Difference between revisions of "Dental Formula - Dog"
(Created page with "===The Dog=== '''Dental Formula''' 2 (I3/3 C1/1 P3/3) Deciduous 2 (I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3) Permanent *Toothless at birth *Deciduous teeth complete and functional within 2 mon...") |
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ===The | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| + | ==Overview== | ||
| + | [[Image:Aspinall Slide12.JPG|thumb|right|300px|<small>Image from [http://www.elsevierhealth.co.uk/veterinary-nursing/spe-60136/ Aspinall, The Complete Textbook of Veterinary Nursing], Elsevier Health Sciences, ''All rights reserved''</small>]] | ||
| − | ''' | + | Dogs are toothless at birth. The '''deciduous''' teeth are complete and functional within 2 months of birth in most breeds. '''Permanent''' teeth are complete and functional by the end of the 7th month. |
| − | |||
| − | 2 ( | + | Formula for '''deciduous''' teeth: 2 (i3/3 c1/1 p3/3) |
| − | + | Formula for '''permanent''' teeth: 2 (I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3) | |
| − | + | ===Incisors=== | |
| + | Dogs have six incisors in the maxilla and six in the mandible. Incisors have a single [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Root|root]]. | ||
| − | + | ===Canine Teeth=== | |
| + | The canine teeth are large, curved and laterally compressed. Their [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Root|root]] is longer than their [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Crown|crown]]. They have a single [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Root|root]]. | ||
| − | + | ===Premolars=== | |
| + | Premolars are irregular and closely-spaced. They are more complex and larger caudally. The first maxillary premolar has a single root, the second and third maxillary premolar have two roots and the fourth maxillary premolar (carnasial tooth) has three roots. | ||
| − | + | ===Molars=== | |
| + | The molars are broader than the premolars. The large flat surface is used for grinding. The maxillary molars have three roots each. | ||
| − | + | ==Breed Differences== | |
| − | + | Eruption times differ between breeds so it is difficult to age dogs by their teeth. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{Template:Learning | |
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/Content/Freeform/fre00587.asp, Canine dentition and chart] | ||
| + | |OVAM = [http://www.onlineveterinaryanatomy.net/content/canine-dentition Image - Canine Dentition] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{Lisa Milella reviewed | |
| − | + | |date = 9 September 2014}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{Waltham}} | ||
| + | ==Webinars== | ||
| + | <rss max="10" highlight="canine">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/dentistry/webinars/feed</rss> | ||
[[Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Dog]] | + | [[Category:Dog - Alimentary System]] |
| + | [[Category:Oral Examination]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Waltham reviewed]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Lisa Milella reviewed]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:21, 2 November 2022
Overview
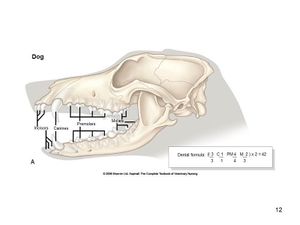
Dogs are toothless at birth. The deciduous teeth are complete and functional within 2 months of birth in most breeds. Permanent teeth are complete and functional by the end of the 7th month.
Formula for deciduous teeth: 2 (i3/3 c1/1 p3/3)
Formula for permanent teeth: 2 (I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3)
Incisors
Dogs have six incisors in the maxilla and six in the mandible. Incisors have a single root.
Canine Teeth
The canine teeth are large, curved and laterally compressed. Their root is longer than their crown. They have a single root.
Premolars
Premolars are irregular and closely-spaced. They are more complex and larger caudally. The first maxillary premolar has a single root, the second and third maxillary premolar have two roots and the fourth maxillary premolar (carnasial tooth) has three roots.
Molars
The molars are broader than the premolars. The large flat surface is used for grinding. The maxillary molars have three roots each.
Breed Differences
Eruption times differ between breeds so it is difficult to age dogs by their teeth.
| Dental Formula - Dog Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
Anatomy Museum Resources |
Image - Canine Dentition |
| This article was expert reviewed by Lisa Milella BVSc DipEVDC MRCVS. Date reviewed: 9 September 2014 |
| Endorsed by WALTHAM®, a leading authority in companion animal nutrition and wellbeing for over 50 years and the science institute for Mars Petcare. |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/dentistry/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS