Difference between revisions of "Tick Morphology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Deer tick.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Deer tick - Scott Bauer]] | [[Image:Deer tick.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Deer tick - Scott Bauer]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===Hard ticks=== |
| − | |||
| − | + | *Hard, chitinous covering over dorsal surface called the '''scutum''' | |
| − | + | **Unique to hard ticks | |
| − | + | **Males have a scutum which covers the entire body surface | |
| + | **Females have a scutum which only covers a small area behind the head | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Prominent biting mouthparts | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Festoons ('pie crust edging') around the posterior body margins | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Enamel coloured patches on scutum are present on '''ornate ticks''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Female hard ticks may swell up to 3 times their normal size when taking a blood meal | ||
===Soft ticks=== | ===Soft ticks=== | ||
| − | + | *No scutum | |
| + | |||
| + | *Mouthparts are not visible from dorsal surface | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Feed little and often as cannot swell as much as hard ticks | ||
===Mouthparts=== | ===Mouthparts=== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 28: | ||
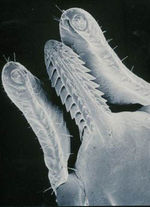
There are 3 major constituents of the mouthparts of ticks; palps, chelicerae and the hypostome. The palps are sensory organs on protuding on either side of the capitulum, they are used to locate a suitable site for feeding. Once a suitable feeding site has been located the sharp chelicerae are used to create a puncture wound in the skin of the host. The hypostome is then pushed through the wound into the host, where it attaches using backwards facing teeth. A dorsal groove on the hypostome allows the downward flow of tick saliva into the host as well as the upward flow of host blood during tick feeding. | There are 3 major constituents of the mouthparts of ticks; palps, chelicerae and the hypostome. The palps are sensory organs on protuding on either side of the capitulum, they are used to locate a suitable site for feeding. Once a suitable feeding site has been located the sharp chelicerae are used to create a puncture wound in the skin of the host. The hypostome is then pushed through the wound into the host, where it attaches using backwards facing teeth. A dorsal groove on the hypostome allows the downward flow of tick saliva into the host as well as the upward flow of host blood during tick feeding. | ||
| − | + | ==Feeding== | |
[[Image:Engorged Ixodes scapularis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Engorged ''Ixodes scapularis'' - Thomas Hedden]] | [[Image:Engorged Ixodes scapularis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Engorged ''Ixodes scapularis'' - Thomas Hedden]] | ||
| + | *Ticks stand upright | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Chelicerae cut through skin creating a pool of blood | ||
| − | + | *Hypostome is inserted deep into the skin | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Mouthparts are cemented into place | |
| − | + | *Ticks feed continuously | |
| + | *Tick saliva flows into host and contains | ||
| + | **Histamine blocking agents to minimise the host inflammatory response | ||
| + | **Anticoagulants to ensure the free flow of blood | ||
| + | **Cytolysins to enlarge the feeding lesion | ||
| + | **Vasoactive mediators, enterases and carbohydrate splitting enzymes to increase the vascular permeability, facilitating feeding | ||
| + | **Paralytic toxins | ||
| − | + | *Host tissue is broken down leaving a zone of necrosis creating a '''feeding lesion'''[[Category:Ticks]] | |
| − | [[Category:Ticks | + | [[Category:To_Do_-_NickJ]] |
| − | [[Category:To_Do_- | ||
Revision as of 11:04, 7 July 2010
Hard ticks
- Hard, chitinous covering over dorsal surface called the scutum
- Unique to hard ticks
- Males have a scutum which covers the entire body surface
- Females have a scutum which only covers a small area behind the head
- Prominent biting mouthparts
- Festoons ('pie crust edging') around the posterior body margins
- Enamel coloured patches on scutum are present on ornate ticks
- Female hard ticks may swell up to 3 times their normal size when taking a blood meal
Soft ticks
- No scutum
- Mouthparts are not visible from dorsal surface
- Feed little and often as cannot swell as much as hard ticks
Mouthparts
There are 3 major constituents of the mouthparts of ticks; palps, chelicerae and the hypostome. The palps are sensory organs on protuding on either side of the capitulum, they are used to locate a suitable site for feeding. Once a suitable feeding site has been located the sharp chelicerae are used to create a puncture wound in the skin of the host. The hypostome is then pushed through the wound into the host, where it attaches using backwards facing teeth. A dorsal groove on the hypostome allows the downward flow of tick saliva into the host as well as the upward flow of host blood during tick feeding.
Feeding
- Ticks stand upright
- Chelicerae cut through skin creating a pool of blood
- Hypostome is inserted deep into the skin
- Mouthparts are cemented into place
- Ticks feed continuously
- Tick saliva flows into host and contains
- Histamine blocking agents to minimise the host inflammatory response
- Anticoagulants to ensure the free flow of blood
- Cytolysins to enlarge the feeding lesion
- Vasoactive mediators, enterases and carbohydrate splitting enzymes to increase the vascular permeability, facilitating feeding
- Paralytic toxins
- Host tissue is broken down leaving a zone of necrosis creating a feeding lesion