Difference between revisions of "Crustacea"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Crustacea) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | {{unfinished}} |
| + | |||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour = | ||
| + | |linkpage =Parasites | ||
| + | |linktext =PARASITES | ||
| + | |pagetype=Bugs | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The crustacea are a latge group of arthropods but are ususally treated as a subphylum. The majority of crustaceans are aquatic but some have adapted to terrestrial life. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are only two species of parasitic crustacea of veterinary importance, the tongue worm ''Linguatula serrata'' and sealice ''Lepeophtheirus and Caligus'' spp. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==''Linguatula serrata''== | ||
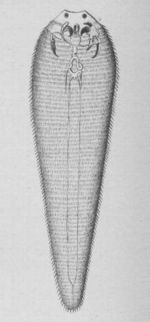
| + | [[Image:Linguatula taenioides.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Copyright Cooper Curtice (Washington, Government Printing Office, 1890) Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | *Also known as the 'tongue worm' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Are highly specialised [[Arthropods|arthropods]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Recognition''' | ||
| + | *Tongue-like appearance | ||
| + | **Expanded anteriorly | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Adults are over 10cm in length | ||
| + | **Females measure betwen 30-130mm in length | ||
| + | **Males measure up to 20mm in length | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Transversely striated | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Life Cycle''' | ||
| + | *6 month life cycle | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Adults inhabit the nasal passages of dogs and sometimes cats | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Eggs are expelled by coughing and sneezing or are passed out with the faeces | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Herbivorous intermediate hosts ingest the eggs | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Eggs hatch in the herbivore intestine | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Larvae migrate to the mesenteric lymph nodes and encyst to become infective nymphs | ||
| + | **Cysts measure 1mm in diameter | ||
| + | |||
| + | *When a dog eats infeced uncooked viscera the life cycle is completed | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Infective nymphs migrate from the viscera during chewing and crawl up into the nasal cavity via the soft palate | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Infective nymphs mature to adults in the nasal cavities and can survive for a year in the final host | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Pathogenesis''' | ||
| + | *Causes [[Nasal Cavity Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of rhinitis|rhinitis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Heavy infection leads to coughing, sneezing and nasal discharge | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Sea Lice== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Economic imortance to the fish farming industries | ||
| + | **Especially in North American and in Northern Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Lepeophtheirus'' is found only the Northern hemisphere | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Caligus'' is found worldwide | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Recognition''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Males measure 6mm in length | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Females measure 1cm long | ||
| + | **Have a long egg sac | ||
| + | |||
| + | *5 pairs of legs | ||
| + | **3 pairs for swimming | ||
| + | **2 pairs modified for eating | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Brown to red in colour | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Similar in appearance to the horse shoe crab | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Life Cycle''' | ||
| + | *Eggs released from long egg sacs into environment | ||
| + | |||
| + | *2 non-parasitic larval stages | ||
| + | |||
| + | *7 parasitic larval stages (nauplius) | ||
| + | **Copepod, chalimus and pre-adult | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Life cycle takes 3 weeks to 4 months depending on temperature | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Epidemiology''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Pathogenesis''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''Control''' | ||
| + | *Ectoparasites | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Hidden antigen vaccine | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Wrasse which feed on sea lice | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Managment improvements | ||
| + | **E.g. ''All in, all out'' and 6 week fallowing | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Stock selection | ||
| + | **e.g. Selective breeding for resistance | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Links== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#Linguatula serrata|Pathology of ''Linguata serrata'' in the nasal passages]] | ||
Revision as of 17:48, 2 November 2008
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
Introduction
The crustacea are a latge group of arthropods but are ususally treated as a subphylum. The majority of crustaceans are aquatic but some have adapted to terrestrial life.
There are only two species of parasitic crustacea of veterinary importance, the tongue worm Linguatula serrata and sealice Lepeophtheirus and Caligus spp.
Linguatula serrata
- Also known as the 'tongue worm'
- Are highly specialised arthropods
Recognition
- Tongue-like appearance
- Expanded anteriorly
- Adults are over 10cm in length
- Females measure betwen 30-130mm in length
- Males measure up to 20mm in length
- Transversely striated
Life Cycle
- 6 month life cycle
- Adults inhabit the nasal passages of dogs and sometimes cats
- Eggs are expelled by coughing and sneezing or are passed out with the faeces
- Herbivorous intermediate hosts ingest the eggs
- Eggs hatch in the herbivore intestine
- Larvae migrate to the mesenteric lymph nodes and encyst to become infective nymphs
- Cysts measure 1mm in diameter
- When a dog eats infeced uncooked viscera the life cycle is completed
- Infective nymphs migrate from the viscera during chewing and crawl up into the nasal cavity via the soft palate
- Infective nymphs mature to adults in the nasal cavities and can survive for a year in the final host
Pathogenesis
- Causes rhinitis
- Heavy infection leads to coughing, sneezing and nasal discharge
Sea Lice
- Economic imortance to the fish farming industries
- Especially in North American and in Northern Europe
- Lepeophtheirus is found only the Northern hemisphere
- Caligus is found worldwide
Recognition
- Males measure 6mm in length
- Females measure 1cm long
- Have a long egg sac
- 5 pairs of legs
- 3 pairs for swimming
- 2 pairs modified for eating
- Brown to red in colour
- Similar in appearance to the horse shoe crab
Life Cycle
- Eggs released from long egg sacs into environment
- 2 non-parasitic larval stages
- 7 parasitic larval stages (nauplius)
- Copepod, chalimus and pre-adult
- Life cycle takes 3 weeks to 4 months depending on temperature
Epidemiology
Pathogenesis
Control'
- Ectoparasites
- Hidden antigen vaccine
- Wrasse which feed on sea lice
- Managment improvements
- E.g. All in, all out and 6 week fallowing
- Stock selection
- e.g. Selective breeding for resistance