Difference between revisions of "Type II Hypersensitivity"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (30 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour = FFE4E1 | ||
| + | |linkpage =Immunology - WikiBlood | ||
| + | |linktext =IMMUNOLOGY | ||
| + | |sublink1 =Hypersensitivity - WikiBlood | ||
| + | |subtext1 =HYPERSENSITIVITY | ||
| + | |pagetype =Blood | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Type II Hypersensitivity.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Type II Hypersensitivity-Brian Catchpole RVC 2008]] | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Production of | + | Production of IgM or IgG to cell surface antigens or extracellular matrix proteins. |
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
| + | |||
''' "Neutralisation" blockade of receptors:''' | ''' "Neutralisation" blockade of receptors:''' | ||
| − | * Antibodies attach to receptors | + | * Antibodies attach to receptors which prevents other molecules attaching. |
* For example in myasthenia gravis antibodies attach to acetylcholine receptors which in turn prevents acetylcholine from attaching to the receptor and thus muscle contraction of that cell does not occur. | * For example in myasthenia gravis antibodies attach to acetylcholine receptors which in turn prevents acetylcholine from attaching to the receptor and thus muscle contraction of that cell does not occur. | ||
| + | |||
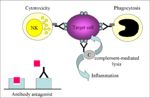
''' Immunological attack on target cells, destroying them by (see diagram):''' | ''' Immunological attack on target cells, destroying them by (see diagram):''' | ||
| − | + | 1. Antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) | |
| − | * | + | * Pemphigus vulgaris |
| − | * | + | * Bullous pemphigoid |
| − | 2. | + | 2. Complement mediated lysis |
| − | * Self | + | * Self RBC antigen: |
| − | ** | + | ** Immune mediated haemolytic anaemia |
| − | * Foreign | + | * Foreign RBC: |
** Blood transfusion reaction | ** Blood transfusion reaction | ||
| − | ** | + | ** Haemolytic disease of new born (Rhesus disease in humans and neonatal isoerythrolysis in foals and kittens) |
* RBC parasite: | * RBC parasite: | ||
** Feline infectious anaemia (''Mycoplasma haemofelis'') | ** Feline infectious anaemia (''Mycoplasma haemofelis'') | ||
3. Phagocytosis | 3. Phagocytosis | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 15:38, 29 August 2008
|
|
Introduction
Production of IgM or IgG to cell surface antigens or extracellular matrix proteins.
Mechanism
"Neutralisation" blockade of receptors:
- Antibodies attach to receptors which prevents other molecules attaching.
- For example in myasthenia gravis antibodies attach to acetylcholine receptors which in turn prevents acetylcholine from attaching to the receptor and thus muscle contraction of that cell does not occur.
Immunological attack on target cells, destroying them by (see diagram):
1. Antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Bullous pemphigoid
2. Complement mediated lysis
- Self RBC antigen:
- Immune mediated haemolytic anaemia
- Foreign RBC:
- Blood transfusion reaction
- Haemolytic disease of new born (Rhesus disease in humans and neonatal isoerythrolysis in foals and kittens)
- RBC parasite:
- Feline infectious anaemia (Mycoplasma haemofelis)
3. Phagocytosis