Difference between revisions of "Yeast-like Fungi - Flashcards"
m |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
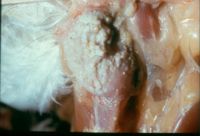
[[Image:Sour Crop.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Sour Crop - Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath]] | [[Image:Sour Crop.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Sour Crop - Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath]] | ||
| − | == | + | ===Candidosis=== |
| − | + | <FlashCard questions="4"> | |
| − | + | |q1=What are the three important species of ''Candida'' in animal infections? | |
| − | + | |a1= | |
| − | + | *C. albicans | |
| − | + | *C. tropicalis | |
| − | | | + | *C. pelliculosa |
| − | | | + | |l1=Candida_spp. |
| − | * | + | |q2=What are the clinical signs of a sour crop infection? |
| − | * | + | |a2= |
| − | + | *White-grey lesions in mouth, oesophagus and crop | |
| − | | | + | *Thickened crop wall |
| − | + | *Yellow-white necrotic material in crop | |
| − | | | + | |l2=Candida_spp. |
| − | | | + | |q3=What other conditions are ''Candida'' spp. implicated in? |
| − | * | + | |a3= |
| − | * | + | *Thrush in humans |
| − | *' | + | *Metritis, pyometra and vaginitis in mares |
| − | | | + | *Genital candidiosis in stallions |
| − | + | *Bovine mastitis | |
| − | + | *Porcine stomach ulcers | |
| − | || | + | |l3=Candida_spp. |
| − | + | |q4=How would you demonstrate a ''Candida'' infection? | |
| − | * | + | |a4= |
| − | * | + | *Skin scrapings in 20% KOH for microscopy |
| − | * | + | *Lactophenol Cotton Blue and stained by Gram or Methylene Blue stain |
| − | * | + | *Grows on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar |
| − | | | + | *Gram positive, oval, thin-walled budding cells with hyphal fragments |
| − | | | + | |l4=Candida_spp. |
| − | + | </FlashCard> | |
| − | || | + | |
| − | + | ===Cryptococcosis=== | |
| − | * | + | <FlashCard questions="5"> |
| − | * | + | |q1=What is the main pathogenic species of ''Cryptococcus''? |
| − | * | + | |a1=C. neoformans |
| − | | | + | |l1=Cryptococcosis |
| − | + | |q2=Where is ''Cryptococcus'' found in the environment? | |
| − | + | |a2= | |
| − | ==< | + | *Pigeon droppings |
| − | + | *Fruit | |
| − | + | *Milk | |
| − | + | *Soil | |
| − | + | |l2=Cryptococcosis | |
| − | | | + | |q3=Which body systems are affected? |
| − | |< | + | |a3= |
| − | + | *Respiratory | |
| − | + | *Visceral | |
| − | | | + | *Ocular |
| − | + | *Skeletal | |
| − | + | *Systemic | |
| − | | | + | *Cutaneous |
| − | * | + | |l3=Cryptococcosis |
| − | + | |q4=Where is the most common site of infection in cats? | |
| − | * | + | |a4=The tip of the nose |
| − | + | |l4=Cryptococcosis | |
| − | + | |q5=How would you demonstrate a cryptococcosis infection? | |
| − | + | |a5= | |
| − | + | *India Ink | |
| − | | | + | *PAS |
| − | * | + | *Gram stain (positive) |
| − | * | + | *Grows on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar |
| − | + | *Carbohydrate assimilation tests | |
| − | + | *Latex agglutination for antigen, complement fixation, ELISA and IFAT can be used | |
| − | + | |l5=Cryptococcosis | |
| − | * | + | </FlashCard> |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | ===Geotrichosis=== |
| − | + | <FlashCard questions="2"> | |
| − | | | + | |q1=Which organs are usually affected in geotrichosis infections? |
| − | + | |a1= | |
| − | | | + | *Udder |
| − | + | *Mucous membranes | |
| − | + | *Bronchi | |
| − | + | *Lungs | |
| − | + | |l1=Geotrichosis | |
| − | + | |q2=True or False: Geotrichosis infections are usually diagnosed post-mortem | |
| − | + | |a2=True | |
| − | + | |l2=Geotrichosis | |
| − | + | </FlashCard> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Malassezia pachydermidis=== | |
| − | + | <FlashCard questions="2"> | |
| − | + | |q1=Where in the body is ''Malassezia pachydermidis'' usually found? | |
| − | + | |a1= | |
| − | + | *Oily areas | |
| − | + | *Ear canal | |
| − | + | *Skin | |
| − | + | |l1=Yeast-like fungi#Malassezia pachydermatis | |
| − | + | |q2=What is the pathogenesis of ''Malassezia pachydermatis'' infections? | |
| − | + | |a2= | |
