Difference between revisions of "Reproductive System Overview - Anatomy & Physiology"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (59 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{toplink | |
| + | |thispagenormal = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| + | |thispagemap = Reproductive System (Content Map) - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
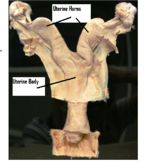
[[Image:Mare Uterus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|The Mare Uterus- Courtesy of A.Crook, Copyright RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Mare Uterus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|The Mare Uterus- Courtesy of A.Crook, Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
== Introduction to the Reproductive System == | == Introduction to the Reproductive System == | ||
| − | Reproduction is the complex set of biological processes that result in the formation of a new organism; it is crucial that we understand how these processes occur normally and have a good grasp of the role of [[Reproductive Hormones | + | Reproduction is the complex set of biological processes that result in the formation of a new organism; it is crucial that we understand how these processes occur normally and have a good grasp of the role of [[Overview of the Reproductive System - Overview of Reproductive Hormones - Anatomy & Physiology|hormones]] in the reproductive process. Pathology and disease are common within the reproductive system and can not only lead to a sick animal but also to a loss in production. In this section we hope to cover all the main processes in domestic animals, laying a foundation for understanding the associated pathological states. |
== Puberty == | == Puberty == | ||
| − | [[Puberty Defining - Anatomy & Physiology|Puberty]] is the process of aquiring reproductive capability, and age at onset of puberty varies from between [[Puberty Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|species]]. There are several factors involved in triggering the [[Puberty Onset | + | [[Puberty - Defining Puberty - Anatomy & Physiology|Puberty]] is the process of aquiring reproductive capability, and age at onset of puberty varies from between [[Puberty- Overview of Puberty - Anatomy & Physiology|species]]. There are several factors involved in triggering the [[Puberty - Factors Influencing the Onset of Puberty - Anatomy & Physiology|onset]] of puberty, including body size, nutritional factors, day length, genetic factors and environmental and social factors. The onset depends on the ability of specific hypothalamic neurons to produce [[Puberty - Endocrine Events of Puberty - Anatomy & Physiology|gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)]] in sufficient quantities to both promote and support gametogenesis. The hypothalamus itself is influenced by hormonal factors that are [[Puberty - Differences in the Male and Female Hypothalamus- Anatomy & Physiology|male or female specific]]. |
== Female Reproductive Tract and Reproductive Behaviour== | == Female Reproductive Tract and Reproductive Behaviour== | ||
| − | The anatomy of the female reproductive tract includes the [[Vagina | + | The anatomy of the female reproductive tract includes the [[Female Reproductive Tract -The Vagina/Vestibule - Anatomy & Physiology|external genitalia and vagina]], [[Female Reproductive Tract -The Cervix - Anatomy & Physiology|the cervix]], [[Female Reproductive Tract -The Uterus - Anatomy & Physiology|the uterus]], [[Female Reproductive Tract -The Oviduct - Anatomy & Physiology|the oviduct]] and [[Female Reproductive Tract -The Ovary - Anatomy & Physiology|the ovary]]. |
| − | Female animals regularly enter a phase where they are sexually active and receptive to males; this is known as the [[Oestrous Cycle - Anatomy & Physiology|oestrous cycle]]. Some animals are able to reproduce all year round, but many have an anoestrus phase which requires a [[Seasonality of Reproduction - Anatomy & Physiology|seasonal response]] for cycling to begin. In some species [[Oestrus Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|detection of seasonal cycling]] can be crucial to productivity. | + | Female animals regularly enter a phase where they are sexually active and receptive to males; this is known as the [[Female Reproductive Tract -Oestrous Cycle - Anatomy & Physiology|oestrous cycle]]. Some animals are able to reproduce all year round, but many have an anoestrus phase which requires a [[Female Reproductive Tract -Seasonality of Reproduction - Anatomy & Physiology|seasonal response]] for cycling to begin. In some species [[Reproductive Behaviour - Oestrus Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|detection of seasonal cycling]] can be crucial to productivity. |
