Difference between revisions of "Nematode Life Cycle"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
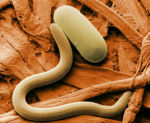
[[Image:Soybean cyst nematode EM.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soybean Cyst Nematode and Egg, Scanning Electron Micrograph - Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Soybean cyst nematode EM.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soybean Cyst Nematode and Egg, Scanning Electron Micrograph - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
=== General Life-Cycle === | === General Life-Cycle === | ||
| − | + | *The basic life-cycle is very simple: | |
| − | + | **egg → L1 → L2 → L3 → L4 → adult | |
| − | + | *With a moult in between each larval stage | |
| − | egg → L1 → L2 → L3 → L4 → adult | + | *But there are many variations on this theme |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Nematode Eggs === | === Nematode Eggs === | ||
| − | + | *These vary greatly in appearance and are very useful for diagnosis as they can often be detected and counted in faecal samples | |
| − | These vary greatly in appearance and are very useful for diagnosis as they can often be detected and counted in faecal samples | + | *NOTE: we use the typical '''strongyle''' egg to provide us with a yard-stick for comparing sizes. A "large egg", for example, means larger than a strongyle egg. A typical strongyle egg is approximately '''80µm''' long |
| − | NOTE: we use the typical '''strongyle''' egg to provide us with a yard-stick for comparing sizes. A "large egg", for example, means larger than a strongyle egg. | + | [[Category:Nematodes]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Nematodes | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 10:12, 21 May 2010
General Life-Cycle
- The basic life-cycle is very simple:
- egg → L1 → L2 → L3 → L4 → adult
- With a moult in between each larval stage
- But there are many variations on this theme
Nematode Eggs
- These vary greatly in appearance and are very useful for diagnosis as they can often be detected and counted in faecal samples
- NOTE: we use the typical strongyle egg to provide us with a yard-stick for comparing sizes. A "large egg", for example, means larger than a strongyle egg. A typical strongyle egg is approximately 80µm long