Difference between revisions of "Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|WNV encephalitis | |WNV encephalitis | ||
| − | |Systemically ill, pyrexia | + | |Systemically ill, pyrexia. Difficult if horse afebrile and has no excessive muscle fasciculations<ref name="Long">Long, M.T (2010) ''Flavivirus Encephalitis'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> |
| − | |CSF | + | |Leukogram, CSF analysis, IgM capture ELISA |
|- | |- | ||
|EEE | |EEE | ||
| − | |Systemically ill, pyrexia | + | |Systemically ill, pyrexia, abnormal motor function<ref name="Long">Long, M.T (2010) ''Flavivirus Encephalitis'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref, rapidly progressive (seino, p134) |
| − | |CSF | + | |Leukogram, CSF analysis |
|- | |- | ||
|WEE | |WEE | ||
| − | |Systemically ill, pyrexia | + | |Systemically ill, pyrexia, abnormal motor function<ref name="Long">Long, M.T (2010) ''Flavivirus Encephalitis'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> |
| − | | | + | |Leukogram |
|- | |- | ||
|VEE | |VEE | ||
| − | |Systemically ill, pyrexia | + | |Systemically ill, pyrexia. |
| − | |IgM ELISA ( | + | |Leukogram, IgM ELISA<ref>Bertone, J.J (2010) ''Viral Encephalitis'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
|Equine herpesvirus-1 myeloencephalopathy | |Equine herpesvirus-1 myeloencephalopathy | ||
| − | |Sudden onset and early stabilization of neuro signs, multiple horses affected, recent fever, abortion ( | + | |Sudden onset and early stabilization of neuro signs, multiple horses affected, recent fever, abortion<ref>Wilson, W.D, Pusterla, N (2010) ''Equine Herpesvirus-1 Myeloencephalopathy'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref>dysuria not often seen in EPM. |
|CSF abnormal, PCR<ref name="Furr">Furr, M (2010) ''Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> | |CSF abnormal, PCR<ref name="Furr">Furr, M (2010) ''Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Rabies | |Rabies | ||
| − | |Rapid progression ( | + | |Rapid progression<ref name="Sommardahl">Sommardahl, C.S (2010) ''Rabies'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref>, behavioural alterations, depression, seizure, coma.<ref name="Long">Long, M.T (2010) ''Flavivirus Encephalitis'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> |
| − | |Post-mortem | + | |Post-mortem required for definitive diagnosis.<ref name="Sommardahl">Sommardahl, C.S (2010) ''Rabies'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
|Polyneuritis equi | |Polyneuritis equi | ||
| − | |Cranial nerve deficits peripheral with no change in attitude ( | + | |Cranial nerve deficits peripheral with no change in attitude<ref>Scaratt, W.K, Jortner, B.S (1985) Neuritis of the cauda equina in a yearling filly. ''Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet'', 7:S197-S202. In: Saville, W.J (2010) ''Polyneuritis equi'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> |
| − | |Western blot analysis of CSF( | + | |Western blot analysis of CSF<ref>Granstrom, D.E, Dubey, J.P, Giles, R.C (1994) Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis: biology and epidemiology. In Nakajima, H, Plowright, W, editors: ''Refereed Proceedings'', Newmarket, England, R & W Publications. In: Saville, W.J (2010) ''Polyneuritis equi'' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) '''Equine Internal Medicine''' (Third Edition), ''Saunders'', Chapter 12.</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
|Equine degenerative myeloencephalopathy | |Equine degenerative myeloencephalopathy | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Spinal trauma<ref name="Pasq">Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) '''Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine''' (Third edition), ''SUDZ Publishing'', 245-250.</ref> | |Spinal trauma<ref name="Pasq">Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) '''Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine''' (Third edition), ''SUDZ Publishing'', 245-250.</ref> | ||
| − | |Hx (usually acute | + | |Hx (usually acute onset neurologica signs), usually solitary lesion loclaised by neurological exam (71 p589) |