| − | Female animals have various [[Reproductive Behaviour Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|behavioural]] and chemical signals which increase their [[Attractivity Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|attractiveness]] to males and others which signal their [[Proceptivity Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|acceptance]] of attention from the male. Further cues indicate that the female is [[Receptivity Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|receptive]] to mating. Other reproductive female behaviours include [[Maternal Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|maternal]] and [[Nursing Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|nursing]] behaviour. In [[Nervous Pathway Eliciting Reproductive Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|neurological terms]] sensory information from behavioural and chemical cues are processed by the hypothalamus, which induces the appropriate mating response via specific peptides which activate neurons in the midbrain and brainstem. | + | Female animals have various [[Reproductive Behaviour - Overview of Reproductive Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|behavioural]] and chemical signals which increase their [[Reproductive Behaviour - Attractivity Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|attractiveness]] to males and others which signal their [[Reproductive Behaviour - Proceptivity Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|acceptance]] of attention from the male. Further cues indicate that the female is [[Reproductive Behaviour - Receptivity Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|receptive]] to mating. Other reproductive female behaviours include [[Reproductive Behaviour - Maternal Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|maternal]] and [[Reproductive Behaviour - Nursing Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|nursing]] behaviour. In [[Reproductive Behaviour - Nervous Pathway Eliciting Reproductive Motor Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|neurological terms]] sensory information from behavioural and chemical cues are processed by the hypothalamus, which induces the appropriate mating response via specific peptides which activate neurons in the midbrain and brainstem. |
== Male Reproductive Tract and Reproductive Behaviour== | == Male Reproductive Tract and Reproductive Behaviour== | ||
| − | The anatomy of the male reproductive tract includes the [[ | + | The anatomy of the male reproductive tract includes the [[Male Reproductive Tract -The External Genetalia - Anatomy & Physiology|penis]], the [[Male Reproductive Tract -The Testes and Epididymis - Anatomy & Physiology|testes]], the [[Male Reproductive Tract -The Testes and Epididymis - Anatomy & Physiology|epididymis]] and the [[Male Reproductive Tract -Accessory Sex Glands - Anatomy & Physiology|accessory sex glands]]. Males of different species are often referred to by specific [[Male Reproductive Tract -Useful Terms - Anatomy & Physiology|names]] which reflect their repoductive status. Males differ from females in the [[Male Reproductive Tract -Spermatogenesis and Spermiation - Anatomy & Physiology|production of sperm]] which takes place from puberty onwards - unlike females where ova are produced prior to birth. The [[Male Reproductive Tract -Spermatogenesis and Spermiation - Anatomy & Physiology|hormones]] controlling sperm production, or spermatogenesis are luteinising hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). |
| − | The [[Nervous Pathway Eliciting Reproductive Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|neurological pathways]] that control reproductive behaviour are similar to the female, but the response is male specific and includes [[Pre-copulatory Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|pre-copulatory]], [[Copulatory Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|copulatory]] and [[Post-Copulatory Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|post-copulatory]] behaviour. | + | The [[Reproductive Behaviour - Nervous Pathway Eliciting Reproductive Motor Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|neurological pathways]] that control reproductive behaviour are similar to the female, but the response is male specific and includes [[Reproductive Behaviour - Pre-copulatory Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|pre-copulatory]], [[Reproductive Behaviour - Copulatory Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|copulatory]] and [[Reproductive Behaviour - Post-Copulatory Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology|post-copulatory]] behaviour. |
== Fertilisation, Implantation and Early Embryonic Development == | == Fertilisation, Implantation and Early Embryonic Development == | ||
