Difference between revisions of "Energy Requirements - Donkey"
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
[[Image:Feeding donkeys.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>Donkeys at The Donkey Sanctuary being fed on a diet of hay and ''ad lib'' straw. (Image courtesy of [http://drupal.thedonkeysanctuary.org.uk The Donkey Sanctuary])</center></small>]] | [[Image:Feeding donkeys.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>Donkeys at The Donkey Sanctuary being fed on a diet of hay and ''ad lib'' straw. (Image courtesy of [http://drupal.thedonkeysanctuary.org.uk The Donkey Sanctuary])</center></small>]] | ||
| − | Energy is required both to live (i.e. for maintenance), and to grow, work, lactate and reproduce (i.e. for production) | + | Energy is required both to live (i.e. for maintenance), and to grow, work, lactate and reproduce (i.e. for production). Fibrous feeds that are rich in the structural carbohydrate cellulose, which is broken down to yield volatile fatty acids (VFA), provide ideal fodder for donkeys. Both glucose and VFA are used by the donkey to supply its body with energy. As well as carbohydrates, the donkey can use dietary fats and proteins as a source of energy. |
| − | If energy intake exceeds the energy requirements, the surplus is stored as fat. It is important to know the energy requirements of donkeys in order to avoid under- or over-feeding. Typically, donkeys in tropical countries are under-fed and have body condition scores of less than 3. In temperate regions donkeys are generally over-fed (condition score 3 to 4). The consequences of both acute and chronic over-feeding in donkeys are very serious and can result in death. Management of weight loss in overweight donkeys is particularly problematic, because rapid loss in condition is likely to trigger | + | If energy intake exceeds the energy requirements, the surplus is stored as fat. It is important to know the energy requirements of donkeys in order to avoid under- or over-feeding. Typically, donkeys in tropical countries are under-fed and have body condition scores of less than 3. In temperate regions donkeys are generally over-fed (condition score 3 to 4). The consequences of both acute and chronic over-feeding in donkeys are very serious and can result in death. Management of weight loss in overweight donkeys is particularly problematic, because rapid loss in condition is likely to trigger hyperlipaemia, a disease that can be fatal. Prevention of obesity is better than cure. |
==Recent research== | ==Recent research== | ||
| − | + | Research funded and carried out by the Donkey Sanctuary in 2005 established scientifically validated guidelines for donkeys kept in temperate and in tropical climates. | |
[[Image:Digestible energy table.jpg|thumb|500px|center|Table 1 (Courtesy of [http://drupal.thedonkeysanctuary.org.uk The Donkey Sanctuary)]]] | [[Image:Digestible energy table.jpg|thumb|500px|center|Table 1 (Courtesy of [http://drupal.thedonkeysanctuary.org.uk The Donkey Sanctuary)]]] | ||
Mature donkeys that are kept at maintenance levels (neither gaining nor losing weight) require between 80-95 KJ of digestible energy (DE) per kilogram of live weight per day (see Table 1 above, and Figures 1 and 2 for practical examples). In temperate climates, the upper value will apply during the winter months of December to February, when the energy requirement of donkeys | Mature donkeys that are kept at maintenance levels (neither gaining nor losing weight) require between 80-95 KJ of digestible energy (DE) per kilogram of live weight per day (see Table 1 above, and Figures 1 and 2 for practical examples). In temperate climates, the upper value will apply during the winter months of December to February, when the energy requirement of donkeys | ||
tends to increase slightly. The lower value will apply during the height of summer. | tends to increase slightly. The lower value will apply during the height of summer. | ||
[[Image:Digestion figure 1.jpg|thumb|800px|center|Figure 1 (Courtesy of [http://drupal.thedonkeysanctuary.org.uk The Donkey Sanctuary)]]][[Image:Digestion figure 2.jpg|thumb|800px|center|Figure 2 (Courtesy of [http://drupal.thedonkeysanctuary.org.uk The Donkey Sanctuary)]]] | [[Image:Digestion figure 1.jpg|thumb|800px|center|Figure 1 (Courtesy of [http://drupal.thedonkeysanctuary.org.uk The Donkey Sanctuary)]]][[Image:Digestion figure 2.jpg|thumb|800px|center|Figure 2 (Courtesy of [http://drupal.thedonkeysanctuary.org.uk The Donkey Sanctuary)]]] | ||
