Difference between revisions of "Small Mammals Q&A 17"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | [[File:Manson_logo.gif|90px|Mansonlogo]] | | align="center" | [[File:Manson_logo.gif|90px|Mansonlogo]] | ||
| − | | align="left" | This question was provided by [[:Category:Manson|Manson Publishing]] as part of the [[OVAL Project]]. See more [[Category: Small Mammals Q&A|Small Mammals questions]] | + | | align="left" | This question was provided by [[:Category:Manson|Manson Publishing]] as part of the [[OVAL Project]]. See more [[:Category: Small Mammals Q&A|Small Mammals questions]] |
|} | |} | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
In sexually mature males, the scrotal sacs may be seen lateral to the perineum. Male rabbits can retract the testicles into the inguinal canal making sex determination more difficult. | In sexually mature males, the scrotal sacs may be seen lateral to the perineum. Male rabbits can retract the testicles into the inguinal canal making sex determination more difficult. | ||
| − | |l1= Rabbit Reproduction - Anatomy & Physiology | + | |l1= Rabbit Reproduction - Anatomy & Physiology#Sexing |
|q2= What is the gestation period of the rabbit? | |q2= What is the gestation period of the rabbit? | ||
|a2= Twenty-nine to 35 days, with a litter size ranging from 4 to 12. | |a2= Twenty-nine to 35 days, with a litter size ranging from 4 to 12. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
At 18 days postbreeding, the fetuses are approximately 2.5–3 cm in length. | At 18 days postbreeding, the fetuses are approximately 2.5–3 cm in length. | ||
Palpation must be gentle to avoid damage to the fetuses. If necessary, use radiography or ultrasonography after 21 days to determine pregnancy. | Palpation must be gentle to avoid damage to the fetuses. If necessary, use radiography or ultrasonography after 21 days to determine pregnancy. | ||
| − | |l3= Rabbit Reproduction - Anatomy & Physiology | + | |l3= Rabbit Reproduction - Anatomy & Physiology#Pregnancy diagnosis |
|q4= How should you cage a breeding pair of rabbits? | |q4= How should you cage a breeding pair of rabbits? | ||
|a4= Does are territorial and may kill a new rabbit introduced into the cage. For this reason, it is important to bring the doe to the buck’s cage for breeding. If the doe does not accept the buck within a few minutes and fighting occurs, separate them. | |a4= Does are territorial and may kill a new rabbit introduced into the cage. For this reason, it is important to bring the doe to the buck’s cage for breeding. If the doe does not accept the buck within a few minutes and fighting occurs, separate them. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
desc none}} | desc none}} | ||
[[Category: Small Mammals Q&A]] | [[Category: Small Mammals Q&A]] | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 17:55, 23 August 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Small Mammals questions |
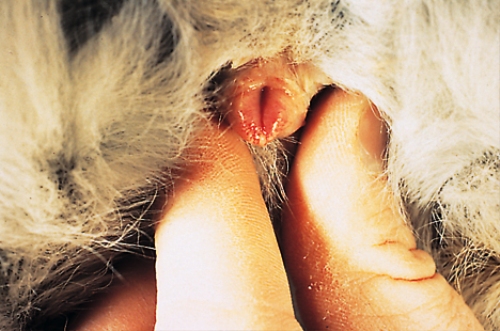
Rabbits become sexually mature from three and a half to nine months of age. The smaller the breed, the earlier the onset of sexual maturity. Separate young rabbits into same sex groups by 10–12 weeks of age to avoid unwanted litters. The photographs show a litter of five-week-old rabbits and a rabbit examined for sexing.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| At what age can the kits be sexed and how would you do this? What sex is the rabbit shown in the second photograph. | The kits are best sexed at birth or at weaning (five to eight weeks of age).
In the interim, it is difficult to exteriorize the genitalia. Stretch the perineum to expose the anogenital structures. The male has a conical- to cylindrical-shaped penis with a rounded to oval urethral opening. The female has a vulva that protrudes slightly with a slit-like opening. The rabbit in the photograph is female. In sexually mature males, the scrotal sacs may be seen lateral to the perineum. Male rabbits can retract the testicles into the inguinal canal making sex determination more difficult. |
Link to Article | |
| What is the gestation period of the rabbit? | Twenty-nine to 35 days, with a litter size ranging from 4 to 12.
|
Link to Article | |
| How soon can the doe be palpated for pregnancy? | Fetuses can be palpated as early as 10 days postbreeding. At this stage they can be felt as masses approximately 1–1.5 cm in diameter located in the caudal ventral abdomen.
At 18 days postbreeding, the fetuses are approximately 2.5–3 cm in length. Palpation must be gentle to avoid damage to the fetuses. If necessary, use radiography or ultrasonography after 21 days to determine pregnancy. |
Link to Article | |
| How should you cage a breeding pair of rabbits? | Does are territorial and may kill a new rabbit introduced into the cage. For this reason, it is important to bring the doe to the buck’s cage for breeding. If the doe does not accept the buck within a few minutes and fighting occurs, separate them.
Introduce them again at 12–24 hour intervals until one to two successful matings have occurred. |
Link to Article | |