Difference between revisions of "Bones and Cartilage Flashcards - Pathology"
(New page: {{toplink |backcolour =CDE472 |linkpage =Musculoskeletal System - Pathology |linktext =Musculoskeletal System |maplink = Musculoskeletal System (Content Map) - Pathology |pagetype =Patholo...) |
m |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <FlashCard questions="4"> | |
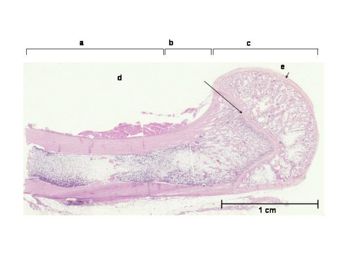
| − | | | + | |q1=What do the letters represent with respect to the image shown below? |
| − | | | + | |a1= |
| − | | | + | * A. Diaphysis |
| − | | | + | * B. Metaphysis |
| − | | | + | * C. Epiphysis |
| − | | | + | * D. Epiphyseal growth plate |
| − | | | + | * E. Articular cartilage |
| − | + | |l1=Bones - Anatomy & Physiology | |
| − | + | |q2=Which cells produce osteoid? | |
| + | |a2=Osteoblasts | ||
| + | |l2=Bones - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |q3=True or False - Cancellous bone forms Haversian systems? | ||
| + | |a3=False | ||
| + | |l3=Bones - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |q4=Which developmental disorder is considered normal in some breeds of dog, eg. skulls of Pekingese and Bulldogs or the limbs of Dachshunds and Bassett hounds? | ||
| + | |a4=Chondrodysplasia | ||
| + | |l4=Chondrodysplasia | ||
| + | </FlashCard> | ||
| + | [[Image:Question bone histo.jpg|350px|Courtesy RVC]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Pathology Flashcards]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Musculoskeletal System Flashcards]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Bones - Pathology|Z]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Musculoskeletal System - Pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:40, 22 June 2011
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What do the letters represent with respect to the image shown below? |
|
Link to Article | |
| Which cells produce osteoid? | Osteoblasts
|
Link to Article | |
| True or False - Cancellous bone forms Haversian systems? | False
|
Link to Article | |
| Which developmental disorder is considered normal in some breeds of dog, eg. skulls of Pekingese and Bulldogs or the limbs of Dachshunds and Bassett hounds? | Chondrodysplasia
|
Link to Article | |