Difference between revisions of "Lizard Enteritis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with '{{unfinished}} [[Image:Lizard_enteritis.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Intussusception may occur as a secondary to enteritis''' (Copyright © RVC and its licensors, Sean Bobbit, Sue E…') |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{unfinished}} | |
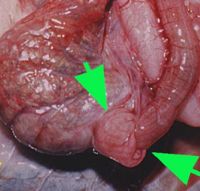
| − | [[Image:Lizard_enteritis.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Intussusception may occur as secondary to enteritis''' (Copyright © RVC)]] | + | [[Image:Lizard_enteritis.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Intussusception may occur as a secondary to enteritis''' (Copyright © RVC and its licensors, Sean Bobbit, Sue Evans, Andrew Devare and Claire Moore. All rights reserved)]] |
| − | Enteric infections that result in clinical problems are, in general, uncommon. They | + | Enteric infections that result in clinical problems are, in general, uncommon. They are usually related to poor husbandry. |
'''Clinical signs''' include vomiting (grave prognosis) and diarrhoea. | '''Clinical signs''' include vomiting (grave prognosis) and diarrhoea. | ||
| − | '''Diagnosis''' - history, [[Lizard Physical Examination|physical examination]], faecal cultures, | + | '''Diagnosis''' - history, [[Lizard Physical Examination|physical examination]], faecal cultures, radiology, haematology and biochemistry. |
'''Treatment''': | '''Treatment''': | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* Increased dietary fibre (bran, hay, alfalfa pellets) | * Increased dietary fibre (bran, hay, alfalfa pellets) | ||
* Oral inoculation of parasite-free faeces from a healthy iguana | * Oral inoculation of parasite-free faeces from a healthy iguana | ||
| − | * Antibiotics | + | * Antibiotics |
| − | * [[Lizard Supportive Care|Supportive care]] | + | * [[Lizard Supportive Care|Supportive care]] |
[[Category:Lizard_Gastrointestinal_Diseases|E]] | [[Category:Lizard_Gastrointestinal_Diseases|E]] | ||
Revision as of 15:54, 17 March 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
Enteric infections that result in clinical problems are, in general, uncommon. They are usually related to poor husbandry.
Clinical signs include vomiting (grave prognosis) and diarrhoea.
Diagnosis - history, physical examination, faecal cultures, radiology, haematology and biochemistry.
Treatment:
- Symptomatic therapy (e.g. kaolin)
- Increased dietary fibre (bran, hay, alfalfa pellets)
- Oral inoculation of parasite-free faeces from a healthy iguana
- Antibiotics
- Supportive care