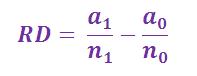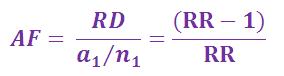Difference between revisions of "Measures of effect and impact"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
The '''attributable fraction''' is the proportion of disease in exposed individuals that is due to the exposure, alternatively, it is the proportion of cases that could have been prevented if exposure had been avoided. It is calculated by dividing the risk difference by the risk of disease in the exposed group, or directly from the risk ratio.</big><br /> | The '''attributable fraction''' is the proportion of disease in exposed individuals that is due to the exposure, alternatively, it is the proportion of cases that could have been prevented if exposure had been avoided. It is calculated by dividing the risk difference by the risk of disease in the exposed group, or directly from the risk ratio.</big><br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
[[File:AF.jpg]] | [[File:AF.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 19 May 2011
| Disease status | Exposed | Unexposed | Total |
| Diseased | a1 | a0 | m1 |
| Non-diseased | b1 | b0 | m0 |
| Total | n1 | n0 | n |
Risk difference (RD)
Risk difference or Attributable risk is the amount of disease observed in the population which is attributable to the exposure of interest and is calculated by subtracting the risk of disease in the unexposed group from the risk of disease in the exposed group. It assumes that the risk of disease in the non-exposed group is the ‘baseline’ risk of disease, therefore in order to calculate a risk difference groups of animals must be similar with regards to all other factors associated with disease.
Attributable fraction (AF)
The attributable fraction is the proportion of disease in exposed individuals that is due to the exposure, alternatively, it is the proportion of cases that could have been prevented if exposure had been avoided. It is calculated by dividing the risk difference by the risk of disease in the exposed group, or directly from the risk ratio.