| − | After mating has occured, sperm must [[Sperm in the Female Tract - Anatomy & Physiology|travel]] along the female reproductive tract towards the uterus in order to [[Fertilisation - Anatomy & Physiology|fertilise]] the oocyte. A single spermatazoon penetrates the oocyte and the male and female pronuclei fuse to form an ootid which divides repeatedly to form the [[ | + | After mating has occured, sperm must [[Copulation -Sperm in the Female Tract - Anatomy & Physiology|travel]] along the female reproductive tract towards the uterus in order to [[Fertilisation, Implantation and Early Embryonic Development -Fertilisation- Anatomy & Physiology|fertilise]] the oocyte. A single spermatazoon penetrates the oocyte and the male and female pronuclei fuse to form an ootid which divides repeatedly to form the [[Fertilisation, Implantation and Early Embryonic Development -Embryonic Development of the Blastocyst- Anatomy & Physiology|blastocyst]]. At this stage the genetic sex of the offspring is determined as male gametes are [[Fertilisation, Implantation and Early Embryonic Development -Sexual Differentiation- Anatomy & Physiology|heterogametic]]. The blastocyst continues to divide and grow until the outer layer, the zona pellucida ruptures and the blastocyst 'hatches' and becomes free floating within the uterus. The blastocyt continues to grow and develop until it becomes an embryo with placental and embryonic membranes such as the amniotic sac; the placental membranes then attach to the uterine endometrium in a process known as [[Fertilisation, Implantation and Early Embryonic Development -Implantation- Anatomy & Physiology|implantation]]. During embryonic development the process of [[Male Reproductive Tract -Internal and External Genitalia Development - Anatomy & Physiology|sexual differentiation]] begins. |
== Pregnancy and Parturition == | == Pregnancy and Parturition == | ||
| − | In most domestic species, pregnancy is maintained by hormonal feedback from the corpus luteum and, in many species, the placenta. The corpus luteum is maintained in early pregnancy and progesterone levels remain elevated as a result. This maintains negative feedback to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland which inhibits further follicular development and ovulation. In polyoestrous species, it prevents the return to oestrus. In many species the [[ | + | In most domestic species, pregnancy is maintained by hormonal feedback from the corpus luteum and, in many species, the placenta. The corpus luteum is maintained in early pregnancy and progesterone levels remain elevated as a result. This maintains negative feedback to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland which inhibits further follicular development and ovulation. In polyoestrous species, it prevents the return to oestrus. In many species the [[Endocrine System_-_Placenta_-_Anatomy_%26_Physiology|placenta]] will take over or supplement the corpus luteum as the source of progesterone during pregnancy; the placenta is a source of many of the hormones that regulate changes during preganancy, stimulating mammary growth, the growth of the myometrium, preparation for parturition, and secreting chorionic gonadotrophin in species where this is required for the [[Gestation -Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy - Anatomy & Physiology|maternal recognition of pregnancy]]. [[Gestation -Litter Sizes - Anatomy & Physiology|Litter sizes]] vary between species, as do methods of [[Gestation -Diagnosis of Pregnancy - Anatomy & Physiology|pregnancy diagnosis]]. |
| − | * [[Gestation Lengths in Various Species - Anatomy & Physiology|Summary of Gestation Lengths in Various Species]] | + | * [[Gestation -Reference Table of Gestation Lengths in Various Species - Anatomy & Physiology|Summary of Gestation Lengths in Various Species]] |
| − | The process of giving birth, or [[Normal Parturition - Anatomy & Physiology|parturition ]] is conventionally divided into [[Normal Parturition - Anatomy & Physiology|three stages]]; stage one includes the movement of the foetus into the birthing position and preparation of the reproductive tract for birth, which is followed by stage two - contractions and the birth itself. Finally, stage three involves the expulsion of the foetal membranes. The timings of each stage vary from species to species, and a good knowledge of the normal progression of parturition is essential to detect when things are not proceeding normally. There are several [[ | + | The process of giving birth, or [[Parturition - Normal Parturition - Anatomy & Physiology|parturition ]] is conventionally divided into [[Parturition - Normal Parturition - Anatomy & Physiology|three stages]]; stage one includes the movement of the foetus into the birthing position and preparation of the reproductive tract for birth, which is followed by stage two - contractions and the birth itself. Finally, stage three involves the expulsion of the foetal membranes. The timings of each stage vary from species to species, and a good knowledge of the normal progression of parturition is essential to detect when things are not proceeding normally. There are several [[Parturition - Risks in Parturition - Anatomy & Physiology|conditions]] that can occur to disturb the normal progress of parturition, including dystocia, uterine inertia, ring womb, prolapses, retained placenta, endometritis and foetal abnormalities. Like pregnancy, parturition is under complex [[Parturition - Endocrine Control of Parturition - Anatomy & Physiology|hormonal control]], and this can be manipulated [[Parturition - Pharmacological Manipulation of Parturition - Anatomy & Physiology|pharmacalogically]] to alter the timing of parturition. |
