Difference between revisions of "Pharynx - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (69 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Musculoskeletal System - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO MUSCULOSKELETAL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | [[Image:Developing Head.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Developing Head.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Developing Head - Copyright RVC]] |
| − | The pharynx is part of both the [[Cardiorespiratory System | + | The pharynx is part of both the [[Cardiorespiratory System - Anatomy & Physiology|respiratory]] and [[Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology|digestive]] system. Both systems have entrances to the pharynx but they are separated from each other by the [[Soft Palate - Anatomy & Physiology|soft palate]]. |
| − | During exercise or during respiratory distress, the mouth can be used as an additional opening of the respiratory system and then the [[Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]] also becomes an air-way. | + | |
| + | During exercise or during respiratory distress, the mouth can be used as an additional opening of the respiratory system and then the [[Oral Cavity - Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]] also becomes an air-way. | ||
| − | The pharynx can be split into different regions - the [[Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]], [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Laryngeal Pharynx|laryngeal pharynx]] (sometimes referred to as the oesophageal pharynx) and the | + | The pharynx can be split into different regions- the [[Oral Cavity - Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]], [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Laryngeal Pharynx|laryngeal pharynx]] (sometimes referred to as the oesophageal pharynx) and the [[Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|nasopharynx]] |
| − | [[ | ||
==Structure and Function== | ==Structure and Function== | ||
| − | + | *Opening of the [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology|larynx]] is on the floor of the pharynx | |
| − | + | ||
| + | *Caudal and dorsal to the laryngeal opening is the opening into the [[Oesophagus - Anatomy & Physiology|oesophagus]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In the dorsal region of the [[Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|nasopharynx]] there are paired openings into the Auditory (Eustacian) Tubes | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The lining of the middle ear cavity and auditory tube is continuous with that of the [[Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|nasopharynx]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Located between the base of the skull and the first two cervical vertebrae dorsally | ||
| − | + | *[[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology|larynx]] ventrally | |
| − | + | *Mandible, pterygoid muscles and [[Hyoid Apparatus - Anatomy & Physiology|hyoid apparatus]] laterally | |
| − | |||
| + | *Walls contain striated muscle | ||
| + | |||
| + | *During [[Deglutition|swallowing]] the [[Soft Palate - Anatomy & Physiology|soft palate]] is raised which divided the pharynx into dorsal and ventral sections | ||
| + | **Laterally, two pairs of palatopharyngeal arches are present from the [[Soft Palate - Anatomy & Physiology|soft palate]] to the [[Oesophagus - Anatomy & Physiology|oesophagus]] | ||
| + | **The dorsal compartment is the [[Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|nasopharynx]] | ||
| + | **The rostral compartment is the [[Oral Cavity - Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Laryngeal Pharynx|laryngeal pharynx]] is separated from the [[Oral Cavity - Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]] by the [[Epiglottis|epiglottis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Tonsils are present on the lateral walls of the [[Oral Cavity - Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]] | ||
| + | **Covered by flaps of mucosa | ||
| + | **Partially visible in the open mouth | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The pharynx plays an important role in [[Deglutition|deglutition]] | ||
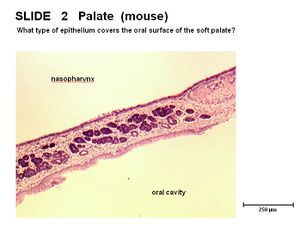
| + | [[Image:Soft Palate Separating Pharyngeal Cavities.jpg|thumb|right|150x|Soft palate dividing the oropharynx and the nasopharynx - Copyright RVC]] | ||
==Musculature== | ==Musculature== | ||
| − | |||
| − | ===Muscles that | + | ===Muscles that constict=== |
| − | + | ||
| + | *Run dorsally to roof of pharynx | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Rostral constrictor muscles are the '''hyopharyngeous''', '''pterygopharyngeous''' and the '''palatopharyngeous muscles''' | ||
| + | **Originate from the pyerygoid region of the skull and the aponeurosis of the [[Soft Palate - Anatomy & Physiology|soft palate]] | ||
| + | **Shorten the pharynx | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Middle constictor muscle is the '''thyopharyngeous muscle''' | ||
| + | **Origniates from the [[Hyoid Apparatus - Anatomy & Physiology|hyoid bone]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Caudal constictor muscles are the '''cricopharyngeous muscle''' | ||
| + | **Originates from the [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Thyroid Cartilage|thyroid cartilage]] of the [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology|larynx]] | ||
===Muscles that dilate=== | ===Muscles that dilate=== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | *Enclose pharynx laterally and dorsally | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Dilator muscle is the '''stylopharyngeous muscle''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Originates from the [[Hyoid Apparatus - Anatomy & Physiology|hyoid apparatus]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Widens the rostral pharynx | ||
===Muscles that shorten=== | ===Muscles that shorten=== | ||
| − | The ''' | + | |
| + | *The '''pterygopharyngeous muscle''' shortens the pharynx | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Enclose pharynx laterally and dorsally | ||
===Muscles that close the Pharyngeal Arch=== | ===Muscles that close the Pharyngeal Arch=== | ||
| − | The '''palatopharyngeous muscle''' also closes the pharyngeal arch | + | |
