Difference between revisions of "Taenia solium"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{{Taxobox |name = ''Taenia solium |kingdom = Animalia |phylum = Platyhelminthes |class = Cestoda |sub-class ...") |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
|name = ''Taenia solium | |name = ''Taenia solium | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Image:Taenia solium.jpg|200px|thumb|right|''Taenia solium'' <br> Roberto J. Galindo, Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Taenia solium.jpg|200px|thumb|right|''Taenia solium'' <br> Roberto J. Galindo, Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| − | Also known as: '''''Cysticercus cellulosae | + | |
| + | {| cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
| + | | Also known as: | ||
| + | | '''''Cysticercus cellulosae''<br>Human pork tapeworm | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
==Hosts== | ==Hosts== | ||
| − | '''Intermediate host''': Pig | + | '''Intermediate host''': Pig, and also occasionally the dog and man. |
'''Definitive host''': Man. | '''Definitive host''': Man. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 29: | ||
==Life Cycle== | ==Life Cycle== | ||
| − | The life-cycle is similar to that of [[Taenia saginata|''T. saginata'']], except now the pig is the intermediate host. Gravid segments, containing the parasite eggs are passed in faeces. The oncospheres are then ingested by the intermediate host, in this case the pig, and pass into the blood system, infecting striated muscles. The cysticerci may also develop in the lungs, liver, kidney and the brain. Like ''T. saginata'', humans, which are the definitive | + | The life-cycle is similar to that of [[Taenia saginata|''T. saginata'']], except now the pig is the intermediate host. Gravid segments, containing the parasite eggs are passed in faeces. The oncospheres are then ingested by the intermediate host, in this case the pig, and pass into the blood system, infecting striated muscles. The cysticerci may also develop in the lungs, liver, kidney and the brain. Like ''T. saginata'', humans, which are the definitive host becomes infected via ingestion of poorly cooked meat. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Taylor, M.A, Coop, R.L., Wall,R.L. (2007) '''Veterinary Parasitology''' ''Blackwell Publishing'' | Taylor, M.A, Coop, R.L., Wall,R.L. (2007) '''Veterinary Parasitology''' ''Blackwell Publishing'' | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Taeniidae]] | |
| + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Max]][[Category:Zoonoses]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Expert_Review]] | [[Category:Expert_Review]] | ||
Revision as of 12:02, 3 August 2010
| Taenia solium | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Platyhelminthes |
| Class | Cestoda |
| Order | Cyclophyllidea |
| Family | Taeniidae |
| Genus | Taenia |
| Species | T. solium |
| Also known as: | Cysticercus cellulosae Human pork tapeworm |
Hosts
Intermediate host: Pig, and also occasionally the dog and man.
Definitive host: Man.
Identification
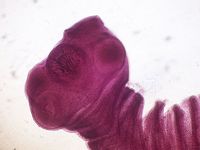
The adults are 3-5m in length, have a scolex, and several rows of hooks.
Life Cycle
The life-cycle is similar to that of T. saginata, except now the pig is the intermediate host. Gravid segments, containing the parasite eggs are passed in faeces. The oncospheres are then ingested by the intermediate host, in this case the pig, and pass into the blood system, infecting striated muscles. The cysticerci may also develop in the lungs, liver, kidney and the brain. Like T. saginata, humans, which are the definitive host becomes infected via ingestion of poorly cooked meat.
References
Taylor, M.A, Coop, R.L., Wall,R.L. (2007) Veterinary Parasitology Blackwell Publishing