Difference between revisions of "Sarcocystis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with 'thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocytis'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC [[Image:Sarcocystic.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocytis'' -…') |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Sarcocystis Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocytis'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | [[Image:Sarcocystis Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocytis'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | ||
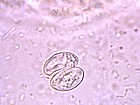
[[Image:Sarcocystic.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocytis'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | [[Image:Sarcocystic.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocytis'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | ||
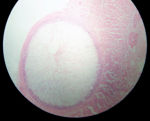
| − | [[Image:Sarcocystis in sheep oesophagus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocystis in sheep oesophagus | + | [[Image:Sarcocystis in sheep oesophagus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocystis'' in sheep oesophagus - Adam Cuerden]] |
[[Image:Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis - Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
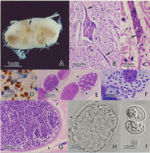
[[Image:Sarcocystis cruzi.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocystis cruzi'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | [[Image:Sarcocystis cruzi.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocystis cruzi'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
*Cause meat inspection losses | *Cause meat inspection losses | ||
| − | *''Sarcocystis'' in [[ | + | *''Sarcocystis'' in [[Muscles Inflammatory - Pathology#Protozoa|myositis]] |
*Experimental infections cause severe, acute pyrexic disease when the organism multiplies in the vascular endothelium | *Experimental infections cause severe, acute pyrexic disease when the organism multiplies in the vascular endothelium | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
**Causes abortion and post-natal disease in sheep | **Causes abortion and post-natal disease in sheep | ||
| − | * | + | *Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis |
| − | + | **Necrotising encephalomyelitis affecting the grey and white matter of the CNS | |
| − | * | + | **Caused by ''S.neurona'' |
| − | + | **Opossum thought to be the definitive host | |
| − | ** | + | **Horses thought to be accidental hosts |
| − | *** | + | **Natural intermediate hosts currently unknown |
| − | *** | + | **Western Blotting shows 50% of horses in the USA are seropositive |
| − | *** | + | **Risk factors poorly understood |
| − | ** | + | **Causes spinal cord dysfunction |
| − | + | ***Ataxia and paralysis[[Category:Tissue_Cyst_Forming_Coccidia]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Tissue_Cyst_Forming_Coccidia | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 22:59, 9 April 2010
- Most infections are asymptomatic
- Heavy infections are causes of chronic wasting in large animals, hide condemnation and downgrading of carcasses
- Sarcocystis should be differentiated from other tissue-cyst forming coccidia
- There are many species of Sarcocystis which differ in size from microscopic to several centimetres in length
- S.neurona is an important equine pathogen in the USA
- Infective cyst in the intermediate host is called a sarcocyst
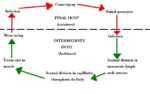
Life Cycle
- The individual life cycle of some species is incompletely understood
- Indirect life cycle
- Life cycle alternates between the final and the obligatory intermediate host
- Only one final and one intermediate host
- Sporulated oocyst has 2 sporocysts containing 4 sporozoites
- Naked sporocyst usually seen in faeces as the oocyst wall is very delicate
- Oocyst measures 15μm in length
- No schizogony in final host
- Gametogeny occurs deep in subepithelial tissue
- Faecal oocyst count is low
- Oocysts are sporulated when passed
- Difficult to find on faecal examination as the sporocysts are few in number and small
- Ingestion of sporocyst by intermediate host
- 2 phases of rapid asexual reproduction in vascular endothelial cells
- Slow multiplication of bradyzoites in muscle tissue
- Sarcocyst forms with bradyzoites inside, surrounded by a cyst wall and divided into compartments
Epidemiology
- Final hosts are carnivores and omnivores
- Intermediate hosts are herbivores and omnivores
- Humans are the final host for some species and the intermediate hosts for others
- Final host for species infecting cattle and pigs
- Dogs are final hosts for species infecting cattle, sheep, goats, pigs and horses
- Cats are final hosts for species infecting cattle, sheep and pigs
Pathogenesis
- Widespread infection but mostly asymptomatic
- Cause meat inspection losses
- Sarcocystis in myositis
- Experimental infections cause severe, acute pyrexic disease when the organism multiplies in the vascular endothelium
- Can cause chronic wasting disease in cattle and horses
- Causes abortion and post-natal disease in sheep
- Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis
- Necrotising encephalomyelitis affecting the grey and white matter of the CNS
- Caused by S.neurona
- Opossum thought to be the definitive host
- Horses thought to be accidental hosts
- Natural intermediate hosts currently unknown
- Western Blotting shows 50% of horses in the USA are seropositive
- Risk factors poorly understood
- Causes spinal cord dysfunction
- Ataxia and paralysis