Difference between revisions of "Natural Killer cells"
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
[[Image:NK healthy.jpg|thumb|right|175px|Healthy cells present MHC to NK cells to suppress their activation - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:NK healthy.jpg|thumb|right|175px|Healthy cells present MHC to NK cells to suppress their activation - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | ||
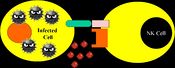
[[Image:NK infected.jpg|thumb|right|175px|Infected cells lack MHC, which means they cannot switch off the NK activation signal - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:NK infected.jpg|thumb|right|175px|Infected cells lack MHC, which means they cannot switch off the NK activation signal - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | ||
[[Image:NK activated.jpg|thumb|right|175px|Natural Killer cells release enzymes to kill cells with inadequate MHC presentation - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:NK activated.jpg|thumb|right|175px|Natural Killer cells release enzymes to kill cells with inadequate MHC presentation - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | [[Image:NK kill.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:NK kill.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Infected cells are destroyed before replication - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] |
NK cells can be classified as lymphocytes because they are capable of recognising antigen, however they are more often associated with the [[Innate Immune System - Introduction|'''innate immune response''']]. They target cells by monitoring [[Major Histocompatability Complexes|MHC]] production, which is expressed by healthy cells to present antigen to T-cells. Low MHC levels can be used as a marker for a cell whose machinery is compromised by a replicating virus. When MHC levels drop, it acts as a danger signal to the NK cells, which then release enzymes to kill the infected cells. | NK cells can be classified as lymphocytes because they are capable of recognising antigen, however they are more often associated with the [[Innate Immune System - Introduction|'''innate immune response''']]. They target cells by monitoring [[Major Histocompatability Complexes|MHC]] production, which is expressed by healthy cells to present antigen to T-cells. Low MHC levels can be used as a marker for a cell whose machinery is compromised by a replicating virus. When MHC levels drop, it acts as a danger signal to the NK cells, which then release enzymes to kill the infected cells. | ||
NK cells do not develop in the thymus and represent 5-10% of the circulating lymphocytes. They recognise and kill transformed cells by releasing perforins and granzymes which create channels in the target cell membrane causing lysis. They express the markers CD16, CD56 and CD94. | NK cells do not develop in the thymus and represent 5-10% of the circulating lymphocytes. They recognise and kill transformed cells by releasing perforins and granzymes which create channels in the target cell membrane causing lysis. They express the markers CD16, CD56 and CD94. | ||
| − | Natural Killer cells also play a role in [[ | + | Natural Killer cells also play a role in [[Adaptive Immunity to Viruses|'''Antibody-Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity''']] |
| − | |||
==NK Receptors== | ==NK Receptors== | ||
| − | Some viruses | + | * Some viruses down-regulate MHC expression of the infected cell |
| − | + | ** This is used as a protection against the host immune system | |
| − | The receptors on NK cells do not act like antigen-specific receptors | + | *** Lack of MHC inhibits normal T-cell activity |
| − | + | * NK cells can counteract the down-regulation tactic | |
| − | + | ** They are mainly associated with activity against virus-infected cells and tumour cells, which can also have lowered MHC expression | |
| − | When an NK cell interacts with a target cell it will be activated via R1 | + | * The receptors on NK cells '''do not''' act like antigen-specific receptors |
| − | + | ** Although they trigger functional activity of the cell, they do not stimulate proliferation | |
| − | If the target cell does not express MHC, the suppressing receptors are not engaged | + | *** There is no clonal expansion of NK cells |
| − | + | * NK cells work through two different types of receptors | |
| − | + | ** '''Activating receptors, R1''' | |
| − | + | *** Recognise pathogen-associated glycolipids or Fc receptors | |