| − | In order to formulate an appropriate ration for donkeys, it is necessary to estimate how much dry matter a donkey will eat per | + | In order to formulate an appropriate ration for donkeys, it is necessary to estimate how much dry matter a donkey will eat per day. In the 2005 study at the Donkey Sanctuary, dry matter intakes of between 1.3-1.7% of live weight were measured in donkeys fed on straw and hay (straw was available ad libitum). Other published studies have reported dry matter intake values in donkeys of between 0.9% and 2.5% that were given a variety of feeds; the higher values in this range were recorded in donkeys fed on chopped lucerne. A reasonable assumption of the appetite limit of a typical donkey is therefore approximately 1.5% of its live weight in dry forage per day (i.e. a 100 kg donkey can consume 1.5 kg of dry food per day). |
| − | day. In the | ||
| − | It is important to satisfy the energy requirement of donkeys, their appetite and their psychological need to spend large parts of the day foraging. For most of the year a ration that contains 70-75% barley straw and 25-30% of moderate quality hay will supply all the energy requirements of donkeys. During the winter when energy requirements increase, the proportion of hay needs to be increased to 50 | + | It is important to satisfy the energy requirement of donkeys, their appetite and their psychological need to spend large parts of the day foraging. For most of the year a ration that contains 70-75% barley straw and 25-30% of moderate quality hay or carefully controlled access to grazing will supply all the energy requirements of donkeys. Ideal grazing for donkeys is unimproved or unfertilised pasture land. Rich grazing, the type often cultivated for dairy or other farm animals, is too rich for donkeys and will cause unwanted weight gain at best and laminitis at worst. During the winter when energy requirements increase, the proportion of hay needs to be increased to up to 50% and the proportion of straw decreased correspondingly. |
| − | In practice, donkeys select hay in preference to straw | + | In practice, donkeys select hay in preference to straw; therefore simply by limiting the amount of hay fed to the required levels and offering straw ad libitum, animals are unlikely to exceed their energy requirements. |
| − | + | Most donkeys would benefit from the addition of a forage balancer to their diet, in order to ensure that all their vitamin, mineral and trace elements requirements are met. The Donkey Sanctuary recommend the use of TopSpec Donkey Forage Balancer for the majority of healthy, mature donkeys and TopSpec Comprehensive Feed Balancer for donkeys with additional needs such as growing/breeding/elderly. | |
| − | A careful eye should be kept on the quality of fodders being fed; the digestible energy value can vary considerably between bales and consignments. | + | A careful eye should be kept on the quality of fodders being fed; the digestible energy value can vary considerably between bales and consignments. Fodders that are mouldy should be avoided as inhaling mould spores is detrimental to respiratory health. Fodders that are excessively stemmy are likely to be lower in energy and may be more suited to maintenance or overweight animals, and may not be suitable for older donkeys or those with dental disease. All these recommendations should be supported by regular body condition scoring of donkeys. Using these guidelines, it is apparent that the vast majority of healthy donkeys kept at maintenance levels only require to be fed good quality feeding straw, high fibre hay or haylage and have no requirement for supplementary feeds, even during winter. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Donkeys with special requirements== | ==Donkeys with special requirements== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 32: | ||
* Ideally, immature growing donkeys should be provided with sufficient energy to allow them to grow at a steady rate, avoiding periods of rapid growth acceleration or retardation | * Ideally, immature growing donkeys should be provided with sufficient energy to allow them to grow at a steady rate, avoiding periods of rapid growth acceleration or retardation | ||
* Providing too much energy to a growing donkey, especially when not balanced with adequate protein, calcium and phosphorus, may result in the development of orthopaedic problems | * Providing too much energy to a growing donkey, especially when not balanced with adequate protein, calcium and phosphorus, may result in the development of orthopaedic problems | ||
| − | * The available time for young donkeys to attain their full mature stature is approximately two to three years | + | * The available time for young donkeys to attain their full mature stature is approximately two to three years, larger breed donkeys (e.g. poitous and mammoths) and mules may take longer to mature and may require supplementary feeding for longer. |
| − | * Growing donkeys may face problems at weaning and during their first winter and some supplementation with | + | * Growing donkeys may face problems at weaning and during their first winter and some supplementation with appropriate feed may be required in order to avoid prolonged growth checks or permanent stunting |
