Difference between revisions of "CNS Development - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{unfinished}} | {{unfinished}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:WIKIVETformationofneuraltissue.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Formation of Neural Tissue - © Sophie Stenner]] | [[Image:WIKIVETformationofneuraltissue.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Formation of Neural Tissue - © Sophie Stenner]] | ||
| − | |||
[[Image:WIKIVETneuraltubeformation.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Neural Tube Formation - © Sophie Stenner]] | [[Image:WIKIVETneuraltubeformation.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Neural Tube Formation - © Sophie Stenner]] | ||
| − | |||
The Central Nervous System's embryological origin is from the '''neural ectoderm'''. This is formed as the default pathway from ectoderm to neuroectoderm during development. In the presence of the Lateral Plate Mesoderm (LPM) factor however, ectoderm forms epidermis. To overcome this in development the notochord secretes a LPM factor antagonist allowing the formation of neuroectoderm directly above it. This forms the '''neural plate''' and folds to form the '''neural tube'''. | The Central Nervous System's embryological origin is from the '''neural ectoderm'''. This is formed as the default pathway from ectoderm to neuroectoderm during development. In the presence of the Lateral Plate Mesoderm (LPM) factor however, ectoderm forms epidermis. To overcome this in development the notochord secretes a LPM factor antagonist allowing the formation of neuroectoderm directly above it. This forms the '''neural plate''' and folds to form the '''neural tube'''. | ||
| − | |||
[[Image:WIKIVETneuraltubeformation.jpg]] | [[Image:WIKIVETneuraltubeformation.jpg]] | ||
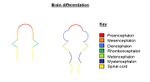
[[Image:WIKIVETbraindifferentiation.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Brain Differentiation - © Sophie Stenner]] | [[Image:WIKIVETbraindifferentiation.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Brain Differentiation - © Sophie Stenner]] | ||
*'''Differentiation''' of the neural tube at the anterior then forms the '''brain'''. | *'''Differentiation''' of the neural tube at the anterior then forms the '''brain'''. | ||
*The diagram on the right shows how the brain transforms during development. | *The diagram on the right shows how the brain transforms during development. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====Origins of Functional Types of Neurone==== | ====Origins of Functional Types of Neurone==== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 29: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | [[Category:Nervous System]] | + | [[Category:Nervous System - Anatomy & Physiology]][[Category:Developmental Biology]] |
Revision as of 11:42, 9 November 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
The Central Nervous System's embryological origin is from the neural ectoderm. This is formed as the default pathway from ectoderm to neuroectoderm during development. In the presence of the Lateral Plate Mesoderm (LPM) factor however, ectoderm forms epidermis. To overcome this in development the notochord secretes a LPM factor antagonist allowing the formation of neuroectoderm directly above it. This forms the neural plate and folds to form the neural tube.

- Differentiation of the neural tube at the anterior then forms the brain.
- The diagram on the right shows how the brain transforms during development.
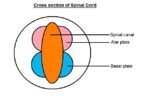
Origins of Functional Types of Neurone
| Nerve | Origin |
|---|---|
| Sensory - Afferent | Neural crest |
| Motor - Efferent | Basal plate of neural tube |
| Association - Interneurones | Alar plate of neural tube |