Difference between revisions of "Category:Helminths"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<categorytree mode=pages style="float:right; clear:right; margin-left:1ex; border:1px solid gray; padding:0.7ex; background-color:white;">Parasites</categorytree> | <categorytree mode=pages style="float:right; clear:right; margin-left:1ex; border:1px solid gray; padding:0.7ex; background-color:white;">Parasites</categorytree> | ||
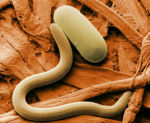
[[Image:Soybean cyst nematode EM.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soybean Cyst Nematode and Egg, Scanning Electron Micrograph - Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Soybean cyst nematode EM.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soybean Cyst Nematode and Egg, Scanning Electron Micrograph - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The term helminth is commonly used to describe parasitic worms, all with eukaryotic cell structures. The two main groups are the '''Nematodes''' (roundworms) and the '''Platyhelminthes''' (flatworms).[[Image:729px-Soybean cyst nematode and egg SEM.jpg|thumb|right|100px|Soybean cyst nematode and egg]] | ||
| + | *'''Nematodes''': typically long and slender, the nematodes are dioecious (male and female individuals) and are generally found attached to the intestinal wall | ||
| + | **Hookworms- widely endemic in the tropics, hookworms hatch on soil and enter the host through the feet. Pathogenesis involves intestinal irritation and haemorrhage. | ||
| + | **Giant roundworms- found worldwide, hosts are infected by ingesting eggs from faeces of infected individuals. Symptoms include intestinal irritation and malnutrition | ||
| + | **Pinworms- found in temperate areas, eggs hatch in the intestine after ingestion | ||
| + | **Pork worm- found worldwide, pork worms can infect most carnivorous animals, causing trichinosis. | ||
| + | **Filarial worms- various species found in tropical and subtropical areas depending on distribution of insect vectors, causes allergic reactions and potentially blindness | ||
| + | *'''Platyhelminthes'''[[Image:Tenia solium scolex.jpg|thumb|right|100px|Scolex, with hooks, of ''T. solium'' tapeworm]] | ||
| + | **Trematodes- commonly known as the 'flukes,' trematodes are non-segmented and have alternate sexual and non-sexual generations in different hosts. They are mostly hermaphroditic except the blood flukes, which are dioecious. | ||
| + | **Cestodes- commonly known as the 'tapeworms,' these consist of an enlarged head section ('scolex'), with suckers or hooks for attachment in the intestine and successive flat segments forming a chain of 'proglottids' | ||
| + | |||
==Helminths of Veterinary Importance== | ==Helminths of Veterinary Importance== | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 17 May 2010
The term helminth is commonly used to describe parasitic worms, all with eukaryotic cell structures. The two main groups are the Nematodes (roundworms) and the Platyhelminthes (flatworms).
- Nematodes: typically long and slender, the nematodes are dioecious (male and female individuals) and are generally found attached to the intestinal wall
- Hookworms- widely endemic in the tropics, hookworms hatch on soil and enter the host through the feet. Pathogenesis involves intestinal irritation and haemorrhage.
- Giant roundworms- found worldwide, hosts are infected by ingesting eggs from faeces of infected individuals. Symptoms include intestinal irritation and malnutrition
- Pinworms- found in temperate areas, eggs hatch in the intestine after ingestion
- Pork worm- found worldwide, pork worms can infect most carnivorous animals, causing trichinosis.
- Filarial worms- various species found in tropical and subtropical areas depending on distribution of insect vectors, causes allergic reactions and potentially blindness
- Platyhelminthes
- Trematodes- commonly known as the 'flukes,' trematodes are non-segmented and have alternate sexual and non-sexual generations in different hosts. They are mostly hermaphroditic except the blood flukes, which are dioecious.
- Cestodes- commonly known as the 'tapeworms,' these consist of an enlarged head section ('scolex'), with suckers or hooks for attachment in the intestine and successive flat segments forming a chain of 'proglottids'
Helminths of Veterinary Importance
<ncl style=compact maxdepth=3 headings=bullet headstart=2 showcats=1 showarts=1>Category:Helminths</ncl>
Useful Resources
Brilliant microscopic pictures of protozoa and helminths
Subcategories
This category has the following 3 subcategories, out of 3 total.
Pages in category "Helminths"
The following 2 pages are in this category, out of 2 total.