* Pasture-fed immature donkeys are unlikely to require energy supplements, but should be given access to mineral licks | * Pasture-fed immature donkeys are unlikely to require energy supplements, but should be given access to mineral licks | ||
| + | * Immature donkeys are unlikely to require anything more than fibre in the form of straw, hay or haylage, limited grazing and an appropriate multi-supplement to provide adequate provision of vitamins, minerals and trace elements. | ||
| + | |||
===Pregnant donkeys=== | ===Pregnant donkeys=== | ||
| Line 45: | Line 42: | ||
* In pregnant donkeys, the demands of the growing foetus only exceed the normal requirements in the final three months of pregnancy | * In pregnant donkeys, the demands of the growing foetus only exceed the normal requirements in the final three months of pregnancy | ||
* Digestible energy allowances should be increased by 11% above maintenance in the ninth month, 13% in the penultimate month and 20% in the final month of pregnancy | * Digestible energy allowances should be increased by 11% above maintenance in the ninth month, 13% in the penultimate month and 20% in the final month of pregnancy | ||
| + | * In practical terms providing adlib haylage and an appropriate balancer in the final three months has been seen to meet these needs | ||
===Lactating donkeys=== | ===Lactating donkeys=== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 49: | ||
* Preparation for this loss should be made in the final months of pregnancy by allowing pregnant jennies of [[Body Condition Score - Donkey|body condition score]] 3 to gain ½-1 point of body condition by additional feeding (i.e. at foaling they should have a body condition of 3½ to 4) | * Preparation for this loss should be made in the final months of pregnancy by allowing pregnant jennies of [[Body Condition Score - Donkey|body condition score]] 3 to gain ½-1 point of body condition by additional feeding (i.e. at foaling they should have a body condition of 3½ to 4) | ||
* The jenny should receive sufficient additional feeding during her first two to three months of lactation to minimise body weight loss, aiming to achieve a body condition score of 3 for the remainder of the pre-weaning period | * The jenny should receive sufficient additional feeding during her first two to three months of lactation to minimise body weight loss, aiming to achieve a body condition score of 3 for the remainder of the pre-weaning period | ||
| + | * Appropriate supplementary feeds include ‘laminitic safe’ high fibre products, particularly those containing lucerne, plus an appropriate balancer providing protein, vitamins, minerals and trace elements. | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
|linkpage =Nutrition - Donkey | |linkpage =Nutrition - Donkey | ||
|linktext =Nutrition - Donkey | |linktext =Nutrition - Donkey | ||
| − | |||
|pagetype=Donkey | |pagetype=Donkey | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | {{infotable | ||
| + | |Maintitle = [[Sponsors#The Donkey Sanctuary|This section was sponsored and content provided by '''THE DONKEY SANCTUARY''']] | ||
| + | |Maintitlebackcolour = B4CDCD | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | [[Category:Donkey]] | ||
| + | ''Italic text''[[Category:Nutrition_-_Donkey]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:25, 26 March 2014
Introduction

Energy is required both to live (i.e. for maintenance), and to grow, work, lactate and reproduce (i.e. for production). Fibrous feeds that are rich in the structural carbohydrate cellulose, which is broken down to yield volatile fatty acids (VFA), provide ideal fodder for donkeys. Both glucose and VFA are used by the donkey to supply its body with energy. As well as carbohydrates, the donkey can use dietary fats and proteins as a source of energy.
If energy intake exceeds the energy requirements, the surplus is stored as fat. It is important to know the energy requirements of donkeys in order to avoid under- or over-feeding. Typically, donkeys in tropical countries are under-fed and have body condition scores of less than 3. In temperate regions donkeys are generally over-fed (condition score 3 to 4). The consequences of both acute and chronic over-feeding in donkeys are very serious and can result in death. Management of weight loss in overweight donkeys is particularly problematic, because rapid loss in condition is likely to trigger hyperlipaemia, a disease that can be fatal. Prevention of obesity is better than cure.
Recent research
Research funded and carried out by the Donkey Sanctuary in 2005 established scientifically validated guidelines for donkeys kept in temperate and in tropical climates.
