Difference between revisions of "Feline Medicine Q&A 01"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
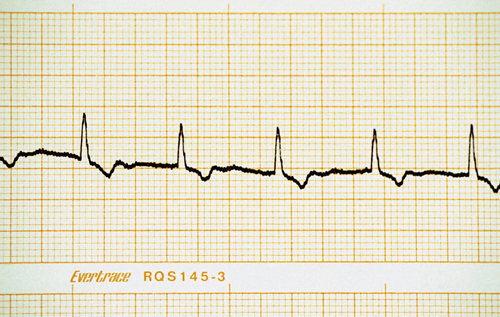
There are no visible P waves and the QRS complexes are wider than they should be (around 0.06 seconds; normal QRS duration is <0.04 seconds). <br><br> | There are no visible P waves and the QRS complexes are wider than they should be (around 0.06 seconds; normal QRS duration is <0.04 seconds). <br><br> | ||
It is also important to check the traces from other leads for presence of P waves. | It is also important to check the traces from other leads for presence of P waves. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3=Electrocardiography |
|q4=What is your assessment of this ECG? | |q4=What is your assessment of this ECG? | ||
|a4= | |a4= | ||
Latest revision as of 15:20, 7 September 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Feline Medicine questions |
A lead II ECG is shown. The paper speed is 25 mm/second and amplitude is set so that 1 cm is equivalent to 1 mV.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is the heart rate? | The easiest way to assess heart rate on an ECG is to count the number of complexes present in 6 seconds and then multiply this number by 10 to obtain a heart rate in beats per minute.
|
Link to Article | |
| Is the heart rate regular? | Yes, the heart rate is very regular. |
Link to Article | |
| Describe the complexes present. | There are no visible P waves and the QRS complexes are wider than they should be (around 0.06 seconds; normal QRS duration is <0.04 seconds). |
Link to Article | |
| What is your assessment of this ECG? | This is an example of atrial standstill with an escape rhythm. Failure of atrial activity (which can be confirmed on echocardiography) may be present because of
Escape rhythms are characterized by their slow rate and wide QRS complexes and they occur when the normal pacemaker tissue fails to discharge for a prolonged period. |
Link to Article | |