Difference between revisions of "Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Pathology== | ==Pathology== | ||
| + | |||
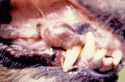
| + | [[Image:epulis.gif|right|thumb|125px|<small><center>Canine Epulis (Courtesy of Alun Williams (RVC))</center></small>]] | ||
Proliferation of fibrous tissue with variety of osteoid, [[Cementum - Anatomy & Physiology|cementum]] or [[Dentine - Anatomy & Physiology|dentine]]-like material. Isolated strands or islands of odontogenic epithelium are always present (ie: suggesting induction of connective tissue by the epithelial cells). | Proliferation of fibrous tissue with variety of osteoid, [[Cementum - Anatomy & Physiology|cementum]] or [[Dentine - Anatomy & Physiology|dentine]]-like material. Isolated strands or islands of odontogenic epithelium are always present (ie: suggesting induction of connective tissue by the epithelial cells). | ||
Revision as of 16:29, 5 August 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
| Also known as: | Fibromatous epulis of periodontal ligament |
Description
Peripheral odontogenic fibroma is a benign tumour that arises from the periodontal ligament. It was previously known as a fibromatous epulis and ossifying epulis depending on the degree of mineralization. They present as firm, smooth swellings of the gingiva and are normally indistinguishable from gingival hyperplasia.
Typical Signalment
Most common benign tumour found in the oral cavity in dogs but is less common in cats. Is seen in dogs of any age but more common in those older than 6 years.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
Include halitosis, oral bleeding, dental disruption or loss, facial or mandibular deformity, excessive salivation, growth protruding from the mouth and rarely dysphagia.
Diagnostic Imaging
Radiographs are required to differentiate this benign neoplasm from malignant or locally aggressive lesions. Skull radiographs will evaluate the oral lesion itself and thoracic radiography to evaluate for metastasies (if a malignancy is a diagnostic possibility). Radiographs typically show a soft tissue opacity in the the gingiva region with varying degrees of mineralization. Bone involvement is not a feature of this neoplasm and hence is not to be confused with Acanthomatous Ameloblastoma which often invades bone. Radiography cannot be used to differentiate a peripheral odontogenic fibroma from a hyperplastic gingival lesion.
Biopsy
An incisional biopsy is required to obtain a definitive diagnosis.
Pathology
Proliferation of fibrous tissue with variety of osteoid, cementum or dentine-like material. Isolated strands or islands of odontogenic epithelium are always present (ie: suggesting induction of connective tissue by the epithelial cells). The stroma contains neoplastic fibroblasts, with varying cellularity and the overlying epitheluim is normal.
Treatment
An excision of the neoplasm should be performed. The depth of the excision is determined by the location of the origin of the neoplasm at the periodontal ligament. Excision may be at the gingival level or a deep resection involving the extraction of the affected tooth and curettage of the alveolar socket.
Prognosis
Good following surgical resection. Recurrence is common following incomplete surgical resection.
References
Tutt, C., Deeprose, J. and Crossley, D. (2007) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dentistry (3rd Edition) BSAVA
Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition) Merial
With thanks to Andrew Jefferies (Cambridge) and Alun Williams (RVC) for providing access to their lecture materials
J Comp. Path. 1992 (106), 169-182 The Histological Nature of Epulides in Dogs F. J. M. Verstraete*, A. J. Ligthelmf and A. WeberT. ... review of 154 oral 'epulis' from dogs reviewed with the current (at the time) human literature.