Difference between revisions of "Type II Hypersensitivity"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (33 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <big><center>[[Hypersensitivity - WikiBlood|'''BACK TO HYPERSENSITIVITY''']]</center></big> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
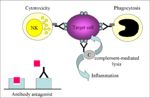
| + | [[Image:Type II Hypersensitivity.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Type II Hypersensitivity-Brian Catchpole RVC 2008]] | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Production of | + | Production of IgM or IgG to cell surface antigens or extracellular matrix proteins. |
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
| + | |||
''' "Neutralisation" blockade of receptors:''' | ''' "Neutralisation" blockade of receptors:''' | ||
| − | * | + | * Myasthenia gravis |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ''' Immunological attack on target cells, destroying them by:''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | 2. | + | 1. Antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) |
| − | * Self | + | * Pemphigus vulgaris |
| − | ** | + | * Bullous pemphigoid |
| − | * Foreign | + | |
| + | 2. Complement mediated lysis | ||
| + | * Self RBC antigen: | ||
| + | ** Immune mediated haemolytic anaemia | ||
| + | * Foreign RBC: | ||
** Blood transfusion reaction | ** Blood transfusion reaction | ||
| − | ** | + | ** Haemolytic disease of new born (Rhesus disease in humans and neonatal isoerythrolysis in foals and kittens) |
* RBC parasite: | * RBC parasite: | ||
** Feline infectious anaemia (''Mycoplasma haemofelis'') | ** Feline infectious anaemia (''Mycoplasma haemofelis'') | ||
3. Phagocytosis | 3. Phagocytosis | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 16:13, 26 August 2008
Introduction
Production of IgM or IgG to cell surface antigens or extracellular matrix proteins.
Mechanism
"Neutralisation" blockade of receptors:
- Myasthenia gravis
Immunological attack on target cells, destroying them by:
1. Antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Bullous pemphigoid
2. Complement mediated lysis
- Self RBC antigen:
- Immune mediated haemolytic anaemia
- Foreign RBC:
- Blood transfusion reaction
- Haemolytic disease of new born (Rhesus disease in humans and neonatal isoerythrolysis in foals and kittens)
- RBC parasite:
- Feline infectious anaemia (Mycoplasma haemofelis)
3. Phagocytosis