Difference between revisions of "Oral Examination - Introduction"
m (Text replace - "[[Category:Waltham reviewing" to "[[Category:Waltham reviewed") |
|||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
A complete, general physical examination should always be carried out and never overlooked in the attempt to move straight to the primary complaint. Most patients will need a [Anaesthesia|general anaesthetic]] for a dental diagnosis, so in order for treatment to be carried out it is important to check the [[Cardiorespiratory System Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|cardiovascular and respiratory]] systems and identify any potential risks. Some oral diseases may also be linked to more generalised disease, for example, [[Atopic Dermatitis|dogs with skin allergies]] often have severely worn incisor teeth, with or without hair impaction, resulting in [[periodontitis]]. Certain autoimmune conditions manifest at all mucocutaneous junctions, so always check the whole body for lesions, not just the mouth. It is also important to remember that oral signs may be secondary to systemic disease, not a disease entity on their own, for example, [[Uremia|uremic ulcerations]], [[Haemorrhage#Petechiae|petechial haemorrhages]] secondary to [[:Category:Haemostasis and Bleeding Disorders|bleeding disorders]]/[[:Category:Liver - Pathology|liver disease]] etc. | A complete, general physical examination should always be carried out and never overlooked in the attempt to move straight to the primary complaint. Most patients will need a [Anaesthesia|general anaesthetic]] for a dental diagnosis, so in order for treatment to be carried out it is important to check the [[Cardiorespiratory System Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|cardiovascular and respiratory]] systems and identify any potential risks. Some oral diseases may also be linked to more generalised disease, for example, [[Atopic Dermatitis|dogs with skin allergies]] often have severely worn incisor teeth, with or without hair impaction, resulting in [[periodontitis]]. Certain autoimmune conditions manifest at all mucocutaneous junctions, so always check the whole body for lesions, not just the mouth. It is also important to remember that oral signs may be secondary to systemic disease, not a disease entity on their own, for example, [[Uremia|uremic ulcerations]], [[Haemorrhage#Petechiae|petechial haemorrhages]] secondary to [[:Category:Haemostasis and Bleeding Disorders|bleeding disorders]]/[[:Category:Liver - Pathology|liver disease]] etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Lisa Milella written | ||
| + | |date = 13 August 2014}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Waltham}} | ||
[[Category:Oral Examination]] | [[Category:Oral Examination]] | ||
[[Category:Waltham reviewed]] | [[Category:Waltham reviewed]] | ||
Revision as of 16:07, 17 October 2014
Overview
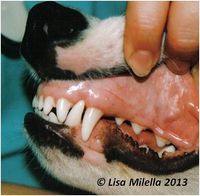
Most pet owners are not aware that their pet has an oral problem so an examination of the oral cavity should form part of every physical examination. Oral examination in a conscious animal can only give limited information and a definitive oral examination can only be performed under general anaesthesia. All detected abnormalities should be recorded.
It is important to examine the whole animal, even when the primary complaint is the mouth. Some dental diseases may be the result of a systemic problem and some may result in systemic complications. In all cases, dental procedures require a general anaesthetic so it is important to establish the cardiovascular and respiratory status and (canine and feline) physiological values of the patient to avoid risks or complications.
Few owners are aware that their pet may have a dental problem. Pain originating from dental problems is very rarely recognized by owners or professionals. Seldom will an animal become anorexic due to a dental problem. The exception to this is in the case of severe soft tissue injury, for example chronic gingivostomatitis. In general dental pain is a chronic pain, and it is only after treatment that an owner reports how much better their pet is doing. Pain is often mistaken for a pet “just getting old”.
Very few clients examine their pets’ teeth unless they are carrying out daily homecare, so actual dental problems often go unnoticed.
It is important to recognize symptoms that may have a link to dental diseases such as a nasal discharge or external facial swellings. In some cases, dental patients may even present with what appear to be neurological symptoms.
The main signs of oral disease include :
- Halitosis
- Broken or discoloured teeth
- Changes in eating behaviour
- Rubbing or pawing at the face
- Ptyalism
- Bleeding from the mouth
- Inability or unwillingness to open or close the mouth
- Change in temperament
- Morbidity
- Weight loss
As well as the presentation, primary complaint and signalment, it is important to obtain a full clinical history of previous illnesses and treatments. Some diseases may have an impact on oral health, for example, FIV, respiratory viruses, immune mediated conditions etc. Although questions related to feeding and diet may be helpful when assessing dental diseases, the information obtained can sometimes be misleading. For example many pets appear to continue eating normally as they eat the same food and quantity but the owner may have failed to notice that they are eating more slowly or that they are only chewing on one side. Any change in feeding behaviour or any vices such as stone chewing provide useful information.
There are subtle changes which often go unnoticed and the client should be questioned as to whether any of these have occurred –
- Ask whether the pet has changed their drinking behaviour (cold water may cause a reaction in dogs with sensitive teeth).
- Ask about any hesitancy when food is being chewed or swallowed, or any exaggerated swallowing actions.
- Ask if there are any changes to the way the pet prehends its food or toys and whether one side of the mouth has been favoured above the other.
A history of all previous dental treatments is also important to determine whether the condition is acute, chronic or recurrent. Where possible, try and ascertain how long the pet has had the problem and whether the main complaint has changed during this time. It is important to enquire about the actual oral symptoms, and remembering that the client is probably not aware of their pets' problem, detailed questioning regarding feeding, behaviour, play time and subtle changes in temperament may be required.
It is also important to find out what level of dental homecare the owner provides prior to any treatment being carried out. This is very important for diseases requiring long term management and where no “cure” is available. It is also important to know what homecare is being provided prior to the full examination to ascertain whether this is adequate.
General Physical Examination
A complete, general physical examination should always be carried out and never overlooked in the attempt to move straight to the primary complaint. Most patients will need a [Anaesthesia|general anaesthetic]] for a dental diagnosis, so in order for treatment to be carried out it is important to check the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and identify any potential risks. Some oral diseases may also be linked to more generalised disease, for example, dogs with skin allergies often have severely worn incisor teeth, with or without hair impaction, resulting in periodontitis. Certain autoimmune conditions manifest at all mucocutaneous junctions, so always check the whole body for lesions, not just the mouth. It is also important to remember that oral signs may be secondary to systemic disease, not a disease entity on their own, for example, uremic ulcerations, petechial haemorrhages secondary to bleeding disorders/liver disease etc.
| This article was written by Lisa Milella BVSc DipEVDC MRCVS. Date reviewed: 13 August 2014 |
| Endorsed by WALTHAM®, a leading authority in companion animal nutrition and wellbeing for over 50 years and the science institute for Mars Petcare. |