Difference between revisions of "Ureters - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[Image:ureterhistoanat.jpg|right|thumb|300px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal ureter (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | [[Image:ureterhistoanat.jpg|right|thumb|300px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal ureter (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | ||
| Line 51: | Line 42: | ||
| − | [[Category:Urinary | + | [[Category:Lower Urinary Tract]] |
Revision as of 14:48, 10 December 2010
Overview
The ureters convey urine from the renal pelvis to the bladder. There are two of them, one for each kidney. The ureters run retroperitoneally along the roof of the abdominal cavity and then enters the pelvis. Once entering the pelvis it moves medially in the broad ligament of the female or the genital fold of the male. It ends at its junction on the dorsolateral surface of the bladder within the lateral ligament.
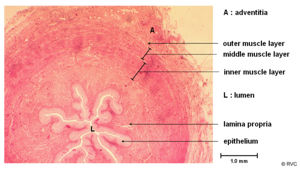
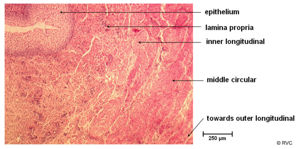
Wall
- It has an internal mucosa layer
- It is formed from transitional epithelium
- Protects against urine
- Followed by a muscularis layer
- This is well developed for peristalsis, though can enter into spasm on irritation
- And finally an external adventitia
Junction with the Bladder
- The ureter enters the bladder obliquely near the neck of the bladder
- Runs between the muscular layers and mucosa
- This stops back flow when the bladder is full as increasing pressure in the [[Urinary Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology* They open through 2 slits on a raised "hillock"
Movement of Urine
The movement of urine along the ureters is achieved by peristalsis which is powered by locally regulated smooth muscle. This maintains a low pressure in the renal pelvis.
Vascular Supply
- Renal pelvis and proximal ureter
- Renal artery
- Distal ureter
- Cranial vesicular artery and the vaginal (female) / prostatic (male)
Lymphatic Drainage
Lumbar lymph nodes
Revision
Use the flash card revision resource for this section to test yourself.