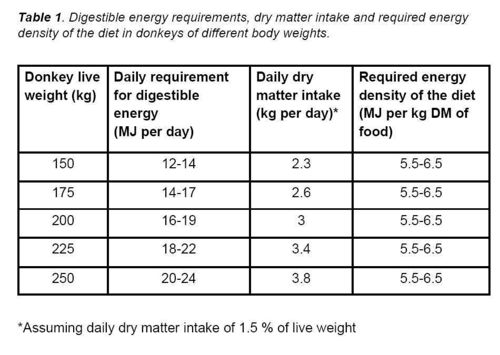
Mature donkeys that are kept at maintenance levels (neither gaining nor losing weight) require between 80-95 KJ of digestible energy (DE) per kilogram of live weight per day (see Table 1 above, and Figures 1 and 2 for practical examples). In temperate climates, the upper value will apply during the winter months of December to February, when the energy requirement of donkeys tends to increase slightly. The lower value will apply during the height of summer.
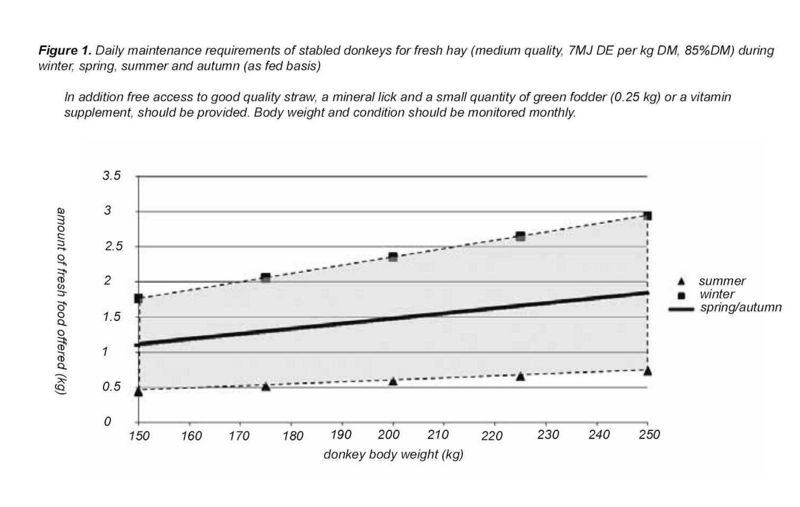
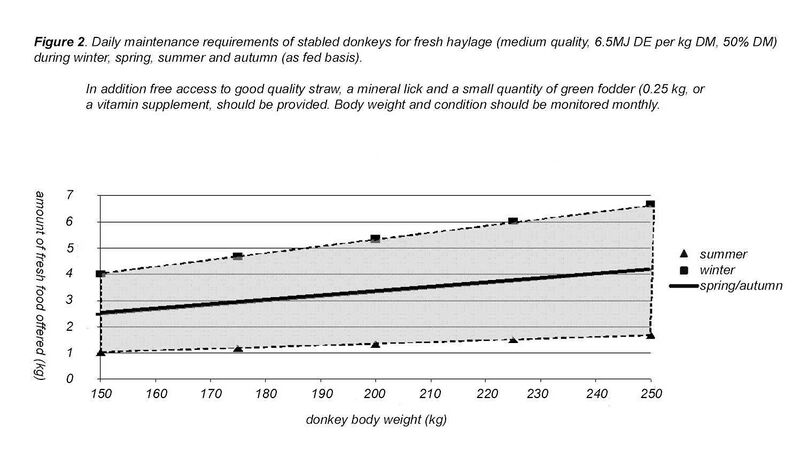
In order to formulate an appropriate ration for donkeys, it is necessary to estimate how much dry matter a donkey will eat per day. In the 2005 study at the Donkey Sanctuary, dry matter intakes of between 1.3-1.7% of live weight were measured in donkeys fed on straw and hay (straw was available ad libitum). Other published studies have reported dry matter intake values in donkeys of between 0.9% and 2.5% that were given a variety of feeds; the higher values in this range were recorded in donkeys fed on chopped lucerne. A reasonable assumption of the appetite limit of a typical donkey is therefore approximately 1.5% of its live weight in dry forage per day (i.e. a 100 kg donkey can consume 1.5 kg of dry food per day).
