the external anal sphincter.
Equine
- Appears to lack the ability to control the external anal sphincter.
Links