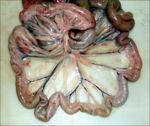
Jejunum - Anatomy & Physiology
Structure
- The jejunum is the longest part of the small intestine.
- It is highly coiled and occupies the ventral part of the abdominal cavity, filling those parts that are not occupied by other viscera. This produces species variation (see comparative aspects).
- It lies on the abdominal floor, separated from the parietal peritoneum by the greater omentum.
- It is suspended by the mesentry (mesojejunum). This conveys the blood vessels and nerves and houses lymph nodes.
- The mesentry converges to its root. This is where the cranial mesenteric artery branches off from the aorta.
Function
- Has digestive and absorptive functions.
Vasculature
- The cranial mesenteric artery, a branch of the abdominal aorta, supplies blood to the jejunum, ileum, caecum, ascending colon and part of the transverse colon.
- It branches greatly within the mesenty of the jejunum.
- There are many anastomoses within the mesentry, which ensure that the intestine can survive even if a major division of the cranial mesenteric is damaged.
- The cranial mesenteric vein drains blood from the jejunum and enters the portal vein.
- It is rich in the products of digestion following a meal.
- The portal vein enters the liver.
Species Differences
- The position of the jejunum is variable between species as it lies in that part of the abdomen not occupied by other viscera.
Canine
- Jejunum lies roughly symmetrically about the midline. It contacts the liver, stomach and spleen cranially and urinary bladder ventrally.
Horse
- The coils of jejunum are confined to the left dorsal part of the abdomen.
- It is restricted to this position by the large caecum on the right, and ascending colon ventrally on both sides.
Ruminant
- It is pushed entirely to the right side of the abdomen by the rumen which is on the left.
- Coils of the jejunum usually lie within the supraomental recess; although this can vary between individuals depending on fullness of the rumen and size of the uterus.
Pig
- Jejunumo lies in the caudoventral aspect of the abdominal cavity, mainly to the right of the midline.
- This is due to the presence of the ascending colon on the left.