Difference between revisions of "Avian Respiration - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
*The '''Infraorbital Sinus''' is a triangular cavity under the skin, rostroventral to the eye. | *The '''Infraorbital Sinus''' is a triangular cavity under the skin, rostroventral to the eye. | ||
*Some marine birds have a ''Salt Gland'' (nasal gland) which excretes sodium. | *Some marine birds have a ''Salt Gland'' (nasal gland) which excretes sodium. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Larynx== | ||
| + | The larynx is on the floor of the oropharynx supported by '''Cricoid''' and paried '''Arytenoid''' Cartilages which are different in structure to those in mammals. | ||
| + | There is no Epiglottis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Trachea | ||
Birds vocalise using a [[Syrinx - Anatomy & Physiology|syrinx]]. | Birds vocalise using a [[Syrinx - Anatomy & Physiology|syrinx]]. | ||
Revision as of 14:55, 13 August 2008
|
|
Introduction
The avian respiratory system contains some fundamental changes to the mammalian system.
Avian Nasopharynx and Oropharynx
- The nostrils of the bird, which lead into the nasal cavity, may have a flap of horn to protect them, known as the Operculum.
- The Oral Cavity and the Nasal Cavity of the bird are interconnecting via a slit in the hard palate called the Choana. Birds lack a soft palate.
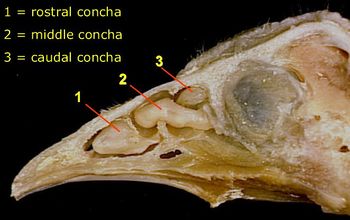
- There are Rostral, Middle and Caudal Conchae arising from the lateral wall, filling part of the nasal cavity.
- Rostral Conchae - Vestibular Region - lined with Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Middle Conchae - Respiratory Region - lined with Respiratory Epithelium.
- Caudal Conchae - Olfactory Region - lined with olfactory epithelium.
- The Infraorbital Sinus is a triangular cavity under the skin, rostroventral to the eye.
- Some marine birds have a Salt Gland (nasal gland) which excretes sodium.
Larynx
The larynx is on the floor of the oropharynx supported by Cricoid and paried Arytenoid Cartilages which are different in structure to those in mammals. There is no Epiglottis.
==Trachea
Birds vocalise using a syrinx.
Air Sacs
Links
References
- Dyce, K.M., Sack, W.O. and Wensing, C.J.G. (2002) Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.