| − | | | + | |Radiography, myelography, CT, MRI, nuclear scintigraphy, CSF analysis, nerve conduction velocities, EMG, transcranial magnetic stimulation (p590) |
|- | |- | ||
|Occipito-atlanto-axial malformation (OAAM) | |Occipito-atlanto-axial malformation (OAAM) | ||
Revision as of 10:49, 17 July 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
| Also known as: | EPM Equine protozoal myelitis |
Description
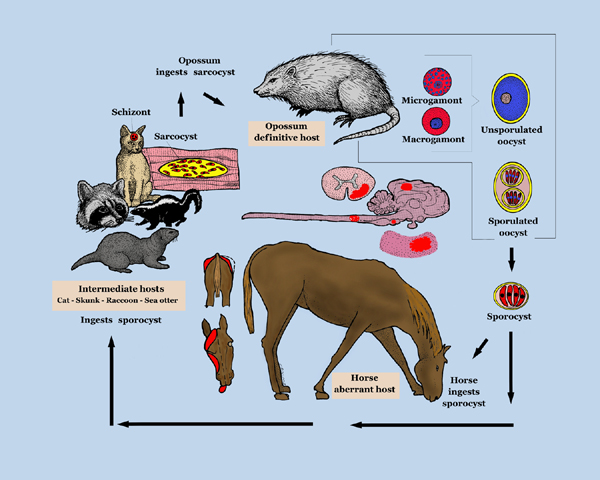
A progressive, infectious,[1]neurological disease of horses, endemic in the USA[2] and only encountered elsewhere in imported equids.[3] EPM is one of the most frequently diagnosed neurological conditions of the Western Hemisphere[4] and the principal differential for multifocal, asymmetric progressive central nervous system (CNS) disease.[1] As it can resemble any neurological disorder, EPM must be considered in any horse with neurological signs if it resides in the Americas or if it has been imported from that area[2][5] The disease is not contagious.[1]
Aetiology
EPM results from infection of the CNS by the apicomplexan parasite Sarcocystis neurona or, less frequently, its close relative Neospora hughesi.[6][7] These protozoans develop within neurons[4] causing immediate or inflammatory-mediated neuronal damage. The organisms migrate randomly through the brain and spinal cord causing asymmetrical lesions of grey and white matter and thus multifocal lower and upper motor neuron deficits.[1]
Signalment
Mostly Standardbreds and Thoroughbreds aged 1-6years.[1] Foal infection may be possible.[2]
Differential Diagnoses
The protozoan can migrate to any region of the CNS[2], thus the differential list comprises almost all diseases of this system.[4]
| Differential | Differentiating signs | Tests to rule out |
| Cervical vertebral malformation (CVM, cervical compressive myelopathy, cervical vertebral instability, cervical spondylomyelopathy, Wobbler's syndrome) | Symmetrical gait deficits, worse in pelvic limbs[8] with spasticity and dysmetria, good retention of strength, no muscle wasting[4] NB:can be concurrent with EPM.[9] | Standing plain lateral radiography of C1 to T1.[9] |
| WNV encephalitis | Systemically ill, pyrexia. Difficult if horse afebrile and has no excessive muscle fasciculations[10] | Leukogram, CSF analysis, IgM capture ELISA |
| EEE | Systemically ill, pyrexia, abnormal motor functionCite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
|
Leukogram |
| VEE | Systemically ill, pyrexia. | Leukogram, IgM ELISA[11] |
| Equine herpesvirus-1 myeloencephalopathy | Sudden onset and early stabilization of neuro signs, multiple horses affected, recent fever, abortion[12]dysuria not often seen in EPM. | CSF abnormal, PCR[4] |
| Rabies | Rapid progression[13], behavioural alterations, depression, seizure, coma.[10] | Post-mortem required for definitive diagnosis.[13] |
| Polyneuritis equi | Cranial nerve deficits peripheral with no change in attitude[14] | Western blot analysis of CSF[15] |
| Equine degenerative myeloencephalopathy | Symmetrical signs[16] | May get increased CSF CK[17] and reduced serum Vitamin E concentrations but unreliable ante mortem dx |
| Verminous encephalomyelitis | Acute onset | CSF analysis[18] |
| Bacterial meningoencephalitis | Stiff neck[1] | |
| CNS abscessation[4] | ||
| Spinal trauma[1] | Hx (usually acute onset neurologica signs), usually solitary lesion loclaised by neurological exam (71 p589) | Radiography, myelography, CT, MRI, nuclear scintigraphy, CSF analysis, nerve conduction velocities, EMG, transcranial magnetic stimulation (p590) |
| Occipito-atlanto-axial malformation (OAAM) | Deficits develop before 6mths in Arabian horse (7,12, Seino) | Radiography |
| Spinal tumors | Signs can usually be localized to one region of the CNS | CT, MRI, definitive dx requires cytology, biopsy, histopathology, CSF analysis[19] |
| Sorghum cystitis/ataxia[1] | Posterior ataxia or paresis, cystitis, hx of grazing Sorghum species (Talcott, ch22 |
Cauda equina neuritis
Prognosis