== The Puerperium == | == The Puerperium == | ||
| − | [[Puerperium - Anatomy & Physiology|Puerperium]] describes the period of time immediately following parturition, when the female enters a period of reproductive repair and begins lactation. For a period of time these two processes overlap. During this time the female experiences regular myometrial contractions which expel the remaining fluid and tissues present following birth, allowing the uterus to begin involution and repair so that the reproductive cycle can begin once more. The discharge appears at the vulva and is known as lochia. The process of birth can predispose the reproductive tract to heavy bacterial contamination, but physiological and hormonal changes encourage the removal of bacteria before infection can become established. There are many environmental and management influences that will affect the length of time that puerperium lasts, as well as differences between species. | + | [[The Puerperium - Overview of the Puerperium - Anatomy & Physiology|Puerperium]] describes the period of time immediately following parturition, when the female enters a period of reproductive repair and begins lactation. For a period of time these two processes overlap. During this time the female experiences regular [[The Puerperium - Myometrial Contraction and Expulsion of Lochia - Anatomy & Physiology|myometrial contractions]] which expel the remaining fluid and tissues present following birth, allowing the uterus to begin [[The Puerperium - Endometrial Repair- Anatomy & Physiology|involution and repair]] so that the reproductive cycle can begin once more. The discharge appears at the vulva and is known as [[The_Puerperium_-_Myometrial_Contraction_and_Expulsion_of_Lochia_-_Anatomy_%26_Physiology#Lochia|lochia]]. The process of birth can predispose the reproductive tract to heavy bacterial contamination, but physiological and hormonal changes encourage the [[The Puerperium - Elimination of Bacterial Contamination of the Reproductive Tract- Anatomy & Physiology|removal of bacteria]] before infection can become established. There are many [[The Puerperium - Factors Influencing the Puerperium- Anatomy & Physiology|environmental and management]] influences that will affect the length of time that puerperium lasts, as well as differences between [[The Puerperium - Species Differences in the Puerperium- Anatomy & Physiology| species]]. |
== Lactation == | == Lactation == | ||
| − | The secretion of milk from the mammary glands is known as [[Lactation - Anatomy & Physiology|lactation]] - the milk provides [Milk Composition and Biosynthesis- Anatomy & Physiology|nourishment]] for the neonate in addition to immunoprotection in the form of anitibodies which are contained in the initial mammary secretions, or [[ | + | The secretion of milk from the mammary glands is known as [[Lactation - Overview of Lactation - Anatomy & Physiology|lactation]] - the milk provides [[Lactation - Milk Composition and Biosynthesis- Anatomy & Physiology|nourishment]] for the neonate in addition to immunoprotection in the form of anitibodies which are contained in the initial mammary secretions, or [[Lactation_-_Milk_Composition_and_Biosynthesis-_Anatomy_%26_Physiology#Colostrum|colostrum]]. Mammary development and milk production and ejection are induced by [[Lactation - Endocrine Control - Anatomy & Physiology|hormonal signals]]. Lactation continues until the neonate is weaned; after weaning the [[Lactation - The Mammary Gland - Anatomy & Physiology|mammary glands]] undergo [[Lactation - Involution - Anatomy & Physiology|involution]] and return to a non-secretory state. |
| − | Various pathological states that affect mammary tissues include [[Neoplasia - Pathology#Examples of Tumour Types|mammary neoplasia]] and [[Healing and Repair - Pathology#Female|mastitis]]. Metabolic disturbances can also occur during lactation, the most common being hypocalcaemia or 'milk fever'. | + | Various pathological states that affect mammary tissues include [[Neoplasia - Pathology#Examples of Tumour Types|mammary neoplasia]] and [[Healing and Repair - Pathology#Female|mastitis]]. Metabolic disturbances can also occur during lactation, the most common being [[General Pathology - Vascular Fluid Balance - Pathology#Calcium|hypocalcaemia]] or 'milk fever'. |
== Reproductive Technologies == | == Reproductive Technologies == | ||