| − | + | **** E.g. CD16 recognises Ig that is bound to pathogen antigens | |
| − | + | ** '''Suppressing receptors, R2''' | |
| − | + | *** Recognise target cell MHC molecules | |
| − | + | * When an NK cell interacts with a target cell it will be activated via R1 | |
| − | + | ** If the target cell expresses MHC this will be seen by R2 | |
| + | *** R2 suppresses the activities of the NK cells | ||
| + | **** Therefore, NK cells do not affect normal cells | ||
| + | ** If the target cell does not express MHC, the suppressing receptors are not engaged | ||
| + | *** Cell activity is not suppressed | ||
| + | **** The engagement of R1 therefore causes activation of the NK cells | ||
| + | When NK cells are activated, they: | ||
| + | *Secrete a range of [[Cytokines|cytokines]], including: | ||
| + | ** '''Tumour necrosis factor alpha'''; (TNFα) | ||
| + | *** A potent stimulator of acute inflammation | ||
| + | ***Can cause target cell killing directly and also via stimulated macrophages | ||
| + | **'''Interferon gamma'''; (IFNγ) | ||
| + | *** Stimulates macrophages | ||
| + | *** Active against the target cells | ||
| + | **** Stimulates target cell expression of MHC | ||
| + | **** Makes target cells susceptible to normal T-cell killing. | ||
| + | *Initiate killing of the target cell | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Lymphocytes|G]] | [[Category:Lymphocytes|G]] | ||
Revision as of 16:06, 27 September 2010
Introduction
NK cells can be classified as lymphocytes because they are capable of recognising antigen, however they are more often associated with the innate immune response. They target cells by monitoring MHC production, which is expressed by healthy cells to present antigen to T-cells. Low MHC levels can be used as a marker for a cell whose machinery is compromised by a replicating virus. When MHC levels drop, it acts as a danger signal to the NK cells, which then release enzymes to kill the infected cells.
NK cells do not develop in the thymus and represent 5-10% of the circulating lymphocytes. They recognise and kill transformed cells by releasing perforins and granzymes which create channels in the target cell membrane causing lysis. They express the markers CD16, CD56 and CD94.
Natural Killer cells also play a role in Antibody-Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity
NK Receptors
- Some viruses down-regulate MHC expression of the infected cell
- This is used as a protection against the host immune system
- Lack of MHC inhibits normal T-cell activity
- This is used as a protection against the host immune system
- NK cells can counteract the down-regulation tactic
- They are mainly associated with activity against virus-infected cells and tumour cells, which can also have lowered MHC expression
- The receptors on NK cells do not act like antigen-specific receptors
- Although they trigger functional activity of the cell, they do not stimulate proliferation
- There is no clonal expansion of NK cells
- Although they trigger functional activity of the cell, they do not stimulate proliferation
- NK cells work through two different types of receptors
- Activating receptors, R1
- Recognise pathogen-associated glycolipids or Fc receptors
- E.g. CD16 recognises Ig that is bound to pathogen antigens
- Recognise pathogen-associated glycolipids or Fc receptors
- Suppressing receptors, R2
- Recognise target cell MHC molecules
- Activating receptors, R1
- When an NK cell interacts with a target cell it will be activated via R1
- If the target cell expresses MHC this will be seen by R2
- R2 suppresses the activities of the NK cells
- Therefore, NK cells do not affect normal cells
- R2 suppresses the activities of the NK cells
- If the target cell does not express MHC, the suppressing receptors are not engaged
- Cell activity is not suppressed
- The engagement of R1 therefore causes activation of the NK cells
- Cell activity is not suppressed
- If the target cell expresses MHC this will be seen by R2
When NK cells are activated, they:
- Secrete a range of cytokines, including:
- Tumour necrosis factor alpha; (TNFα)
- A potent stimulator of acute inflammation
- Can cause target cell killing directly and also via stimulated macrophages
- Interferon gamma; (IFNγ)
- Stimulates macrophages
- Active against the target cells
- Stimulates target cell expression of MHC
- Makes target cells susceptible to normal T-cell killing.
- Tumour necrosis factor alpha; (TNFα)
- Initiate killing of the target cell