| + | *The '''palatopharyngeous muscle''' also closes the pharyngeal arch | ||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| − | + | *Pharyngeal muscles arise from arch 4 | |
| + | |||
| + | *Pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN X]]) from the cranial root of the accessory nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN XI]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Stylopharyngeous muscle comes from arch 3 and is innervated by the accessory nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN XI]]) | ||
| + | *Glossopharyngeal nerve ([[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology#Innervation - Cranial Nerves|CN IX]]) supplies taste to the pharynx | ||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
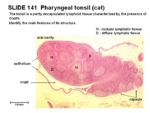
| − | [[Image:Pharyngeal Tonsil.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Pharyngeal Tonsil.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Histology of Pharyngeal Tonsil - Copyright RVC]] |
| − | + | *Fibroelastic aponeurosis supports the mucosa | |
| + | |||
| + | *[[Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|nasopharynx]] has pseudostratified columnar epithelium | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Oral Cavity - Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]] and the [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Laryngeal Pharynx|laryngeal pharynx]] have stratified squamous epithelium | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Oral Cavity - Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|oropharynx]] and the [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Laryngeal Pharynx|laryngeal pharynx]] have salivary glands present | ||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Canine''' | |
| − | + | *Single duct connects [[Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|nasopharynx]] to the nasal cavity | |
| + | |||
| + | *Tonsils are a compact mass which point away from the lumen of the pharynx | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Equine''' | ||
| + | *Auditory tube opens into the [[Special Senses - Auditory - Anatomy & Physiology#Equine Gutteral Pouch|gutteral pouch]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Tonsils are diffuse and raised slightly | ||
| − | + | '''Ruminants''' | |
| − | Tonsils are a compact mass which point towards the lumen of the pharynx | + | *Tonsils are a compact mass which point towards the lumen of the pharynx |
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| − | + | [[Oral Cavity - Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology]] | |
| − | + | [[Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology]] | |
| − | + | [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology#Laryngeal Pharynx|laryngeal pharynx]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Musculoskeletal System - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO MUSCULOSKELETAL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY''']]</center></big> | |
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 17:31, 29 July 2008
Introduction
The pharynx is part of both the respiratory and digestive system. Both systems have entrances to the pharynx but they are separated from each other by the soft palate.
During exercise or during respiratory distress, the mouth can be used as an additional opening of the respiratory system and then the oropharynx also becomes an air-way.
The pharynx can be split into different regions- the oropharynx, laryngeal pharynx (sometimes referred to as the oesophageal pharynx) and the nasopharynx
Structure and Function
- Opening of the larynx is on the floor of the pharynx
- Caudal and dorsal to the laryngeal opening is the opening into the oesophagus
- In the dorsal region of the nasopharynx there are paired openings into the Auditory (Eustacian) Tubes
- The lining of the middle ear cavity and auditory tube is continuous with that of the nasopharynx
- Located between the base of the skull and the first two cervical vertebrae dorsally
- larynx ventrally
- Mandible, pterygoid muscles and hyoid apparatus laterally
- Walls contain striated muscle
- During swallowing the soft palate is raised which divided the pharynx into dorsal and ventral sections
- Laterally, two pairs of palatopharyngeal arches are present from the soft palate to the oesophagus
- The dorsal compartment is the nasopharynx
- The rostral compartment is the oropharynx
- The laryngeal pharynx is separated from the oropharynx by the epiglottis
- Tonsils are present on the lateral walls of the oropharynx
- Covered by flaps of mucosa
- Partially visible in the open mouth
- The pharynx plays an important role in deglutition
Musculature
Muscles that constict
- Run dorsally to roof of pharynx
- Rostral constrictor muscles are the hyopharyngeous, pterygopharyngeous and the palatopharyngeous muscles
- Originate from the pyerygoid region of the skull and the aponeurosis of the soft palate
- Shorten the pharynx
- Middle constictor muscle is the thyopharyngeous muscle
- Origniates from the hyoid bone
- Caudal constictor muscles are the cricopharyngeous muscle
- Originates from the thyroid cartilage of the larynx
Muscles that dilate
- Enclose pharynx laterally and dorsally
- Dilator muscle is the stylopharyngeous muscle
- Originates from the hyoid apparatus
- Widens the rostral pharynx
Muscles that shorten
- The pterygopharyngeous muscle shortens the pharynx
- Enclose pharynx laterally and dorsally
Muscles that close the Pharyngeal Arch
- The palatopharyngeous muscle also closes the pharyngeal arch
Innervation
- Pharyngeal muscles arise from arch 4
- Stylopharyngeous muscle comes from arch 3 and is innervated by the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) supplies taste to the pharynx
Histology
- Fibroelastic aponeurosis supports the mucosa
- nasopharynx has pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- oropharynx and the laryngeal pharynx have stratified squamous epithelium
- oropharynx and the laryngeal pharynx have salivary glands present
Species Differences
Canine
- Single duct connects nasopharynx to the nasal cavity
- Tonsils are a compact mass which point away from the lumen of the pharynx
Equine
- Auditory tube opens into the gutteral pouch
- Tonsils are diffuse and raised slightly
Ruminants
- Tonsils are a compact mass which point towards the lumen of the pharynx
Links
Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology
Nasopharynx - Anatomy & Physiology