| − | Technologies such as [[Artificial Insemination - Anatomy & Physiology|artificial insemination]] (AI) have been in use for some time and in cattle, for example have become standard practice for reproduction purposes; the technique requires [[Semen Collection - Anatomy & Physiology| | + | Technologies such as [[Reproductive Technologies -Artificial Insemination - Anatomy & Physiology|artificial insemination]] (AI) have been in use for some time and in cattle, for example have become standard practice for reproduction purposes; the technique requires collection of [[Reproductive Technologies -Semen Collection - Anatomy & Physiology|semen]] from the male, which is preserved, transported and introduced into the female reporoductive tract in synchrony with her ovulation cycle. Recently other techniques have been developed which permit development of the embryo from a donor animal in a recepient female who will carry the pregnancey to term and nurse the resulting offspring - a technique called [[Reproductive Technologies -Multiple Ovulation and Embryo Transfer- Anatomy & Physiology|embryo transfer]]. This technique has some unique advantages and is becoming popular, for example in some equine studs where successful mares can continue their competative careers and still become part of a breeding programme. Other more specialised techniques used in breeding include: |
| − | * [[In Vitro Fertilization - Anatomy & Physiology|In Vitro Fertilization]] | + | * [[Reproductive Technologies -In Vitro Fertilization- Anatomy & Physiology|In Vitro Fertilization]] |
| − | * [[In Vitro Maturation - Anatomy & Physiology|In Vitro Maturation]] | + | * [[Reproductive Technologies -In Vitro Maturation- Anatomy & Physiology|In Vitro Maturation]] |
| − | * [[Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection - Anatomy & Physiology|Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection]] | + | * [[Reproductive Technologies -Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection- Anatomy & Physiology|Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection]] |
| − | * [[Embryo Sexing - Anatomy & Physiology|Embryo Sexing]] | + | * [[Reproductive Technologies -Embryo Sexing- Anatomy & Physiology|Embryo Sexing]] |
| − | * [[Semen Sexing - Anatomy & Physiology|Semen Sexing]] | + | * [[Reproductive Technologies -Semen Sexing- Anatomy & Physiology|Semen Sexing]] |
| − | * [[Embryo Splitting - Anatomy & Physiology|Embryo Splitting]] | + | * [[Reproductive Technologies -Embryo Splitting- Anatomy & Physiology|Embryo Splitting]] |
| − | * [[Nuclear Transplantation | + | * [[Reproductive Technologies -Nuclear Transplantation:Cloning- Anatomy & Physiology|Nuclear Transplantation:Cloning]] |
| − | * [[Transgenic Animals - Anatomy & Physiology|Transgenic Animals]] | + | * [[Reproductive Technologies -Transgenic Animals- Anatomy & Physiology|Transgenic Animals]] |
== Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) == | == Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) == | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) - Female Anatomy - Anatomy & Physiology|Female Anatomy]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) - Male Anatomy - Anatomy & Physiology|Male Anatomy]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) - Breeding Cycle - Anatomy & Physiology|Breeding Cycle]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) - Mating - Anatomy & Physiology|Mating]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) - Pregnancy Diagnosis - Anatomy & Physiology|Pregnancy Diagnosis]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) - Parturition - Anatomy & Physiology|Parturition]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas) - Lactation & Care of the Newborn - Anatomy & Physiology|Lactation & Care of the Newborn]] |
== Small Domestic Mammals == | == Small Domestic Mammals == | ||
| − | * [[Reproductive Characteristics | + | * [[Small Mammals -Reference Table of Reproductive Characteristics for Small Domestic Mammals- Anatomy & Physiology|Summary of Reproductive Characteristics for Small Domestic Mammals]] |
| − | * [[Guinea Pig | + | * [[Small Mammals -Guinea Pig- Anatomy & Physiology|Guinea Pig]] |
| − | * [[Ferret | + | * [[Small Mammals -Ferret- Anatomy & Physiology|Ferret]] |
| − | * [[Chinchilla | + | * [[Small Mammals -Chinchilla- Anatomy & Physiology|Chinchilla]] |
| − | * [[Chipmunk | + | * [[Small Mammals -Chipmunk- Anatomy & Physiology|Chipmunk]] |
| − | * [[Mouse | + | * [[Small Mammals -Mouse- Anatomy & Physiology|Mouse]] |
| − | * [[Hamster | + | * [[Small Mammals -Hamster- Anatomy & Physiology|Hamster]] |
| − | * [[Rabbit | + | * [[Small Mammals -Rabbit- Anatomy & Physiology|Rabbit]] |
| − | * [[Rat | + | * [[Small Mammals -Rat- Anatomy & Physiology|Rat]] |
| − | * [[Gerbil | + | * [[Small Mammals -Gerbil- Anatomy & Physiology|Gerbil]] |
== Exotics == | == Exotics == | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Exotics - Avian Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology - Anatomy & Physiology|Avian Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology ]] |
