Difference between revisions of "Copulatory Behaviour - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Gerbil) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour =EED2EE | ||
| + | |linkpage =Reproductive System - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |linktext =Reproductive System | ||
| + | |maplink = Reproductive System (Content Map) - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |sublink1=Reproductive System - Anatomy & Physiology#Reproductive Behaviour | ||
| + | |subtext1=REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOUR | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
==Mounting== | ==Mounting== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 37: | ||
** '''Bulbospongiosus''' muscle | ** '''Bulbospongiosus''' muscle | ||
* '''Emission''' and ejaculation | * '''Emission''' and ejaculation | ||
| − | ** Emission is the movement of seminal fluids from the [[Accessory_Sex_Glands_- Anatomy & Physiology|accessory sex glands]] into the pelvic urethra so that they can mix with spermatozoa. | + | ** Emission is the movement of seminal fluids from the [[Reproductive_Tract_-Accessory_Sex_Glands_- Anatomy & Physiology|accessory sex glands]] into the pelvic urethra so that they can mix with spermatozoa. |
** Emission occurs before and during ejaculation. | ** Emission occurs before and during ejaculation. | ||
| Line 75: | Line 84: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | === [[ | + | === [[Reproductive Behaviour - Copulatory Behaviour Dog - Anatomy & Physiology|Dog]] === |
---- | ---- | ||
| − | === [[Cat | + | === [[Reproductive Behaviour - Copulatory Behaviour Cat - Anatomy & Physiology|Cat]] === |
---- | ---- | ||
| − | === [[ | + | === [[Reproductive Behaviour - Copulatory Behaviour Gerbil - Anatomy & Physiology|Gerbil]] === |
---- | ---- | ||
| − | [[Category:Reproductive | + | [[Category:Reproductive System]] |
| − | |||
Revision as of 22:29, 30 November 2010
|
|
Mounting
- Elevation of the front legs of the male to straddle the posterior region of the female.
- Learned behaviour
Intromission
- Successful entrance of the penis into the vagina.
Ejaculation
- The reflex expulsion of spermatozoa and seminal plasma from the male reproductive tract.
- Sensory stimulation, primarily to the glans penis causes a series of coordinated muscular contractions.
- Once intromission has been achieved, reflex impulses are initiated.
- Neural impulses derived mainly from sensory nerves in the glans penis.
- Upon threshold stimulation, impulses are transmitted from the glans penis by the internal pudendal nerve to the lumbosacral region of the spinal cord.
- Sensory impulses result in firing of nerves in the spinal cord.
- Forcing of semen into the urethra by nerves in the hypogastric plexus innervating target muscles.
- Urethralis muscle
- Ischiocavernosus muscle
- Bulbospongiosus muscle
- Emission and ejaculation
- Emission is the movement of seminal fluids from the accessory sex glands into the pelvic urethra so that they can mix with spermatozoa.
- Emission occurs before and during ejaculation.
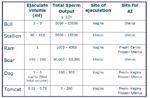
Species Differences
| Species | Ram | Bull | Stallion | Boar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of Copulation | 1-2 seconds (1 Pelvic Thrust with Foreleg Clasp) | 1-3 seconds (1 Pelvic Thrust with Foreleg Clasp) | 20-60 seconds (Multiple Pelvic Thrusts,Flagging,Followed by Innactive Phase) | 5-20 minutes (Rapid Pelvic Thrusting to Engage Penis in Cervix) When Penis is Engaged,Thrusting Stops and Ejaculation Commences |
| Volume of Ejaculate (ml) | 0.8-1.0 | 3-5 | 75-120 | 200-250 |
| Site of Semen Deposition | External Cervical Os | Fornix Vagina | External Cervical Os, but Semen Enters Uterus at High Pressure | Cervix and Uterus |
| Average Numbers of Ejaculations to Satiation | 10 | 20 | 3 | 3 |
| Maximum Number of Ejaculations to Exhaustion (Refractory Period) | 30-40 | 60-80 | 20 | 8 |