It is important to satisfy the energy requirement of donkeys, their appetite and their psychological need to spend large parts of the day foraging. For most of the year a ration that contains 70-75% barley straw and 25-30% of moderate quality hay or carefully controlled access to grazing will supply all the energy requirements of donkeys. Ideal grazing for donkeys is unimproved or unfertilised pasture land. Rich grazing, the type often cultivated for dairy or other farm animals, is too rich for donkeys and will cause unwanted weight gain at best and laminitis at worst. During the winter when energy requirements increase, the proportion of hay needs to be increased to up to 50% and the proportion of straw decreased correspondingly.
In practice, donkeys select hay in preference to straw; therefore simply by limiting the amount of hay fed to the required levels and offering straw ad libitum, animals are unlikely to exceed their energy requirements.
Most donkeys would benefit from the addition of a forage balancer to their diet, in order to ensure that all their vitamin, mineral and trace elements requirements are met. The Donkey Sanctuary recommend the use of TopSpec Donkey Forage Balancer for the majority of healthy, mature donkeys and TopSpec Comprehensive Feed Balancer for donkeys with additional needs such as growing/breeding/elderly.
A careful eye should be kept on the quality of fodders being fed; the digestible energy value can vary considerably between bales and consignments. Fodders that are mouldy should be avoided as inhaling mould spores is detrimental to respiratory health. Fodders that are excessively stemmy are likely to be lower in energy and may be more suited to maintenance or overweight animals, and may not be suitable for older donkeys or those with dental disease. All these recommendations should be supported by regular body condition scoring of donkeys. Using these guidelines, it is apparent that the vast majority of healthy donkeys kept at maintenance levels only require to be fed good quality feeding straw, high fibre hay or haylage and have no requirement for supplementary feeds, even during winter.
Donkeys with special requirements
When donkeys are growing, pregnant or lactating, extra energy needs to be fed. Research in this area has still to be conducted, but general guidelines are provided below.
Growing donkeys
- Ideally, immature growing donkeys should be provided with sufficient energy to allow them to grow at a steady rate, avoiding periods of rapid growth acceleration or retardation
- Providing too much energy to a growing donkey, especially when not balanced with adequate protein, calcium and phosphorus, may result in the development of orthopaedic problems
- The available time for young donkeys to attain their full mature stature is approximately two to three years, larger breed donkeys (e.g. poitous and mammoths) and mules may take longer to mature and may require supplementary feeding for longer.
- Growing donkeys may face problems at weaning and during their first winter and some supplementation with appropriate feed may be required in order to avoid prolonged growth checks or permanent stunting
- Pasture-fed immature donkeys are unlikely to require energy supplements, but should be given access to mineral licks
- Immature donkeys are unlikely to require anything more than fibre in the form of straw, hay or haylage, limited grazing and an appropriate multi-supplement to provide adequate provision of vitamins, minerals and trace elements.
Pregnant donkeys
- In pregnant donkeys, the demands of the growing foetus only exceed the normal requirements in the final three months of pregnancy
- Digestible energy allowances should be increased by 11% above maintenance in the ninth month, 13% in the penultimate month and 20% in the final month of pregnancy
- In practical terms providing adlib haylage and an appropriate balancer in the final three months has been seen to meet these needs
Lactating donkeys
- Lactating jennies are likely to lose weight (½ to 1 body condition score point) during the first two months when their foals are suckling, even when they are receiving moderate feed supplementation
- Preparation for this loss should be made in the final months of pregnancy by allowing pregnant jennies of body condition score 3 to gain ½-1 point of body condition by additional feeding (i.e. at foaling they should have a body condition of 3½ to 4)
- The jenny should receive sufficient additional feeding during her first two to three months of lactation to minimise body weight loss, aiming to achieve a body condition score of 3 for the remainder of the pre-weaning period
- Appropriate supplementary feeds include ‘laminitic safe’ high fibre products, particularly those containing lucerne, plus an appropriate balancer providing protein, vitamins, minerals and trace elements.
References
- Smith, D. and Wood, S. (2008) Donkey nutrition In Svendsen, E.D., Duncan, J. and Hadrill, D. (2008) The Professional Handbook of the Donkey, 4th edition, Whittet Books, Chapter 1
|
|
This section was sponsored and content provided by THE DONKEY SANCTUARY |
|---|
Italic text