| − | * [[Reptile | + | * [[Exotics - Reptile Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology - Anatomy & Physiology|Reptile Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology]] |
| − | * [[Amphibian | + | * [[Exotics - Amphibian Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology - Anatomy & Physiology|Amphibian Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology]] |
| − | * [[Fish | + | * [[Exotics - Fish Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology - Anatomy & Physiology|Fish Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology ]] |
| − | + | ==Test yourself - Reproduction System flashcards== | |
| − | + | *'''[[Reproductive System Flashcards - Anatomy & Physiology|Reproductive System Flashcards]]''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 107: | Line 108: | ||
* B.Young, J.W Heath: Wheater's Functional Histology, A Text and Colour Atlas | * B.Young, J.W Heath: Wheater's Functional Histology, A Text and Colour Atlas | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Reproductive System | + | [[Category:Reproductive System]] |
Revision as of 15:18, 22 August 2010
|
|
Introduction to the Reproductive System
Reproduction is the complex set of biological processes that result in the formation of a new organism; it is crucial that we understand how these processes occur normally and have a good grasp of the role of hormones in the reproductive process. Pathology and disease are common within the reproductive system and can not only lead to a sick animal but also to a loss in production. In this section we hope to cover all the main processes in domestic animals, laying a foundation for understanding the associated pathological states.
Puberty
Puberty is the process of aquiring reproductive capability, and age at onset of puberty varies from between species. There are several factors involved in triggering the onset of puberty, including body size, nutritional factors, day length, genetic factors and environmental and social factors. The onset depends on the ability of specific hypothalamic neurons to produce gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) in sufficient quantities to both promote and support gametogenesis. The hypothalamus itself is influenced by hormonal factors that are male or female specific.
Female Reproductive Tract and Reproductive Behaviour
The anatomy of the female reproductive tract includes the external genitalia and vagina, the cervix, the uterus, the oviduct and the ovary. Female animals regularly enter a phase where they are sexually active and receptive to males; this is known as the oestrous cycle. Some animals are able to reproduce all year round, but many have an anoestrus phase which requires a seasonal response for cycling to begin. In some species detection of seasonal cycling can be crucial to productivity.
Female animals have various behavioural and chemical signals which increase their attractiveness to males and others which signal their acceptance of attention from the male. Further cues indicate that the female is receptive to mating. Other reproductive female behaviours include maternal and nursing behaviour. In neurological terms sensory information from behavioural and chemical cues are processed by the hypothalamus, which induces the appropriate mating response via specific peptides which activate neurons in the midbrain and brainstem.
Male Reproductive Tract and Reproductive Behaviour
The anatomy of the male reproductive tract includes the penis, the testes, the epididymis and the accessory sex glands. Males of different species are often referred to by specific names which reflect their repoductive status. Males differ from females in the production of sperm which takes place from puberty onwards - unlike females where ova are produced prior to birth. The hormones controlling sperm production, or spermatogenesis are luteinising hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
The neurological pathways that control reproductive behaviour are similar to the female, but the response is male specific and includes pre-copulatory, copulatory and post-copulatory behaviour.
Fertilisation, Implantation and Early Embryonic Development
After mating has occured, sperm must travel along the female reproductive tract towards the uterus in order to fertilise the oocyte. A single spermatazoon penetrates the oocyte and the male and female pronuclei fuse to form an ootid which divides repeatedly to form the blastocyst. At this stage the genetic sex of the offspring is determined as male gametes are heterogametic. The blastocyst continues to divide and grow until the outer layer, the zona pellucida ruptures and the blastocyst 'hatches' and becomes free floating within the uterus. The blastocyt continues to grow and develop until it becomes an embryo with placental and embryonic membranes such as the amniotic sac; the placental membranes then attach to the uterine endometrium in a process known as implantation. During embryonic development the process of sexual differentiation begins.