| − | + | *Malassezia spp are part of the normal skin flora in many animal species and overgrowth most commonly occurs secondary to a change in skin microclimate due to underlying disease processes like food allergy, atopic dermatitis, endocrinopathies or keratinization defects | |
| − | + | Regional lesions on the muzzle, ears, interdigital area and the perianal region | |
| − | + | *Infection can also be generalised | |
| − | + | *Erythematous, hyperpigmented, lichenified and scaly lesions with alopecia | |
| − | + | |l2=Yeast-like fungi#Malassezia pachydermidis | |
| − | + | </FlashCard> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Rhodotorula=== | |
| − | + | <FlashCard questions="1"> | |
| − | + | |q1=What infections of dogs and horses are ''Rhodotorula'' spp. involved in? | |
| − | + | |a1= | |
| − | + | *Canine ear infections | |
| − | + | *Equine uterine infections | |
| − | + | |l1=Rhodotorula | |
| − | + | </FlashCard> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Torulopsis glabrata=== | |
| − | + | <FlashCard questions="1"> | |
| − | + | |q1=What infections are ''Torulopsis'' spp. involved in? | |
| − | + | |a1= | |
| − | + | *Pyelonephritis, pneumonia, septicaemia and meningitis in humans | |
| − | + | *Mastitis and abortion in cattle | |
| − | + | *Systemic infection of monkeys and dogs | |
| − | + | |l1=Torulopsis glabrata | |
| − | + | </FlashCard> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Trichosporonosis=== | |
| − | + | <FlashCard questions="2"> | |
| − | + | |q1=What infection is ''T. capitum'' involved in? | |
| − | + | |a1=Bovine mastitis | |
| − | + | |l1=Trichosporonosis | |
| − | + | |q2=What infections are ''Trichosporonosis beigelii'' involved in? | |
| − | + | |a2= | |
| − | + | *Feline nasal granuloma | |
| − | + | *Skin infections in horses and monkeys | |
| − | + | *Bovine and ovine mastitis | |
| − | + | *Feline bladder infections | |
| − | + | |l2=Trichosporonosis | |
| − | + | </FlashCard> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Yeast-like Fungi]][[Category:Fungi Flashcards]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 08:40, 21 October 2013
Candidosis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What are the three important species of Candida in animal infections? |
|
Link to Article | |
| What are the clinical signs of a sour crop infection? |
|
Link to Article | |
| What other conditions are Candida spp. implicated in? |
|
Link to Article | |
| How would you demonstrate a Candida infection? |
|
Link to Article | |
Cryptococcosis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is the main pathogenic species of Cryptococcus? | C. neoformans
|
Link to Article | |
| Where is Cryptococcus found in the environment? |
|
Link to Article | |
| Which body systems are affected? |
|
Link to Article | |
| Where is the most common site of infection in cats? | The tip of the nose
|
Link to Article | |
| How would you demonstrate a cryptococcosis infection? |
|
Link to Article | |
Geotrichosis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| Which organs are usually affected in geotrichosis infections? |
|
Link to Article | |
| True or False: Geotrichosis infections are usually diagnosed post-mortem | True
|
Link to Article | |
Malassezia pachydermidis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| Where in the body is Malassezia pachydermidis usually found? |
|
Link to Article | |
| What is the pathogenesis of Malassezia pachydermatis infections? |
Regional lesions on the muzzle, ears, interdigital area and the perianal region
|
Link to Article | |
Rhodotorula
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What infections of dogs and horses are Rhodotorula spp. involved in? |
|
Link to Article | |
Torulopsis glabrata
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What infections are Torulopsis spp. involved in? |
|
Link to Article | |
Trichosporonosis
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What infection is T. capitum involved in? | Bovine mastitis
|
Link to Article | |
| What infections are Trichosporonosis beigelii involved in? |
|
Link to Article | |