Difference between revisions of "Laryngeal Oedema"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
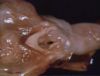
(Created page with "right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Laryngeal oedema in a cat (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small> *In H...") |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
**Anaphylaxis or localised hypersensitivity responses | **Anaphylaxis or localised hypersensitivity responses | ||
* = in 'gut oedema' in pigs | * = in 'gut oedema' in pigs | ||
| − | *Unknown aetiology in feedlot cattle - also [[ | + | *Unknown aetiology in feedlot cattle - also [[Tracheal Oedema|tracheal oedema]] |
*Seen in hot weather and with exercise | *Seen in hot weather and with exercise | ||
*May be due to trauma, tracheal compression, inhaled dust and toxins, acute inflammation (acute [[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Interstitial pneumonia|interstitial pneumonia]]) | *May be due to trauma, tracheal compression, inhaled dust and toxins, acute inflammation (acute [[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Interstitial pneumonia|interstitial pneumonia]]) | ||
Revision as of 14:39, 19 February 2011
- In Horses:
- Can quickly become a medical emergency because of obstruction to airflow
- Causes of laryngeal oedema include:
- Mucosal irritants
- Trauma
- Acute respiratory infections
- Anaphylaxis or localised hypersensitivity responses
- = in 'gut oedema' in pigs
- Unknown aetiology in feedlot cattle - also tracheal oedema
- Seen in hot weather and with exercise
- May be due to trauma, tracheal compression, inhaled dust and toxins, acute inflammation (acute interstitial pneumonia)
- In horses wit purpura haemorrhagica
- In cats with systemic anaphylaxis
- Gross: thickened laryngeal mucosa, gelatinous appearance