Difference between revisions of "Feline Medicine Q&A 06"
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:Manson Sparkes}} | {{Template:Manson Sparkes}} | ||
| − | [[Image:|centre|500px]] | + | [[Image:Feline Medicine 06.jpg|centre|500px]] |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
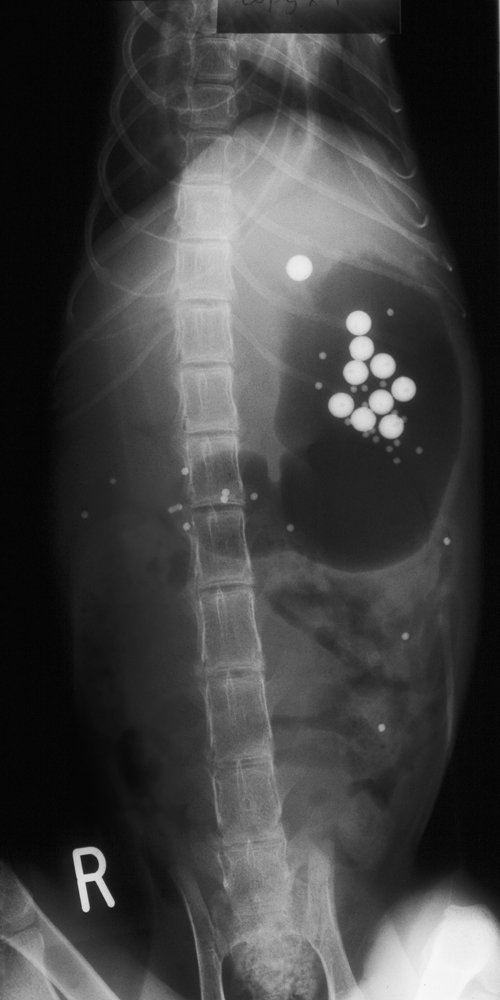
*All the large (5 mm diameter) BIPS, and most of the small (1.5 mm diameter) BIPS are still in the stomach. This suggests there is delayed gastric emptying. Although gastric emptying times are very variable in normal cats, small BIPS will usually completely empty from the stomach within 14 hours (often much quicker) and large BIPS should at least start to empty by this time. <br><br> | *All the large (5 mm diameter) BIPS, and most of the small (1.5 mm diameter) BIPS are still in the stomach. This suggests there is delayed gastric emptying. Although gastric emptying times are very variable in normal cats, small BIPS will usually completely empty from the stomach within 14 hours (often much quicker) and large BIPS should at least start to empty by this time. <br><br> | ||
*In addition to the abnormal retention of BIPS, the stomach body and antrum are gas-filled and dilated. This can be seen with pyloric stenosis and other conditions interfering with gastric emptying, and can also be seen with aerophagia (e.g. secondary to dyspnoea). However, this cat was not dyspnoeic, and there is no abnormal air in the intestines. | *In addition to the abnormal retention of BIPS, the stomach body and antrum are gas-filled and dilated. This can be seen with pyloric stenosis and other conditions interfering with gastric emptying, and can also be seen with aerophagia (e.g. secondary to dyspnoea). However, this cat was not dyspnoeic, and there is no abnormal air in the intestines. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1=Congenital Pyloric Stenosis#Diagnosis |
|q2=What diagnosis does this suggest and what treatment options should be considered? | |q2=What diagnosis does this suggest and what treatment options should be considered? | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
*Pyloromyotomy has also been reported to be helpful in some of these cats. <br><br> | *Pyloromyotomy has also been reported to be helpful in some of these cats. <br><br> | ||
As there is usually no physical obstruction, this should probably be reserved for those cats where medical therapy fails. Pyloromyotomy allows more rapid gastric emptying, but as with the other treatments, the response varies considerably between individuals. | As there is usually no physical obstruction, this should probably be reserved for those cats where medical therapy fails. Pyloromyotomy allows more rapid gastric emptying, but as with the other treatments, the response varies considerably between individuals. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2=Congenital Pyloric Stenosis |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:47, 9 August 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Feline Medicine questions |
A 2-year-old Siamese cat presented with persistent vomiting of partially digested food several hours after feeding. The VD abdominal radiograph was taken 16 hours after the administration of BIPS.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What abnormalities can be seen? |
|
Link to Article | |
| What diagnosis does this suggest and what treatment options should be considered? | These changes are typical of ‘pyloric stenosis’. This is a well recognized congenital problem in Siamese cats, although there is no apparent true ‘stenosis’, but rather a functional motility problem resulting in poor gastric emptying in affected cats.
As there is usually no physical obstruction, this should probably be reserved for those cats where medical therapy fails. Pyloromyotomy allows more rapid gastric emptying, but as with the other treatments, the response varies considerably between individuals. |
Link to Article | |