Difference between revisions of "Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
====Description==== | ====Description==== | ||
| − | A progressive, infectious ( | + | A progressive, infectious<ref name="Pasq">Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) '''Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine''', third edition, SUDZ Publishing, 245-250.</ref>neurological disease of horses, endemic in the USA (EPM8) and only encountered elsewhere in imported equids (EPM 3). EPM is one of the most frequently diagnosed neurological conditions of the Western Hemisphere (Furr) and the principal differential for multifocal, asymmetric progressive central nervous system (CNS) disease.<ref name="Pasq">Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) '''Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine''', third edition, SUDZ Publishing, 245-250.</ref> As it can resemble any neurological disorder, EPM must be considered in any horse with neurological signs if it resides in the Americas or if it has been imported from that area (EPM 8, 9). The disease is not contagious.<ref name="Pasq">Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) '''Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine''', third edition, SUDZ Publishing, 245-250.</ref> |
====Aetiology==== | ====Aetiology==== | ||
| − | EPM results from infection of the CNS by the apicomplexan parasite ''Sarcocystis neurona'' or, less frequently, its close relative ''Neospora hughesi'' (Mayhew and others 1976, Marsh and others 1996, Dubey and others 2001a).(EPM6, Wobeser 2009). These protozoans develop within neurons (Furr) causing immediate or inflammatory-mediated neuronal damage (Vetstream). The organisms migrate randomly through the brain and spinal cord causing asymmetrical lesions of the grey and white matter and thus multifocal lower and upper motor neuron deficits (Pasq). | + | EPM results from infection of the CNS by the apicomplexan parasite ''Sarcocystis neurona'' or, less frequently, its close relative ''Neospora hughesi'' (Mayhew and others 1976, Marsh and others 1996, Dubey and others 2001a).(EPM6, Wobeser 2009). These protozoans develop within neurons (Furr) causing immediate or inflammatory-mediated neuronal damage (Vetstream). The organisms migrate randomly through the brain and spinal cord causing asymmetrical lesions of the grey and white matter and thus multifocal lower and upper motor neuron deficits.<ref name="Pasq">Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) '''Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine''', third edition, SUDZ Publishing, 245-250.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ====Signalment==== | ||
| + | Mostly Standardbreds and Thoroughbreds aged 1-6years.<ref name="Pasq">Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) '''Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine''', third edition, SUDZ Publishing, 245-250.</ref> Foal infection may be possible (EPM 8). | ||
| + | |||
| Line 21: | Line 25: | ||
[[File:Equine_Protozoal_Myeloencephalitis.jpg]] | [[File:Equine_Protozoal_Myeloencephalitis.jpg]] | ||
| − | + | ====References==== | |
| + | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 15:06, 16 July 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
| Also known as: | EPM Equine protozoal myelitis |
Description
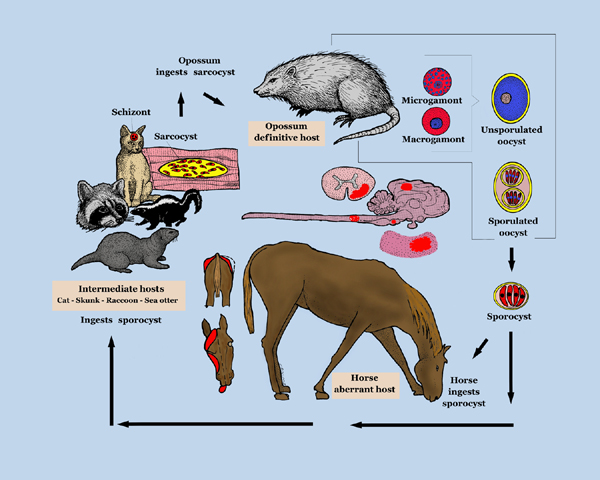
A progressive, infectious[1]neurological disease of horses, endemic in the USA (EPM8) and only encountered elsewhere in imported equids (EPM 3). EPM is one of the most frequently diagnosed neurological conditions of the Western Hemisphere (Furr) and the principal differential for multifocal, asymmetric progressive central nervous system (CNS) disease.[1] As it can resemble any neurological disorder, EPM must be considered in any horse with neurological signs if it resides in the Americas or if it has been imported from that area (EPM 8, 9). The disease is not contagious.[1]
Aetiology
EPM results from infection of the CNS by the apicomplexan parasite Sarcocystis neurona or, less frequently, its close relative Neospora hughesi (Mayhew and others 1976, Marsh and others 1996, Dubey and others 2001a).(EPM6, Wobeser 2009). These protozoans develop within neurons (Furr) causing immediate or inflammatory-mediated neuronal damage (Vetstream). The organisms migrate randomly through the brain and spinal cord causing asymmetrical lesions of the grey and white matter and thus multifocal lower and upper motor neuron deficits.[1]
Signalment
Mostly Standardbreds and Thoroughbreds aged 1-6years.[1] Foal infection may be possible (EPM 8).