Difference between revisions of "Category:Autoimmune Diseases"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ==[[Antibody Mediated Autoimmune Diseases]]== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Cell mediated autoimmune diseases== | ==Cell mediated autoimmune diseases== | ||
Revision as of 14:50, 11 August 2010
Antibody Mediated Autoimmune Diseases
Cell mediated autoimmune diseases
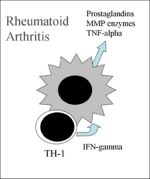
1. Rheumatoid arthritis
Pathogenesis:
- Type IV hypersensitivity: CD4 Th-1 cell mediated.
- Macrophages phagocytose self antigens and can present peptides on their MHC Class II molecules. The autoreactive TH-1 cells release IFN-gamma which activates macrophages to release prostaglandins, MMP enzymes and TNF-alpha (pro-inflammatory mediator), see diagram. These cytokines cause inflammation and tissue destruction.
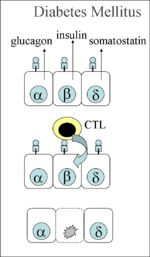
2. Diabetes Mellitus type I
Pathogenesis:
- Type IV hypersensitivity
- The CTLs think that all the beta cells in the pancreas are infected by a virus, as it wrongly detects a self antigen presented by the MHC class I on the surface of the cell as foreign.
- Autoreactive CD8+ CTLs are inadvertently activated, destroying the beta cells, thus preventing the secretion of insulin and causing diabetes type 1 (see diagram).
3. Hypothyroidism (lymphocytic throiditis)
Pathogenesis: Type IV hypersensitivity
- T cell mediated
4. Hypoadrenocorticism (Addisons disease)
Pathogenesis: Type IV hypersensitivity
Subcategories
This category has the following 2 subcategories, out of 2 total.
Pages in category "Autoimmune Diseases"
This category contains only the following page.