Difference between revisions of "Enteritis, Eosinophilic"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (moved Eosinophilic Enteritis to Enteritis, Eosinophilic) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{unfinished}} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{dog}} | |
| + | {{cat}} | ||
| − | |||
==Signalment== | ==Signalment== | ||
| − | + | *Seen in any breed or age | |
| + | *However, more common in younger animal | ||
| + | *More common in | ||
| + | **Boxers | ||
| + | **Dobermans | ||
| + | **German Shepherd Dogs | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Description== | |
| − | + | '''Eosinophilic enteritis (EE)''' is the second most common form of IBD, characterised by a mixed, but predominantly eosiphilic, mucosal inflammatory infiltration. EGE may be limited to the small intestine or it may affect other areas of the gastrointestinal tract such as stomach or colon. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==Clinical Signs== | + | An eosinophilic infiltrate may indicate a diet-induced, type 1 hypersensitivity. However, most dogs do not respond to a purely exclusion diet. Endoparasitism should also be excluded prior to immunosuppressive therapy for EE. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| + | ===Clinical Signs=== | ||
*Vomiting | *Vomiting | ||
| − | *Diarrhoea; small intestinal is more common | + | *Diarrhoea; small intestinal is more common |
| + | **Haematoemesis or malena, and/or haematochezia; EGE is associated with mucosal erosion or ulceration | ||
*Protein-losing enteropathy in severe cases | *Protein-losing enteropathy in severe cases | ||
| − | *Hypoproteinaemia in severe | + | *Hypoproteinaemia in severe casese |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Laboratory Tests=== | ||
| + | ====Haematology==== | ||
| + | *Anaemia if gastrointestinal haemorrhage is severe. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Biochemistry==== | ||
| + | *Eosinophilia | ||
| + | **This is not always present. Even when present, alone, it cannot prove the presence of EE. | ||
| + | **It is also a marker for parasitism, hypoadrenocorticism, allergic dermatological disease, allergic respiratory disease and mast cell tumour. | ||
| + | *Panhypoproteinaemia | ||
| + | **Secoondary to concurrent protein-losing enteropathy | ||
| + | |||
| − | == | + | ===Diagnostic Imaging=== |
| − | + | *Endoscopically, linear ulcers within the duodenal mucosa may be seen grossly. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Histopathology=== | ===Histopathology=== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 49: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
| − | Anti-parasiticide | + | *Anti-parasiticide |
| − | Immunosuppressive therapy | + | **Fenbendazole may be given due to the possible endoparasitism or dietary sensitivity |
| + | *Dietary modification | ||
| + | **A hypoallergenic diet should be used | ||
| + | *Immunosuppressive therapy | ||
| + | |||
| + | Refer to [[Inflammatory Bowel Disease#Treatment|IBD]] for further information | ||
| + | |||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
Guarded if the initial response to treatment is poor. Good if the underlying cause is detected and successfully treated. | Guarded if the initial response to treatment is poor. Good if the underlying cause is detected and successfully treated. | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 67: | ||
*Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) '''Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition)''' ''Mosby Elsevier''. | *Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) '''Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition)''' ''Mosby Elsevier''. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Eosinophilic Enteritis== | |
| − | + | ||
| + | * Can be either focal or diffuse. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Focal=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * A disease of young dogs. | ||
| + | * Associated with [[Toxocara canis|''Toxocara canis'']] infection. | ||
| + | ** Pin-head sized white nodules can be seen under the serosa in the bowel. | ||
| + | *** Consist of of eosinophils and occasionally macrophages and plasma cells. | ||
| + | *** Can sometimes see [[Toxocara canis|''Toxocara'']] larvae in the nodules. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Diffuse=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Seen in the dog, cat and horse. | ||
| + | * Idiopathic | ||
| + | * Has a predilection for German Shepherd Dogs, but also occcurs in other breeds of dogs and in cats. | ||
| + | ** Recurrent episodes of diarrhoea with tissue and circulatory eosinophilia. | ||
| + | *** Eosinophils heavily infiltrate all layers of stomach and intestines. | ||
| + | **It has been suggested that it is a type of hypersensitivity reaction. | ||
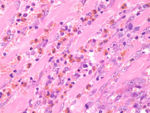
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Image:eosinophilic_enteritis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Eosinophilic enteritis - horse(Courtesy of Susan Rhind, University of Edinburgh)]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Dog]][[Category:Intestine_-_Inflammatory_Pathology_by_Type]][[Category:To_Do_-_Clinical]] |
Revision as of 09:34, 30 June 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
Signalment
- Seen in any breed or age
- However, more common in younger animal
- More common in
- Boxers
- Dobermans
- German Shepherd Dogs
Description
Eosinophilic enteritis (EE) is the second most common form of IBD, characterised by a mixed, but predominantly eosiphilic, mucosal inflammatory infiltration. EGE may be limited to the small intestine or it may affect other areas of the gastrointestinal tract such as stomach or colon.
An eosinophilic infiltrate may indicate a diet-induced, type 1 hypersensitivity. However, most dogs do not respond to a purely exclusion diet. Endoparasitism should also be excluded prior to immunosuppressive therapy for EE.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea; small intestinal is more common
- Haematoemesis or malena, and/or haematochezia; EGE is associated with mucosal erosion or ulceration
- Protein-losing enteropathy in severe cases
- Hypoproteinaemia in severe casese
Laboratory Tests
Haematology
- Anaemia if gastrointestinal haemorrhage is severe.
Biochemistry
- Eosinophilia
- This is not always present. Even when present, alone, it cannot prove the presence of EE.
- It is also a marker for parasitism, hypoadrenocorticism, allergic dermatological disease, allergic respiratory disease and mast cell tumour.
- Panhypoproteinaemia
- Secoondary to concurrent protein-losing enteropathy
Diagnostic Imaging
- Endoscopically, linear ulcers within the duodenal mucosa may be seen grossly.
Histopathology
Biopsy is required for a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment
- Anti-parasiticide
- Fenbendazole may be given due to the possible endoparasitism or dietary sensitivity
- Dietary modification
- A hypoallergenic diet should be used
- Immunosuppressive therapy
Refer to IBD for further information
Prognosis
Guarded if the initial response to treatment is poor. Good if the underlying cause is detected and successfully treated.
References
- Ettinger, S.J. and Feldman, E. C. (2000) Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diseases of the Dog and Cat Volume 2 (Fifth Edition) W.B. Saunders Company.
- Hall, E.J, Simpson, J.W. and Williams, D.A. (2005) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Gastroenterology (2nd Edition) BSAVA
- Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition) Mosby Elsevier.
Eosinophilic Enteritis
- Can be either focal or diffuse.
Focal
- A disease of young dogs.
- Associated with Toxocara canis infection.
- Pin-head sized white nodules can be seen under the serosa in the bowel.
- Consist of of eosinophils and occasionally macrophages and plasma cells.
- Can sometimes see Toxocara larvae in the nodules.
- Pin-head sized white nodules can be seen under the serosa in the bowel.
Diffuse
- Seen in the dog, cat and horse.
- Idiopathic
- Has a predilection for German Shepherd Dogs, but also occcurs in other breeds of dogs and in cats.
- Recurrent episodes of diarrhoea with tissue and circulatory eosinophilia.
- Eosinophils heavily infiltrate all layers of stomach and intestines.
- It has been suggested that it is a type of hypersensitivity reaction.
- Recurrent episodes of diarrhoea with tissue and circulatory eosinophilia.