Depends on duration and severity of neurological signs[3] but clinical resolution is more likely if the condition is diagnosed and treated early.[2] With standard therapy, involving 6-8months of ponazuzril or pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine (V), there is a recovery rate of around 25% and an improvement in 60-75% of cases.[20] A good prognosis might be expected if there is an improvement in clinical signs within two weeks of commencing anti-protozoal and anti-inflammatory treatment (V). The prognosis will be guarded to poor[1] for a horse with severe irreversible neuronal damage or one that has not been diagnosed or treated appropriately (V).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine (Third edition), SUDZ Publishing, 245-250. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Gray, L.C, Magdesian, K.G, Sturges, B.K, Madigan, J.E (2001) Suspected protozoal myeloencephalitis in a two-month-old colt. Vet Rec, 149:269-273. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "EPM8" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 3.0 3.1 Vatistas, N, Mayhew, J (1995) Differential diagnosis of polyneuritis equi. In Practice, Jan, 26-29.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Furr, M (2010) Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ DEFRA, The Animal Health Trust, The British Equine Veterinary Association (2009) Surveillance: Equine disease surveillance, April to June 2009, The Vet Rec, Oct 24:489-492.
- ↑ Dubey, J.P, Lindsay, D.S, Saville, W.J, Reed, S.M, Granstrom, D.E, Speer, C.A (2001)A review of Sarcocystis neurona and equine protozoal myeloencephalitis (EPM). Vet Parasitol, 95:89-131. In: Pusterla, N, Wilson, W.D, Conrad, P.A, Barr, B.C, Ferraro, G.L, Daft, B.M, Leutenegger, C.M (2006) Cytokine gene signatures in neural tissue of horses with equine protozoal myeloencephalitis or equine herpes type 1 myeloencephalopathy. Vet Rec, Sep 9:Papers & Articles.
- ↑ Wobeser, B.K, Godson, D.L, Rejmanek, D, Dowling, P (2009) Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis caused by Neospora hughesi in an adult horse in Saskatchewan. Can Vet J, 50(8):851-3.
- ↑ Mayhew, I.G, deLahunta, A, Whitlock, R.H, Krook, L, Tasker, J.B (1978) Spinal cord disease in the horse, Cornell Vet, 68(Suppl 8):110-120. In: Hahn, C.N (2010) Cervical Vertebral Malformation in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Hahn, C.N (2010) Cervical Vertebral Malformation in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Long, M.T (2010) Flavivirus Encephalitis in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ Bertone, J.J (2010) Viral Encephalitis in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ Wilson, W.D, Pusterla, N (2010) Equine Herpesvirus-1 Myeloencephalopathy in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Sommardahl, C.S (2010) Rabies in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ Scaratt, W.K, Jortner, B.S (1985) Neuritis of the cauda equina in a yearling filly. Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet, 7:S197-S202. In: Saville, W.J (2010) Polyneuritis equi in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ Granstrom, D.E, Dubey, J.P, Giles, R.C (1994) Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis: biology and epidemiology. In Nakajima, H, Plowright, W, editors: Refereed Proceedings, Newmarket, England, R & W Publications. In: Saville, W.J (2010) Polyneuritis equi in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ Nout, Y.S (2010) Equine Degenerative Myeloencephalopathy in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ Mayhew, I.G, deLahunta, A, Whitlock, R.H, Krook, L, Tasker, J.B (1978) Spinal cord disease in the horse, Cornell Vet, 68(Suppl 8):1-207. In: Nout, Y.S (2010) Equine Degenerative Myeloencephalopathy in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ Jose-Cunilleras, E (2010) Verminous Encephalomyelitis in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ Sellon, D.C (2010) Miscellaneous Neurologic Disorders in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ MacKay, R.J (2006) Equine protozoa myeloencephalitis: treatment, prognosis and prevention. Clin Tech Equine Pract, 5:9-16. In: Furr, M (2010) Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.