Difference between revisions of "Tunga penetrans"
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
==Identification== | ==Identification== | ||
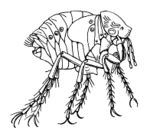
The female is around 1mm, and the male is smaller at around 0.5mm in length. The thorax is rather short, and a reddy-brown in colour. | The female is around 1mm, and the male is smaller at around 0.5mm in length. The thorax is rather short, and a reddy-brown in colour. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See [[Flea Structure|general flea structure]]. | ||
==Life Cycle== | ==Life Cycle== | ||
Revision as of 11:39, 27 July 2010
| Also known as: | Chigger
|
Hosts
Humans and Pigs are the primary hosts. Reservoir hosts include: cattle, sheep, horses, mules, rats, mice, dogs and some wild animals.
Identification
The female is around 1mm, and the male is smaller at around 0.5mm in length. The thorax is rather short, and a reddy-brown in colour.
Life Cycle
The breeding female burrow into exposed skin on the feet of mammals. They remain there for around 14 days while they develop their eggs. They enter the host using their adapted mouthparts, and the female will feed on the host body fluids.
The skin surrounding the parasite will expand and swell, leaving an opening for eggs to pass, and infect the environment.
The eggs require around 3 days to hatch, and the total life cycle requires about 12 days.