Difference between revisions of "Histoplasmosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
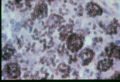
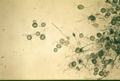
Image:Histoplasmosis tuberculate chlamydospores.jpg|<center><p>'''Histoplasmosis tuberculate chlamydospores'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center></gallery> | Image:Histoplasmosis tuberculate chlamydospores.jpg|<center><p>'''Histoplasmosis tuberculate chlamydospores'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center></gallery> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Systemic_Mycoses]] | [[Category:Systemic_Mycoses]] | ||
| − | [[Category:To_Do_- | + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Fungi]] |
| − | |||
Revision as of 11:28, 25 June 2010
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Non-contageous, systemic mycosis
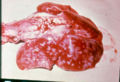
- Commonly pulmonary infections occur
- Other organs can be involved
- Involves the reticuloendothelial system
- Intestinal form can also occur
- Acute and chronic disease can occur
- Endemic to the USA
- Isolated cases have been reported in Europe
- Respiratory infection
- Infection via ingestion can also occur
- Affects dogs, cats, cattle, horses and humans
- Found in soil contaminated by bird droppings, decaying vegetation and in caves inhabited by bats
- Fine, branching, septate hyphae with smooth-walled pyriform to spherical microconidia and large, thick-walled tuberculate macroconidia on simple conidiophores
- Dimorphic fungi
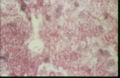
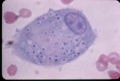
- Hard to demonstrate in smears as the organisms is very small
- Stain with Giemsa or Wright and examine under oil immersion lens
- Present intracellularly in macrophages as oval yeast cells with few buds
- Clear halo is seen around the darker staining central material
- Grows on Sabouraud's Dextrose agar
- Creamy white colonies, turning tan coloured and then brown
- Also grows on Blood agar
- Small, white yeast-like colonies
- Test using immunodiffusion, complement fixation and counterimmunoelectrophoresis
- Skin test of little value as it only indicates exposure
- Treatment with Amphotericin B
- If Amphotericin B is contra-indicated, imidazoles can be given orally
- The prognosis is poor in acute and disseminated cases