Pregnancy and Parturition
In most domestic species, pregnancy is maintained by hormonal feedback from the corpus luteum and, in many species, the placenta. The corpus luteum is maintained in early pregnancy and progesterone levels remain elevated as a result. This maintains negative feedback to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland which inhibits further follicular development and ovulation. In polyoestrous species, it prevents the return to oestrus. In many species the placenta will take over or supplement the corpus luteum as the source of progesterone during pregnancy; the placenta is a source of many of the hormones that regulate changes during preganancy, stimulating mammary growth, the growth of the myometrium, preparation for parturition, and secreting chorionic gonadotrophin in species where this is required for the maternal recognition of pregnancy. Litter sizes vary between species, as do methods of pregnancy diagnosis.
The process of giving birth, or parturition is conventionally divided into three stages; stage one includes the movement of the foetus into the birthing position and preparation of the reproductive tract for birth, which is followed by stage two - contractions and the birth itself. Finally, stage three involves the expulsion of the foetal membranes. The timings of each stage vary from species to species, and a good knowledge of the normal progression of parturition is essential to detect when things are not proceeding normally. There are several conditions that can occur to disturb the normal progress of parturition, including dystocia, uterine inertia, ring womb, prolapses, retained placenta, endometritis and foetal abnormalities. Like pregnancy, parturition is under complex hormonal control, and this can be manipulated pharmacalogically to alter the timing of parturition.
The Puerperium
Puerperium describes the period of time immediately following parturition, when the female enters a period of reproductive repair and begins lactation. For a period of time these two processes overlap. During this time the female experiences regular myometrial contractions which expel the remaining fluid and tissues present following birth, allowing the uterus to begin involution and repair so that the reproductive cycle can begin once more. The discharge appears at the vulva and is known as lochia. The process of birth can predispose the reproductive tract to heavy bacterial contamination, but physiological and hormonal changes encourage the removal of bacteria before infection can become established. There are many environmental and management influences that will affect the length of time that puerperium lasts, as well as differences between species.
Lactation
The secretion of milk from the mammary glands is known as lactation - the milk provides nourishment for the neonate in addition to immunoprotection in the form of anitibodies which are contained in the initial mammary secretions, or colostrum. Mammary development and milk production and ejection are induced by hormonal signals. Lactation continues until the neonate is weaned; after weaning the mammary glands undergo involution and return to a non-secretory state. Various pathological states that affect mammary tissues include mammary neoplasia and mastitis. Metabolic disturbances can also occur during lactation, the most common being hypocalcaemia or 'milk fever'.
Reproductive Technologies
Technologies such as artificial insemination (AI) have been in use for some time and in cattle, for example have become standard practice for reproduction purposes; the technique requires collection of semen from the male, which is preserved, transported and introduced into the female reporoductive tract in synchrony with her ovulation cycle. Recently other techniques have been developed which permit development of the embryo from a donor animal in a recepient female who will carry the pregnancey to term and nurse the resulting offspring - a technique called embryo transfer. This technique has some unique advantages and is becoming popular, for example in some equine studs where successful mares can continue their competative careers and still become part of a breeding programme. Other more specialised techniques used in breeding include:
Camelids (LLamas & Alpacas)
- Female Anatomy
- Male Anatomy
- Breeding Cycle
- Mating
- Pregnancy Diagnosis
- Parturition
- Lactation & Care of the Newborn
Small Domestic Mammals
- Summary of Reproductive Characteristics for Small Domestic Mammals
- Guinea Pig
- Ferret
- Chinchilla
- Chipmunk
- Mouse
- Hamster
- Rabbit
- Rat
- Gerbil
Exotics
- Avian Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
- Reptile Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
- Amphibian Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
- Fish Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
Test yourself - Reproduction System flashcards
References
- P.L Senger: Pathways to Pregnancy and Parturition,2nd Edition
- David E. Noakes,Timothy J. Parkinson,Gary C. W. England,Geoffrey H. Arthur: Arthur's Veterinary Reproduction and Obstetrics
- Bairbre O'Malley:Clinical Anatomy and Physiology of Exotic Species
- Dyce, Sack and Wensing: Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy, 3rd Edition
- Konig and Liebich: Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals, 3rd Edition
- Victoria Aspinall, Melanie Cappello: Introduction to Veterinary Anatomy & Physiology
- Gina Bromage: Llamas and Alpacas: A Guide to Management
- R.J. Roberts,Lydia Brown: Aquaculture for Veterinarians - Fish Husbandry and Medicine (Pergamon Veterinary Handbook)
- B.Young, J.W Heath: Wheater's Functional Histology, A Text and Colour Atlas